presentation
advertisement

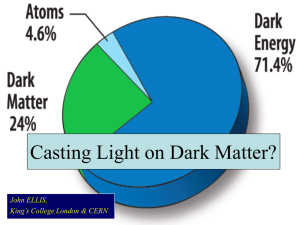
2014 Network Science: An Introduction Xiaofan Wang xfwang@sjtu.edu.cn Course Website http://cnc.sjtu.edu.cn Textbook: 汪小帆、李翔、陈关荣, 网络科学导论 高等教育出版社,2013 TA:王瑛(电院2-310) wangyingdove@gmail.com Goals and Objectives A bird’s eye view of the networked world & network science • 平时表现(参与程度):30% • 一篇网络科学相关的报告(可以2-3人合作):70% • WORD文档,科研文章格式,一般不少于8页 • 介绍别人的或者自己的工作,一定要有自己的观点 • 考核标准:选题的品味、介绍的清晰、文章的规范 • 严禁任何形式的抄袭!12月30日之前邮件发给助教 • “Our lives are not our own. We are bound to others, past and present, and by each crime and every kindness, we birth our future.” • Six unique yet connected stories • Span nearly six hundred years • about how lives are all linked in the past, present and future. Various souls cross the ages like clouds cross the skies It’s all about NETWORK! We will never understand complex systems unless we gain a deep understanding of the networks behind them. OUTLINE Complex Networks Everywhere It’s a Small World After All Rise of Network Science NETWORK VIEW OF THE WORLD Communication Transportation Power Grid Social Biological Language 1969 ARPANET 1970 ARPANET 1986 NSFNET 1995 INTERNET Nodes? Links? IP level Router level Domain (AS) level • How many of the world’s population does not yet have Internet access? 2/3 Towards a comparative science of cities: using mobile traffic records in New York, London and Hong Kong S. Grauwin, S. Sobolevsky, S. Moritz, I. Gódor, C. Ratti,2014 Modelling the Air Transport with Complex Networks: a short review. M Zanin, F Lillo, 2013, http://arxiv.org/abs/1302.7017 • less than 10% of the land is more than 48 hours of ground-based travel from the nearest city (>50000p) • “New Scientist”: 02 Apr., 2009 Mike Barry and Brian Card - June 10, 2014 better understand the trains, how people use the trains, and how the people and trains interact with each other. Internet Mobile C Transportation 上海沪闵高架今开通 严重拥堵造成多起事故 2003-12-29 新民晚报 Braess 悖论 -selfish routing 今天晚上沪闵高架往徐家汇方向的上匝道将竖立有关提示“高峰 拥堵,车辆分流”的标志,明天清晨一支由十多人组成的排堵纠 违小分队将开始专门在此段道路执勤。 A great example of network thinking The Largest Power Outage in World History The July 2012 India Blackout The Largest Power Outage in World History The July 2012 India Blackout. Four factors: Weak inter-regional power transmission corridors due to multiple existing outages High Loading on 400 kV Bina-Gwalior-Agra link. Inadequate response by State Load Despatch Centers (SLDCs) to the instructions of Regional Load Despatch Centres (RLDCs) to reduce overdrawal by the Northern Region utilities and underdrawal/excess generation by the Western Region utilities. Loss of 400 kV Bina-Gwalior link due to mis-operation of its protection system. http://www.powermin.nic.in/pdf/GRID_ENQ_REP_16_8_12.pdf Academic Paper in China Sets Off Alarms in U.S. March 20, 2010 WANG JW, RONG LL. Cascade-based attack vulnerability on the US power grid. Safety Science, 2009, 47 • Main subject: The challenges to economic stability posed by complex financial networks. • Network scientists, economists and regulators team-up for the first time to discuss this problem. • Special issue, Science 6 June 2014: 344(6188) A.-L. Barabási, N. Gulbahce, J. Loscalzo, Network medicine: a network-based approach to human disease , Nature Reviews Genetics 12, 56-68 (2011) Human Brain has between 10-100 billion neurons.(video) Network Science: Introduction 2012 Säterberg T, Sellman S, Ebenman B.High frequency of functional extinctions in ecological networks, Nature 499, 468–470 (25 July 2013) • Network theory can provide a prominent set of techniques for the exploratory analysis of large complex software systems. • Different network-based quality indicators that address software design, efficiency, reusability, vulnerability, controllability. L. Šubelj, M. Bajec, Software systems through complex networks science: Review, analysis and applications. Proc. of the KDD Workshop on Software Mining, 8-19, 2012. http://arxiv.org/abs/1208.2518 • NeighborNet analyses of the Indo-European lexical data. Grey et al. 2010, Phil. Trans. R. Soc. B 365: 3923-3933 http://arxiv.org/abs/1310.2963 A Network Framework of Cultural History Birth and death data of notable individuals reveal interactions between culturally relevant locations over two millennia. Schich, M. et al. Science 345(6196), 558–562 (August,2014) J. Adams, Nature, 490, 335–336, 18 Oct., 2012 • How many authors? • 2004: >1000 authors; 2008: >3000 authors • 2011: 120 phys. papers had >1000 authors, 44 papers had >3000 authors • 2011 US: 19141 with China, 19090 with UK, 16753 with Germany • So what are the costs and benefits of collaboration? Collaborative grand challenges seize headlines, but so do Nobel prizes — and only three people can share one of those! • players as nodes and ball movements as links Fewell JH, Armbruster D, Ingraham J, Petersen A, Waters JS (2012) Basketball Teams as Strategic Networks. PLoS ONE 7(11): e47445 J L Pena & H Touchette, A Network Theory Analysis of Football Strategies. C. Clanet (ed.), Sports Physics: Proc. 2012 Euromech Physics of Sports Conference, p. 517-528, arxiv.org/abs/1206.6904 NetSci2014 Berkeley DARPA Network Challenge, 2009 PICKARD G, PAN W, RAHWAN I, …PENTLAND A. Science, 2011, 334(28): 509-512. Xiang Li, Xin Liu, C. K. Tse, Recent Advances in Bridging Time Series and Complex Networks, 2013 IEEE ISCAS, 2505-2508 同一个人 QQ 人人 微博 Email 飞信 S. Boccaletti et al., The structure and dynamics of multilayer networks, Physics Reports, 2014, http://arxiv.org/abs/1407.0742 M. Kivelä et al., Multilayer networks, Journal of Complex Networks, 2014, arXiv:1309.7233. NETWORK VIEW OF THE WORLD Communication Transportation Power Grid Social Biological Language • Despite the apparent differences, the emergence and evolution of different networks is driven by a common set of fundamental laws and reproducible mechanism. OUTLINE Complex Networks Everywhere It’s a Small World After All! Rise of Network Science First Lesson: Is it really a small world? Erdös: > 1,500 papers > 500 coauthors Erdös Number: Einstein 2; A-L Barabasi 3; Paul Samuelson 5 P. Erdös C. K. Chui G. R. Chen Me • Chain letters • The destination: Boston, Massachusetts • Starting Points: Omaha, Nebraska & Wichita, Kansas Milgram. Psychology Today 1, 60-67 (1967) MA NE 20% of initiated chains reached target average chain length = 6.5 The distance between two randomly individuals in the USA : 6 Milgram S. The small world problem. Psychology Today, May 1967, 60 – 67 Chain emails from Jan. 2002 •18 targets •13 different countries •60,000+ participants •24,163 message chains •384 reached their targets •average path length 4.0 P S Dodds, R Muhamad, D J Watts. An Experimental Study of Search in Global Social Networks, Science, 2003, 301 (5634), 827 • June 2006: 240 million users, 30 billion conversations • Network: 180 million active users, 1.3 billion edges Average distance: 6.6 J Leskovec, E Horvitz: Planetary-scale views on a large instant-messaging network. WWW 2008 • Crawling RenRen (2009, 30 crawlers): • 42million users, 1.6 billion friendship links Average distance: 5.38 • I. Jiang, C. Wilson, X. Wang et al. Understanding Latent Interactions in Online Social Networks. IMC 2010 • May 2011: 721 million active users, 69 billion links Average distance: 4.74 BACKSTROM L, BOLDI P, ROSA M, et al. Four degrees of separation, P4th ACM Int'l Conf. on Web Science (WebSci), 2012, 45-54 OUTLINE Complex Networks Everywhere It’s a Small World After All! Rise of Network Science • WATTS D J, STROGATZ S H. Collective dynamics of ‘smallworld’ networks. Nature, 1998, 393(6684): 440–442. • BARABÁSI A-L, ALBERT R. Emergence of scaling in random networks. Science, 1999, 286(5439): 509-512. 1998 Nature The emergence of network maps The universality of network characteristics 1999 Science Network Science Discovering Property Measuring Data Modeling Network Analysis Behavior Design Performance Collect enough information so that you can • • • • • Describe (correctly) Quantify (properly) Formulate (mathematically ) Predict (reasonably) Control (powerfully) Communication Transportation Power Grid Social Network Spreading Biological Economical Virus Rumor 肥胖 Spreading on Social Networks (video) Fasion Behavior 自杀 Belief Opinion Theoretical Science Applied Science • Graph Theory • Communication Science • Game Theory • Power Engineering • Statistical Physics • Life Science • Computer Science • Social Science • For every technology, • the first ten years is the development, and • the second ten years is when the market follows. • Science, in general, is a lot better at breaking complex things into tiny parts than it is at figuring out how tiny parts turn into complex things. • • • • Interdisciplinary nature Data-driven nature Quantitative nature Computational nature • Graph Theory • Spectral Graph Theory • Markov Chain Theory Fan Chung金芳蓉 UCSD • Mean-Field Theory • Phase Transition • Percolation Theory • A.-L. Barabási • Mark Newman • Northeastern • Michigan • Jon Kleinberg • Cornell Liu Y Y, Slotine J J, Barabási A L. Nature, 2011, 473(7346): 167-173. Sinan Aral MIT 大众点评的餐厅评价 豆瓣的电影评价 购物网站的商品评价 差评师的影响有多大 • 事先为101281篇网上文章随机给好评或差评,并与对照组相比 • 事先给好评有引导性:读者给好评的可能性提高了32% • 事先给差评没有引导性:对文章最后的评分几乎没有影响 Lev Muchnik, Sinan Aral, and Sean J. Taylor, Social Influence Bias: A Randomized Experiment, Science 9 August 2013: 341 (6146), 647-651. • 要让数据更好地说话,既 依赖于数据科学与技术的 发展,更需要政府、机构 和公民的数据意识的不断 提高。 • 随着大数据热潮的不断升温,相信 今后几年会有更多以大数据为主题 的著作问世。这本先河之作用各种 案例生动阐述了大数据所带来的变 革。你可以不同意书中的某些观点 ,但是大数据所带来的变革已经开 始发生并将继续深入。我们需要共 同面临的挑战是:越来越大的数据 如何才能让世界变得越来越美丽? 穷人和富人的人脉结构 英国2005年8月通话记录,6500万节点,3.68亿条边 最大连通片:99.5%的节点;平均距离:9.4 32482个社区:越是富裕的小区,交往多样性越明显 越是富人越跟不同阶层和不同地区的人联络,而且阶层多样 性要比地区多样性更重要 相关性而非因果性:是因为你富,才与不同类的人接触;还 是因为你愿意跟不同类型的人接触,才导致你富? • N. Eagle, M. Macy & R. Claxton,Network Diversity and Economic Development, Science 21 May 2010 • 大连接,大数据,大合作:网络 因大而小 • 我非常期待本书中文版的面世, 并且会推荐给学习网络科学的学 子。所有希望了解社会网络如何 越来越深刻地影响着人类行为的 读者,即使并不完全赞同作者的 观点,也都能够从书中受益 • 数据资源:人力和物质以外的第三大资源 • 数据产业:以数据为中心的服务产业转型 • 数据战略:多国政府把大数据上升为国家战略 • 数据科学:基于数据和针对数据的科学 Global Thinking, Local Action • 假设你是人人或微信或微博的研究人员,你可 以经公司允许在网络上做实验以验证情绪是如 何在人们之间传播的。例如:如果一个人看到 更多的positive的帖子,是否自己也会变得更 为positive? • 请问你应该如何设计实验? A. D. I. Kramer et al., Experimental evidence of massive-scale emotional contagion through social networks, PNAS, 111(24), 87888790, 2014 1. 阅读并介绍文献:A. D. I. Kramer et al., Experimental evidence of massive-scale emotional contagion through social networks, PNAS, 111(24), 8788-8790, 2014 2. 查阅并综述网上关于该文的技术、道德和法律的争论 3. http://ideas.ted.com/2014/07/02/need-to-knowabout-facebooks-emotional-contagion-study/ 4. 阐述你自己的观点 Xiaofan Wang Shanghai Jiao Tong University xfwang@sjtu.edu.cn Complex Networks & Control Lab, SJTU