Pearson Prentice Hall
Physical Science: Concepts in Action
Chapter 18
The Electromagnetic
Spectrum and Light
18.1 Electromagnetic Waves
• Objectives:
• 1. Describe the characteristics of
electromagnetic waves in a vacuum
• 2. Calculate the wavelength and frequency of
an electromagnetic wave
• 3. Describe the evidence for the dual nature
of electromagnetic radiation
• 4. Describe how the intensity of light changes
with distance from a light source
Characteristics of EM Waves
• Def: electromagnetic waves are transverse
waves consisting of changing electric fields and
changing magnetic fields
• Def: an electric field is a region of space that
exerts electric forces on charged particles
• Def: a magnetic field is a region of space that
produces magnetic forces
• Magnetic forces are produced by magnets,
changing electric fields and vibrating charges
• EM waves can travel through a
vacuum as well as through matter
• Def: EM radiation is the transfer of
energy by EM waves traveling through
matter or across space
• Light and all EM waves travel at the
same speed but the wavelength (λ) &
frequency (f) can differ
• The speed of light (& all EM waves) is
3.00 x 108 m/s
Calculations
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Speed = wavelength x frequency
For EM waves, speed = 3.0 x 108 m/s
Frequency = speed/wavelength OR f= c/λ
Wavelength = speed/frequency OR λ=c/f
The units for speed (c) are m/s
The unit for wavelength (λ) is m
The unit for frequency (f) is Hz
(1/seconds)
EM Radiation/ Light Intensity
• EM radiation sometimes behaves like a
wave and sometimes like a particle
• Light, therefore, is classified both as an EM
wave and as a particle
• Def: a photon is an EM packet of energy
• Each photon’s energy is proportional to the
frequency of the light
• The intensity of light decreases as photons
travel farther from the source
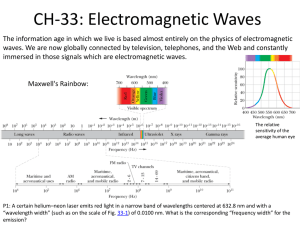
18.2 The Electromagnetic Spectrum
• Objectives:
• 1. Rank and classify EM waves
based on their f (frequency)
and λ (wavelength)
• 2. Describe the uses for
different waves of the EM
spectrum
Rank and Classify
• The prism separates the wavelengths
present in sunlight which is visible light
• From longest to shortest: ROY G B(I)V
• The electromagnetic spectrum includes
visible plus invisible radiation
• Increasing frequency from left to right
(longest to shortest): radio waves, infrared
rays, visible light, UV ray, X rays, and gamma
rays
Uses for EM Waves
• Radio waves are used in radio, television,
microwaves and radar
• The shortest radio waves are microwaves
• Radar is an acronym: radio detection and
ranging
• Radar often uses the Doppler effect to
determine how fast something is moving
• Infrared rays are used as a source of heat &
to discover areas of heat difference
• Thermograms use infrared to sensors to show
differences in temperature of objects
• Visible light is used to see, stay safe and
communicate
• UV rays are used in health, medicine and agriculture
• X rays are used in medicine, industry and
transportation to make pictures of the inside of
solid objects
• Gamma rays are used medically to kill cancer cells,
make brain pictures and in certain industrial
situations such as checking pipelines for cracks or
other damage
18.3 Behavior of Light
• Objectives:
• 1. Describe three types of
materials that affect the
behavior of light
• 2. Explain how light behaves
when it enters a new medium
Three Types of Materials
• The behavior of light is affected by
transparent, translucent and opaque
materials
• Transparent materials transmits light,
allowing most light to pass through it
• Translucent material scatters light
• Opaque material either absorbs or reflects
all the light that strikes it
• No light passes through opaque materials
How Light Behaves
When light strikes a new medium, the light
can be reflected, absorbed or transmitted
When light is transmitted, it can be
refracted, polarized or scattered
Def: an image is a copy of an object formed
by reflected light waves
Def: regular reflection is parallel light waves
striking a surface and reflecting all in the
same direction
• Def: diffuse reflection is parallel light waves
striking a rough, uneven surface, reflecting in
many directions
• Def: refraction is the bending of light waves
• Def: a mirage is a false, distorted image
• Mirages occur due to light traveling faster in hot
air than in cool air
• It is a form of refraction
• Def: polarization is light with waves that vibrate
only in one direction
• Def: scattering is light redirect as it passes
through a medium