Canine and Feline Distemper
advertisement

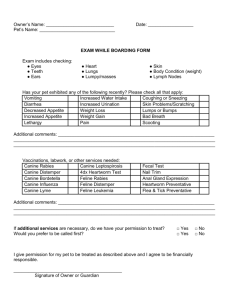
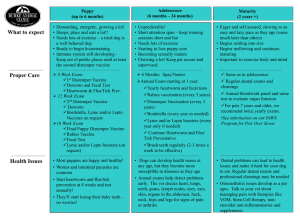
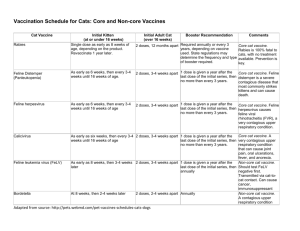
Canine and Feline Distemper Marie Rhodes Description Diseases that affect both wildlife and domesticated carnivores Caused by two different viral agents Both diseases can cause acute illness and death Affected Families Family Canidae Canine Distemper Yes Feline Distemper No No Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes wolf, coyote, fox, domestic dog Felidae bobcat, lynx, domestic cat Procyonidae raccoon Mustelidae ferret, mink, weasel, marten, fisher, otter, badger, skunk, wolverine (Mink and possibly skunk and otter) Canine Distemper Caused by a paramyxovirus Highly contagious among carnivores Seen in both domesticated and wild animals Transmission Direct contact or possibly contact of contaminated objects Shed through feces and urine of infected animals Some evidence shows transplacental transmission Symptoms and Treatment Domestic dogs show signs such as coughing, diarrhea, vomiting, nasal and ocular discharge Wild carnivores may only show abnormal behavior and apparent lack of fear Only treatment is supportive care Feline Distemper Also called feline panleukopenia, cat plague, and cat fever Acute, highly contagious infectious viral disease Transmission Shed in all body secretions and excretions of affected animals Recovered animals may shed virus for months Fleas and other insects, especially flies, may play a role in transmission Spread by either inhalation or ingestion Symptoms and Treatment High fever is followed by depression, vomiting, anorexia, diarrhea, and a profound leukopenia No treatment after infection except for supportive care