Human
Reproduction
Influenced by gene expression,
hormones, and the environment
Structure and Function
of the Male
Reproductive System
Lesson 1
Do Now
Brain Pop Video: Reproductive System
Label the Male Sex Organs worksheet
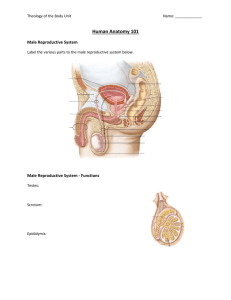
Male Reproductive System
Testes produce sperm cells and
testosterone – the hormone associated with
male secondary sex characteristics and the
production of sperm ex: body hair, deep
voice, increased muscle mass
Structures that produce fluid and nutrients
needed for proper function and delivery of
gametes (sperm) to the male reproductive
system
Male Anatomy
2 paired testes hang outside the body in a
sac of skin called the scrotum (this keeps the
temperature slightly lower than inside the
body and allows for the survival of sperm.)
Testes initially develop inside the body
and descend about 1 month before birth –
failure to descend can lead to an
increased risk of cancer so it must be
surgically brought down
Each testis is composed of hundreds of
small tubules where the sperm are made
Sperm are made continually throughout life
though the number of healthy sperm
decreases as one ages
From the testes the sperm move into an
epididymis – storage tubule – where they
mature
Next they move into the Vas Deferens –
long tube that goes up into the body
Empties into the urethra which passes
through the penis and delivers sperm to
the female
3 structures that secrete fluid to nourish
and transport sperm. This fluid + sperm
= Semen
Involuntary contractions force semen
through the urethra and outside the
body = ejaculation
Muscle closes bladder to urethra so
urine does not exit with semen
In class assignment
Labeling Diagram
Homework
Labeling diagram
Structure and Function
of the Female
Reproductive System
Lesson 2
Do Now
Brain Pop Video: Reproductive System
Label the Female Sex Organs Diagram
Female Reproductive System
Internal fertilization in oviduct
Internal development in uterus
Production of sex cells in ovaries
Provide essential nutrients to embryo
and fetus through the placenta
Provide nutrition through milk to the
newborn
Gonads are ovaries produce eggs,
hormones (estrogen and progesterone)
ESTROGEN – determines female sex
characteristics: breasts, fat distribution,
regulate menstrual cycle
PROGESTERONE – maintains uterus
during pregnancy
Female Anatomy
Ovaries (2) 4cm X 2cm in lower abdomen –
each contains small sacs known as follicles
that hold an egg (~500 in mature ovary)
When egg matures follicle ruptures (1 each
month) and egg pops out (ovulation)
Egg enters tubes known as oviducts (egg
ducts) or fallopian tubes – it lives ~24-48
hours and this is where is can be fertilized
Leads to uterus – muscular organ where
embryo develops into fetus. Where embryo
sinks into wall – Placenta forms which
provides nutrients to fetus
Delivery – Uterus
contracts and pushes
through cervix
opening of uterus to
the vagina (birth canal)
Urinary system is totally
separate – urethra
opens anterior to the
vagina
At sexual maturity (puberty) females begin
menstrual cycle
~ 28 days with ovulation occurring at
day 14 timing controlled by 2 hormones
from the pituitary and 2 hormones from
ovaries
The rise and fall of hormones regulates the
cycle (variable lengths) Menstrual cycle
starts around 10-14 years and ends by ~ 5055 at Menopause
4 Stages of the Menstrual Cycle
1. Follicle Stage – Pituitary makes FSH
(follicle stimulating hormone) stimulates
follicle in ovary to get egg ready
- Follicle makes estrogen starts to get
uterine wall thicker in case of pregnancy
(lasts till day 14)
2. Ovulation – Pituitary LH (lutenizing
hormone) Ruptures follicle (ovulation)
egg is out of follicle
4 Stages of the Menstrual Cycle
3. Corpus Luteum Stage – Follicle turns yellow
corpus luteum produces progesterone –
develops in uterus
4. Menstruation – If fertilization does not occur
– corpus luteum disappears no
progesterone lining of the uterine walls
sheds – blood and wall is shed and known as
menstruation (~5 days)
In class assignment
Labeling diagram
Homework
Vocab/Mutiple Choice Worksheet
Menstrual Cycle Lab
Lesson 3
Human Development
Lesson 4
Do Now
Graphic Organizer worksheet
Human Development
Pregnancy = gestation
continues in the uterus
(lasts ~9 months or 40
weeks)
embryo 2 months
“Fetus”
1st part of pregnancy =
development of organs
occurs in the first 3
months
Things can go wrong that affect the
development of the fetus
-
Faults in the genes or DNA
Xrays
STD’s
Environmental factors:
a) alcohol – FAS (fetal alcohol syndrome)
b) drugs – drug addicted babies
c) smoking – low birth weight babies
d) poor diet in mother
e) infections – especially German
Measles and AIDS can cause defects
Mother needs Pre-Natal care and should
avoid harmful things that can cause birth
defects
- After birth – development and
differentiation and growth continue until
adulthood when organs are age, weaken,
and die
Process of Birth
Labor = rhythmic contractions of
uterus
1. cervix opens (.1-10 cm)
2. head delivered first
3. amniotic fluid comes out
4. umbilical cord cut
5. Placenta delivered
Reproductive Technology
Birth Control = Contraception methods of
preventing pregnancy
1. pill – disrupts hormones
2. diaphragm or condom – barrier method
and prevents STD’s
3. surgical vasectomy or hysterectomy
4. ABSTINENCE – only 100% affective
form of birth control
Reproductive Technology
Ecology –
1. Build up endangered species – transplant embryos
into different animals
Medicine –
1. Hormone prescription to help women who can’t get
pregnant (fertility drugs)
2. Artificial insemination
3. In-vitro fertilization – test tube embryos implanted
4. Ultrasound and mini camera – view reproductive
organs
5. Amniocentesis – needle to remove cells from fluid
around baby – analyze cells for genetic problems
Homework
Read the article on reproductive
technology and list 5 pros and 5 cons to
reproductive technology
Medical Ethics
In class assignment
A love story: spermy meets eggey
Embryo Development
Lab
Lesson 5
Miracle of Life Video
Lesson 6
In class assignment
Miracle of Life Worksheet