Embryology
advertisement
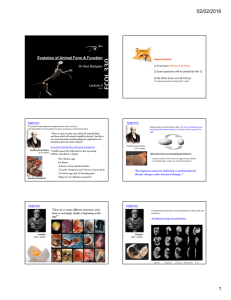
Embryology 2010 History of Embryology • Aristotle (384-322 BC) – The Generation of Animals (350 BC) » Oviparity » Viviparity » Ovoviviparity – Epigenesis (!) – holoblastic pattern of cleavage – meroblastic pattern of cleavage • Leonardo Da Vinci (1452-1519) – Uterus of the cow • Hyeronymus Fabricius of Acquapendente (1533-1619) • Bartolomeo Eustachius (1514-1574) – Gross and comparative anatomy of dog and sheep embryos • Marcello Malpighi (1628-1694) – First microscopic account of chick development Quest for the egg • Epigenesis vs. preformation? • William Harvey (1578-1657) – „Ex ovo omnia” – Blastoderm – Blood islands • Regnier de Graaf (1641-1673) – Detailed study of the ovary – Follicles ~eggs • Karl Ernst von Baer (1792-1876) – First to see the mammalian egg Quest for the spermatozoa • Anton van Leeuwenhoek (1632-1723) New age of embryology • Theodore Schwann – cell theory • Kaspar Friedrich Wolff (1734-1794) – embryonic parts develop from tissues that have no counterpart in the adult organism “When the formation of the intestine in this manner has been duly weighed, almost no doubt can remain, I believe, of the truth of epigenesis.” (1767) • Christian Pander, • Karl Ernst von Baer • Heinrich Rathke Embryology: a specialized branch of science (they used the term embryology to describe their work). • Rudolph Albert von Kölliker (1817-1905) – First textbook on embryology in 1861 • August Weissmann (1834-1914) – Germ cell plasm theory: – Sperm and egg provides equal chromosomal contributions – Had wrong idea about differentiation • Hans Speeman (1869-1941) – Nobel Prize in 1935 for embryonic induction













![Evidences_for_Evolution[1]](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/005782474_2-92d918c9fbb15c5c4fb484555d2a0a0a-300x300.png)