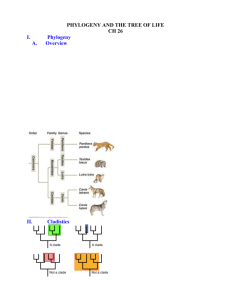
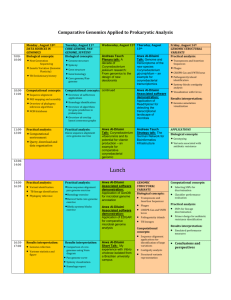
Phylogenetic tree estimation
advertisement

Comparative genomics Joachim Bargsten February 2012 Comparative genomics The study of the relationship of genome structure and function across different biological species or strains. • Why should we do this? • How are we going to do this? Study evolution • Resolve • Differences • Mechanism Tree of life http://www.tolweb.org/tree/ Motivation • Transfer knowledge from and to simpler model organisms C. elegans Human Motivation Overview • Molecular phylogenetics • Multiple sequence alignment • Phylogenetic tree estimation • Ortholog prediction • Genome rearrangements • Large scale inversions, deletions and translocations • Synteny & Collinearity • Structural variations • Presented by Lin Ke Molecular phylogenetics • The use of molecular data to establish the relationship between species, organisms or gene families Homology sequences that share common ancestry. This is a all or nothing relation. Sequences are never “a bit” homologous. • Orthologs: homologs in different species derived by a speciation event • Paralogs: homologs in the same or different species derived by a duplication event Homology last common ancestor (co-)orthologs Homology last common ancestor inparalogs Homology last common ancestor outparalogs Phylogenetic tree estimation • How do we estimate a phylogenetic tree? • Identify evolutionary conserved region • Multiple sequence alignment • MAFFT • Estimate the phylogenetic tree • PhyML Phylogenetic tree estimation • Multiple sequence alignment Phylogenetic tree estimation Phylogenetic tree estimation • Infer evolutionary relationships between species and genes/proteins • Rooted tree • Order of evolutionary events • Unrooted tree • Evolutionary relationships between descendants Non-coding regions • Phylogenetic footprinting • Distantly related species • Phylogenetic shadowing • Closely related species • Use sequence comparison and multiple alignment to find exons and non-coding functional regions • E.g. Transcription factor binding sites What can we do with it? • Gene annotation • Gene or protein function prediction • Identify non-coding elements in the genome • Species phylogeny • Genome evolution Genome alignment • Pairwise alignment • Match chromosome sequence from species A to species B Genome alignment – dot plot Dot-plot chromosome 2L tomato - potato Synteny & collinearity • Synteny gene loci are on the same chromosome • Conserved synteny gene loci are on the same chromosome in different species • Collinearity The order of the gene loci is preserved across species inverted Resources • Comparative genomics plants • Plant Genome Duplication Database • http://chibba.agtec.uga.edu/duplication/ • Plaza • http://bioinformatics.psb.ugent.be/plaza/ Exercise ssh –X USERNAME@137.224.100.212 cd /mnt/geninf15/work/bif_course_2012/comparative_genomics_jwb less assignment.txt kwrite assignment.txt