Part of digestive system
advertisement

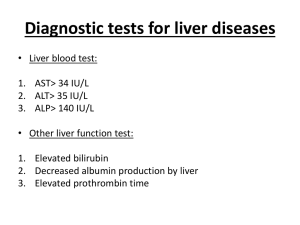
Gilead -Topics in Human Pathophysiology Fall 2010 Drug Safety and Public Health Phagocytosis Inflammation Complement Interferon Figure 21.5 B lymphocytes ◦ Mature in bone marrow, responsible for antibody mediated immunity ◦ When they recognize a pathogen (antigen) and are activated, develop into plasma cells and memory cells ◦ Plasma cells produce 1000s of antibodies (immunoglobulins) per second B lymphocytes – •Recognition •Activation •Attack (cloning and antibody production) Antibody functions Figure 21.14 T lymphocytes ◦ 3 types: helper T cells, cytotoxic T cells, suppressor T cells ◦ When recognize a pathogen and are activated, these attack the pathogen and create a cadre of memory cells Recognize pathogen presented by other WBCs Are activated by cytokines by other WBCs “Clone”themselves to form active cells and memory cells Release cytokines to activate and stimulate other WBCs, including B cells and phagocytes Macrophages act as antigen presenting cells •Helper T cells are presented with antigen by specialized WBCs •When activated these helper T cells clone themselves into memory Figure 21.17 AKA killer T cells Recognize pathogen (antigens) in virally infected cell or cancer cells Activated by cytokines from helper T cells “Clone” themselves into attack cells and memory cells Attack by producing proteins that open holes in infected cells Figure 21.19 Memory cells circulate, sometimes for a lifetime, scanning for that pathogen they recognize A second infection by the same pathogen will yield a stronger, faster immune response that prevents illness Figure 21.12 A retrovirus that infects host cells macrophages and helper T cells Its RNA is reverse transcribed into DNA, then inserted into host chromosomes Protein synthesis of viral DNA makes components of new HIV The components are assembled into new virus and released from host Reverse transcriptase required Protease required Reverse transcriptase Inhibitors work here Protease inhibitor s work here Gilead -Topics in Human Pathophysiology Fall 2010 Drug Safety and Public Health Digestive system The Liver Part of digestive system Located in upper right abdominal quadrant Is served by two blood vessels: the hepatic portal vein, the hepatic artery Has one duct that carries bile away from it to the gall bladder for storage Composed of lobules that contain hepatocytes Blood moves easily from the external vessels, in porous capillaries past the hepatocytes to a central vein Hepatocytes do the work of the liver Figure 14.11 Liver Functions Secretes bile Metabolizes bilirubin - a breakdown product of hemoglobin Produces albumin, and clotting factors Metabolizes fats, proteins, carbohydrates, stores glycogen, makes HDLs and LDLs Inactivates many biologically active chemicals including alcohol, medicinal and recreational drugs, hormones, poisons Stores fat soluble vitamins and iron Converts ammonia (NH3) into soluble urea to be excreted by kidneys Figure 26.19b Hepatitis •Inflammation of the liver •Causes include: • Viruses • Drug toxicity • Wild mushroom poisoning Viral Hepatitis Hepatitis A (HAV) Hepatitis B (HBV) Hepatitis C (HCV) Etiology Causes mild acute Causes acute illness and illnesschronic liver disease, can hepatocyte injury lead to liver cancer May cause acute illness, acts long term leading to chronic liver disease and risk of liver cancer Mode of transmission Fecal-oral primarily in children, young adults Contact with infected body fluids – blood, semen; contaminated needles, mother to newborn Contact with infected blood, mostly through contaminated needles Vaccination Hep A vaccine Hep B vaccine No vaccine From http://www.cdc.gov/hepatitis/index.htm Figure 9.20 Reverse transcriptase required Pathophysiology of Hepatitis • Destruction of hepatocytes by inflammation with edema and altered blood flow Symptoms of Hepatic Damage • • • • Jaundice Dark amber colored urine Nausea/vomiting Abdominal pain - R upper quad • Fatigue • Also- ascites, hepatic encephalopathy, coma, death Cirrhosis • Long term result of liver damage Liver Tests – Liver Panel • AST– liver enzyme, elevated with damage to cells • ALT - liver enzyme, elevated with damage to cells • ALP – enzyme related to bile ducts, levels elevate if there is a blockage • total bilirubin (blood)– may be elevated with liver damage or excessive RBC destruction • Albumin (blood) – checks on synthetic ability of liver cells • prothrombin time - decreased synthesis of clotting factors by kidneys See labtestsonline for more information Additional Liver Tests • Diagnostic tests for viral hepatitis – either serum tests for viral antigens, or serum tests for antibodies to the virus(indicating exposure) • Imaging – CT scan, ultrasound, MRI • Biopsy CT Scan of the Liver Normal liver Nodular cirrhotic liver with ascites www.integris-health.com 40 Drug Induced Hepatotoxicity • More than 900 drugs, toxins and herbs cause drug induced hepatotoxicity, • 20-40% of all fulminant liver failure cases are caused by drug induced hepatotoxicity • It is the most common reason a drug is withdrawn from approval • Damage to liver can be hepatocellular or cholestatic Drug-Induced Hepatotoxicity from http://www.emedicine.com/Med/topic3718 .htm Viral Hepatitis Treatment • Symptomatic support – diuretics, meds to decrease N load, Vit. K • Antivirals: • Interferons • Ribavirin • Surgery