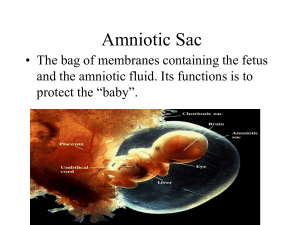
Maternal Physiology in Pregnancy
advertisement

Maternal Physiology in Pregnancy Jennifer McDonald DO Role of Estrogen in Pregnancy • Increases blood flow to uterus by promoting vasodilation • Changes the sensitivity of the system to CO2 • Softens cervix, initiates uterine activity, maintain labor • Develops breast tissue in preparation for breast feeding Role of Progesterone in Pregnancy • Readies the uterus for implantation • Relaxes smooth muscle to prevent SAB • Prevents maternal immunologic response to fetus • Relaxes smooth muscle • Plays role in development of alveoli & ductal system in the breast Changes in Size Increases from 50 g to 1000 grams ! Volume changes from 4 mL to over 4000 mL Uterine blood flow increases progressively and reaches 500 mL/minute at term Cervical & Vaginal Changes • Cervix becomes hypertrophied, soft and bluish in color • Thick secretions fill the endocervical canal (“mucous plug”) • “Chadwick’s” sign – bluish color to cervix/vagina due to increased vascularity Ovarian Changes • Ovulation ceases • Corpus luteum continues to grow until 7-8 weeks Corpus luteum secretes: 1. Estrogen 2. Progesterone 3. Relaxin Blood Volume • Increases 35-45% by 32 weeks • Red blood cell mass increases by 33% The increase in plasma is greater and faster than RBC resulting in physiologic anemia Hb concentrations falls from 14 gm/dL To 12 gm/dL. Purpose of Increase • Meets increased demands of uterus & baby • Protects against supine hypotension syndrome • Protects against fluid loss in labor White Blood Cells • Normal 7.0 mm3 • Rises to 10.5-11 mm3 • Can rise as high as 15-16 mm3 in labor Coagulation Factors • Fibrinogen doubled • Factor VIII tripled • Factor VII and Factor X are doubled Pregnancy is a hyper-coaguable state Cardiovascular Changes • Apex displaced upwards and to the left • Heart size increased 12% Pulse • 1st trimester resting pulse increases by 8 beats/min • By term increased by 15-20 beats Heart Sounds • First heart sound becomes louder and may split • Intensity of the second sound may become louder • Systolic functional murmurs develop in most due to tricuspid regurgitation Cardiac Output CO = HR x Stroke volume • Increases 40% by 20 weeks • Mainly due to increases in SV • Maintained until 4 days post-partum Blood Pressure • Systemic blood pressure overall decreased • Systolic changes little • Diastolic reduced (5-10 mmHg) • Venous pressure upper body unchanged • Venous pressure in the lower body increased • Especially affected by position Supine Hypotension • Compression of the inferior vena cava • Decreased venous return • Decreased cardiac output • Lowered blood pressure Peripheral Vasodilatation • Increased blood flow to the skin especially hands & feet lead to a feeling of warmth • Increased congestion of nasal mucosa leading to nasal congestion • Epistaxis common Venous Pressure • Mechanical pressure on the pelvic veins • Increased venous return from the internal iliac veins increased pressure in the external iliac veins • Increased pressure in lower extremities predisposes women to edema & varicose veins Diaphragm At term diaphragm can be elevated up to 4 cm Diaphragm • Mobility reduced • Respiration becomes mainly thoracic • Widened subcostal angle increasing transverse diameter of the chest Respiratory Physiology TV (30-50%) TLC (4-5%) FRC (20%) RV (20%) ERV (20%) IC (5-10%) Respiration • Shortness of breath common perception by pregnant women • Slight increase in respiratory rate • Increased O2 consumption 15-20% • Increased TV with normal RR increased MV • As MV increases hyperventiliation of pregnancy occurs lowering maternal CO2 • Over-breathing due to progesterone Renal Changes • Renal blood flow and GFR increased by as much as 50% • Increased excretion • Decreased serum creatinine & uric acid Ureters Dilatation of the ureters and renal pelvis Due to … • Relaxation by progesterone • Pressure at the pelvic brim especially on the right Urinary Frequency • Pressure on the bladder by the enlarging uterus • Congestion of the bladder mucosa GI Changes • Gingivitis • Reduced sensitivity of taste buds • Pica • Decreased GI motility due to progesterone • Increased propensity toward gallbladder disease Nausea & Vomiting • 70% of pregnancies • Elevated estrogen, progesterone • Dramatic elevations in hCG • Routinely resolves after 12-14 weeks • Hyperemesis gravidarum Constipation • Decreased motility • Increased water absorption • Pressure on the sigmoid colon • More sedentary • Iron from prenatal vitamins Appendix Appendix displaced upwards & laterally later in pregnancy Weight Gain U n d e rw e ig h t 12 .5 -18 k g (B M I <19 .8 ) (2 8 -4 0 lb s ) A v e r a g e w e ig h t 11.5 -16 k g (B M I 19 .8 -2 6 .0 ) (2 5 -3 5 lb s ) O v e r w e ig h t 7 -11.5 k g (B M I > 2 6 ) (15 -2 5 lb s ) BMI= Weight (kg)/height (m2) Distribution • 6 kg maternal tissues (breast enlargement, blood volume, fat stores) • 5 kg fetal tissues (baby, placenta, amniotic fluid) 7 kg Water 3 kg fat 1 kg protein Maternal Changes 1600 1400 1200 1000 Uterus 800 Mammary Gland 600 Plasma Volume 400 200 0 10 wk 20 wk 30 wk 40 wk Fetal Tissue Changes 3500 3000 2500 2000 Fetus 1500 Placenta 1000 Amniotic Fluid 500 0 10 wk 20 wk 30 wk 40 wk Musculoskeletal Changes • Increased mobility of pelvic joints Progesterone & Relaxin • Flattening of feet • Progressive lordosis • Round ligament pain Dermatologic Changes Linea nigra Cholasmsa Stretch Marks • Mechanical stretching of and rupture of elastic fibers • Glucocorticoid influence Breast Changes • Due to increased estrogenic state • Increased size & vascularity • Mastodynia very common • Increased pigmentation of areola & nipple • Prominence of Montgomery tubercles