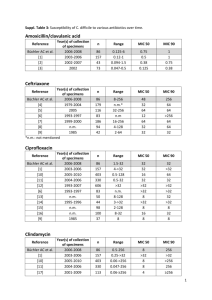
C. Difficile Prevention Collaborative: Hospital Team Kick-off

C. Difficile Prevention Collaborative:
Hospital Team Kick-off
Audio Conference Call
June 2, 2010 www.macoalition.org
C. Difficile Prevention Collaborative
Senior Leaders Call: Agenda
Introduction to C. Difficile Prevention
Collaborative
Driving Unprecedented Reduction in
Clostridium difficile in Acute Care using a Breakthrough Series
Collaborative Model
Susanne Salem-Schatz, Sc.D.
Collaborative Director
Maxine Power
Improvement Advisor
Salford Royal NHS Hospitals Trust
1
Context of the Collaborative
Keeping patients safe
Local and National Priority
Coalition, MHA, DPH Priority
CDC subsidy: American Recovery and
Reinvestment Act
ICU Safe Care Initiative/CUSP – Central Line
Infections
Needs assessment
C. Difficile
2
Collaborative Teams
Bay State Medical Center
Berkshire Medical Center
Brigham and Women’s Hospital
Cape Cod Hospital
Clinton Hospital
Emerson Hospital
Fairview Hospital
Falmouth Hospital
Franciscan Hospital for Children
Harrington Memorial Hospital
HealthAlliance Hospitals, Inc.
Marlborough Hospital
Massachusetts Hospital School
Mercy Hospital
Merrimack Valley Hospital
MetroWest Medical Center
Milford Regional Medical Center
Morton Hospital
Mount Auburn Hospital
Nantucket Hospital
New England Sinai Hospital
Noble Hospital
Northhampton VA Medical Center
Shriner’s Hospital for Children
Southcoast Hospitals Group
Spaulding Rehabilitation Hospital
St. Vincent’s Hospital
Tewksbury Hospital
UMASS Memorial Hospital
Wing Memorial Hospital & Medical Ctrs.
3
Overview of the Collaborative
Leadership engagement – Executive Sponsor
Multidisciplinary team & pilot unit
Beyond the usual suspects
Focus on the what and the how
Audioconferences –
Expert presentations and coaching calls
3 Learning sessions – June 24
Regional coaching sessions & individual support
Measurement & brief monthly reporting
4
Driving Unprecedented Reduction in
Clostridium difficile in Acute Care using a
Breakthrough Series Collaborative Model
Maxine Power
Improvement Advisor
Salford Royal NHS Hospitals Trust
Maxine.power@srft.nhs.uk
5
Clostridium difficile (C. difficile)
C. difficile is a spore forming bacterium
Major cause of antibiotic associated diarrhoea
Spores shed in the stool
Difficult to eradicate from patients; relapses common
Alcohol hand gel is ineffective
Spores survive up to 70 days in the environment
Spores can be re-ingested and re-infect
Primary source of transmission:
hands environmental surfaces
Picture
6
Treatment and remission
First episode
Discontinuation of current antibiotic therapy.
Discuss with Microbiologist.
Replacement of fluid and electrolytes.
Metronidazole PO 400mg TDS for 10 days.
Evaluate response to therapy at days 6-7 .
Symptoms not resolving or worsening, then stop metronidazole
Commence oral vancomycin PO 125mg QDS for 14 days.
30% will relapse within 30 days
20% will have repeated relapses
7
Evidence based management
Hand hygiene
Isolation & containment
Contact Precautions
Environmental cleaning with hydrogen peroxide
Restricted use of broad spectrum antibiotics
8
The problem at Salford Royal (2007)
C. difficile incidence was increasing
027 strain had been isolated
4 th Highest incidence in the North West of England
50 cases per month
30% on five medical wards
Consequences:
Seen as ‘inevitable and unavoidable’ by staff
Morbidity
Mortality
Increased costs at additional cost of £4715 per patient
9
Antibiotic Stewardship
February 2007 – protocols developed & implemented
New emphasis on caution ‘wait and see’
Cultures first
Structured for presenting conditions
Severity scores mandatory e.g. CURB
Cephalosporins and Quinalones removed and accessible only to senior team or via microbiology
Antibiotic pharmacist employed to round
60% compliance overall
10
What else can we do?.....
Set a clear, time limited, measurable aim
Provide clarity about ‘what to do’
Offer time
Offer leadership support
Support teams with measurement and feedback
Provide improvement expertise
Provide a structured & safe environment to test and change
11
Aim
Start date: April 1 st 2007
Duration: one year
To reduce the incidence of clostridium difficile in the elderly care units by 50% by April 2008
12
Why This Is a Great Aim Statement
What
Reduce incidence of c. difficile
By When
April 2008
For Whom
Elderly care units
How Much
By 50%
13
Aim – Why it matters
Establishes clear, unambiguous intent to improve
Time a team spends working on its purpose is a highest predictor of success
Balancing reach with feasibility: inspiring without discouraging
Our recommendations
Minimum: 30% reduction CDI in 18 months
Maximum: elimination of HA-CDI
14
Our Collaborative Aim
30% reduction in C. difficile infection per
10,000 hospital discharges by
December, 2011
15
A Breakthrough Series Collaborative?
www.ihi.org
16
Driver Diagram (Causal Pathway) of Factors influencing
C. difficile
Aim=
50% reduction in
C.difficile
Early identification
& containment
Habits & patterns
Environment
Patient alert to risk
Staff alert to risk
Isolation
Hand hygiene
Rings / nails / clothing
Rounds (medical) / barrier procedures
Information
Cleaning
Waste disposal
Antibiotic use Standardised protocols
17
Compliance
Measures
Primary Outcome Measure:
Incident cases of C. difficile
Process Compliance:
Hand hygiene compliance
Antibiotic prescribing compliance
Balancing Measure:
Sepsis
18
Balanced Set of Measures
Outcome measures
• How is system performing?
• What are results?
Process measures
• Are system parts/steps performing as planned?
Balancing measures
• Are changes designed to improve one part causing problems in another?
19
MA C. diff Collaborative Measures
Primary Outcome Measure:
Incident cases of Health care acquired C. difficile per 10,000 patient days
Process Measures
Choose your own
Link to changes you are making
Guidance and tools for tracking
Balancing Measures
Link to process changes
20
Improvement skills (LS1)
Model for Improvement
Plan do Study Act (PDSA)
Measurement
Reliability Science
Outcome = 1 st test of change
21
Multiple PDSA Cycle Ramps
Early identification
Habits & patterns
Antibiotic protocols
Change Concepts
Environment
22
What we learned?
Measures
Innovation
Extranet
Sharing tests of change
Adopt
Adapt
Abandon
Celebrate Success +++
23
Debbie’s story – success or failure?
24
Make the desired the default
Clean unless proven dirty Dirty unless proven clean
25
Innovation concepts
‘Vuja de’
‘A sense of seeing something for the first time even if you have seen it many times before’
Washing patients Washing ‘at risk’ patients
26
Act
Study
Plan
Do
Test in One Process
Improvement
First Focus
- Select ONE focus area
- Use small scale tests
Ideas and Hunches
27
PDSA Tip #1: Scale Down
Years
Quarters
Months
Weeks
Days
Hours
Minutes
Number of pts
“Drop 2”
28
PDSA Tip #2: “Oneness”
29
In our experience…
One test is rarely enough
The more test cycles completed, the more teams learn
The more teams learn, the more capable they are of making improvements
30
Project Management :
Sharing and Spread
Identification & containment
√ √
Habits & patterns
Antibiotics
L8 L4 L2 L3 L5
√ √ √
√
√ √
√ √
Environment √
31
5
6
7
8
9
3
4
1
2
Non Collaborative Wards
•1.15 (95% CI 1.03 to1.29) cases per 1000 occupied bed days at baseline
•0.64 (95% CI, 0.49 to 0.79) cases per 1000 occupied bed days post collab
New Antibiotic Policy
Learning Session 1
Learning session 2
Learning Session 3
Scale up and Spread
Learning Session 4
Learning Session 5
Learning Session 6
Second Summit
Baseline Collaborative Spread
The shift in the mean identified in August 2007 represents a 56% reduction.
32
Collaborative Wards
•2.60 (95% CI 2.11 to 3.17) cases per 1000 occupied bed days at baseline
•1.91(95% CI 1.44 to 2.38) cases per 1000 occupied bed days post collab
3
4
5
1
2
8
9
6
7
New Antibiotic Policy
Learning Session 1
Learning session 2
Learning Session 3
Scale up and Spread
Learning Session 4
Learning Session 5
Learning Session 6
Second Summit
Baseline Collaborative Spread
The shift in the mean identified in April 2007 represents a 73% reduction.
33
Thanks to………….
Patient and families for their cooperation & patience
Staff of L2, L3, L4, L5 & L8
Executive team
Don Goldmann & Fran Cook
SRFT Infection Control Team
Sandy Murray & Bob Lloyd
34
C. Difficile Prevention Collaborative
Next Steps
1.
2.
3.
4.
Sign your team up for June 24 kick-off meeting at: http://www.regonline.com/cdiffpreventioncollaborativeteamworkshop
Meet and discuss your aim for the collaborative
Schedule first meeting AFTER June 24
Also, if you haven’t yet:
Submit completed Team Grid
Infection Preventionist complete CDI baseline survey
35