Drugs Used in Hyperlipidemia
advertisement

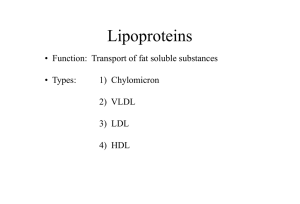
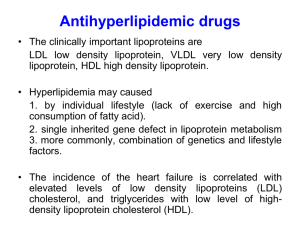
Vilasinee Hirunpanich B. Pharm, M.Sc. In Pharm (Pharmacology) Hyperlipidemia • Hyperlipoproteinemia (cholesterol, Triglyceride, LDL-C ) • เป็ นสาเหตุหลักในการเกิด atherosclerosis และ Coronary artery disease (CAD) Hyperlipidemia Endothelial injury Thrombosis Atherosclerosis Smooth muscle cell proliferation Macrophage inflammatory/immunologic mechanism Atherosclerosis Definition • Atherosclerosis is a disease which characterized by intimal thickening and lipid deposition. Atherosclerosis เป็ นโรคที่เกิดกับ artery wall ซึ่ งมักเกี่ยวข้องกับ การเกิดการทาลายของ endothelial และเกิดการสะสมของไขมันที่เต็มไป ด้วย macrophages. Atherosclerosis Developmental process of atherosclerosis Lipoprotein Transportation Exogenous pathway –Transport of dietary lipids to liver –Chylomicrons Endogenous pathway – – – – – Transport of endogenous synthesized lipids VLDL, IDL, LDL, HDL Transfer lipid between lipoprotein Transport cholesterol back to liver ในตับมีการสังเคราะห์ cholesterol โดยใช้สารตั้งต้นคือ Acetyl CoA และใช้ enzyme ที่เป็ น rate limitting step คือ HMG COA redcutase Exogenous pathway Endogenous pathway NCEP III guideline for hyperlipidemia • LDL-Cholesterol (mg/dl) <100 100-129 130-159 160-189 190 • Total cholesterol (mg/dl) <200 200-239 240 • HDL-Cholesterol (mg/dl) <40 60 Optimal Near or above optimal Borderline high High Very high Desirable Borderline high High Low High Type of hyperlipidemia Typ e Lipoprotein ที่ สูงขึน้ อุบัตกิ าร ณ์ ระดับ choleste rol ระดับ triglyceri des I Chylomicron พบน้ อย มาก + +++ IIa LDL พบบ่อย +++ IIb LDL+VLDL พบบ่อย III IDL IV V Standi ng plasm a ใส,มีครี ม หนา ข้ างบน Risk of atheroscler osis ปกติ ใสสีเหลือง ทอง สูง +++ + ขุ่น สูง พบไม่บ่อย ++ ++ ขุ่นมีครี ม ข้ างบน ปานกลาง VLDL พบบ่อย ปกติ, + ++ ขุ่น ปานกลาง VLDL+chylom icron พบไม่บ่อย + +++ ขุ่นมีครี ม หนา ข้ างบน - - Xanthoma - close-up Hypolipidemic drugs Bile Acid Sequestering resins HMG CoA Reductase Inhibitors Fibric Acid Derivatives Nicotinic Acid (Niacin) Probucol Structure Mechanism of resin Primary action (ที่ลาไส้เล็ก) •จับกับ bile acid ใน intestinal และขับออกทางอุจจาระทาให้ลด ปริ มาณ bile acid ที่ใช้ในการดูดซึ ม cholesterol Secondary responses (ที่ตบั ) •เพิ่มการเปลี่ยน cholesterol ไปเป็ น bile acid มากขึ้น •ระดับ cholesterol ในตับลดลง •ตับจึงพยายามเพิ่ม cholesterol โดยการเพิ่ม LDL-C receptor ที่ เซลล์ตบั ดังนั้นจึงทาให้ระดับ LDL-C ลดลง •แต่อาจมีผลเหนี่ยวนาให้ร่างกายกระตุน้ ให้เพิ่มการทางานของ enzyme HMG CoA reductase activity Effect on Lipids LDL • 15-30% HDL •2-8% TG •10-30% Toxicity • • • • Constipation, bloating (mix with fiber) อาจเพิ่มระดับ TG อาจรบกวนการดูดซึมของ fat soluble vitamin อาจรบกวนการดูดซึมของยาที่มี charge-structure Ex. Digoxin, Iron (Take resin >1h before or >2 h after other drugs) HMG CoA Reductase Inhibitors (Statin) • Structure Mechanism of Statin •Specific competitive inhibitor กับ HMG CoA Reductase Enzyme ซึ่งเป็ น rate limiting step ในกระบวนการ cholesterol biosynthesis. •ซึ่งตับจะตอบสนองต่อการลดการสังเคราะห์ cholesterol โดยการเพิ่ม LDL receptor ใน liver membrane. Effect on Lipids LDL •20-40 HDL •5-12% TG • 10-30% The synergism effect of statin and resin Toxicity อาจมีผลเพิ่ม liver enzyme เช่น aminotransferase (ดังนั้นควรวัดระดับ enzyme ที่เวลา baseline, 2, 4 wks) อาจเพิ่มระดับ Creatine kinase activity (CPK) ซึ่งทาให้เกิด myalgias, muscle tenderness (โดยเฉพาะการใช้ร่วมกับยากลุ่ม cyclosporin, azole antifungal) Clinical Use •Type II hyperlipidemia •Experimental and epidermiological studies showed that statins have the benefit effect in the decreasing of the atherosclerosis event. Fibric acid derivatives (fibrates) •Mediate PPAR-alpha activity PPAR Receptor (Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor) • 3 major type of PPAR (alpha, gamma, beta/delta) • การกระตุน้ ที่ PPAR alpha receptor ทาให้เกิด hypolipidemic effect (TG) and increase HDL level (apo A-I) • นอกจากนั้นจะลด inflammatory process ( IL-6, fibrinogen, C-reactive protein) Effect on Lipids • • • LDL 10% HDL 25% TG 40% Toxicity GI • nausea., vomiting, gall stone Skeletal Muscle • Myopathy, weakness Liver • Increase aminotransferase, alkaline phosphatase Hematologic change • Anemia, leukopenia Clinical Use • Type III hyperlipidemia • Evidence from experimental and epidemiologic data indicated that fibrates have the benefit effect in the decreasing of the atheromatic plaques. structure Nicotinic Acid Nicotinamide Mechanism of niacin Primary effect • กระตุน้ activity ของ lipoprotein lipase enzyme • ลดการนาส่ง free fatty acid ไปที่ตบั • ลดการสร้าง VLDL particles จากตับ Secondary response • ลดระดับ VLDL และ TG • ลดระดับ LDL-C • เพิ่มระดับ HDL Effect on lipids LDL • 10-20% HDL • 15-35% TG • 10-40% Toxicity Dermatology • Flushing, pruritus, rash (May involve with PG) GI • nausea,vomiting, diarrhea, dyspepsia Skeletal muscle • Muscle pain, weakness esp. with statin Hyperuricemia Clinical use • Almost every type of hyperlipidemia (except type I) by using combination with other drugs Apicimox • Similar mechanism to niacin but less side effects Probucol • A potent lipophilic antioxidant Mechanism of probucol • เพิม่ อัตราการกาจัดออกของ LDL จาก plasma Effect on lipids •Decrease LDL, cholesterol •Decrease HDL-C ? ข้อมูลในการทดลองระบุวา่ probucol มี ประสิ ทธิภาพในการป้ องกัน LDL oxidation ซึ่งเชื่อว่าเป็ นสาเหตุหลักที่ทาให้เกิด atherosclerosis event LDL Oxidation Combination drugs • Gemfibrozil+bile acid sequestering • • • • resin Statin+resin Niacin+resin Niacin+statin (monitor liver enzyme) Niacin+resin+statin