Paediatric Hearing Loss - Macquarie University Hospital
advertisement

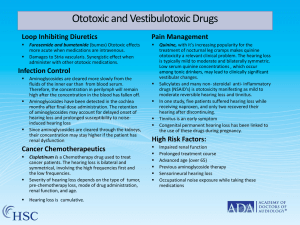
Paediatric Hearing Loss Dr Nirmal Patel MBBS (Hons)(Syd) FRACS (OHNS) MS (UNSW) Associate Professor of Surgery (Macquarie University) Director, Kolling Deafness Research Centre (University of Sydney) Summary Introduction Conductive Hearing Loss Sensorineural Hearing Loss Diagnosis Treatment Introduction Hearing loss is common 1 in 1000 babies have significant hearing loss at birth 10 in 1000 children have significant hearing loss at school (inc. mild and moderate) 80% of all children will have at least one middle ear infection And Mild Unilateral Hearing Loss has an Impact... Significant reduction in language acquisition and speech with prolonged mild unilateral hearing loss. http://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/ehdi/documents/unilateral hl/Mild_Uni_2005%20Workshop_Proceedings.pdf Paediatric Conductive Loss Congenital • Atresia of ear • Congenital stapes fixation • Cholesteatoma Acquired • Acute and chronic otitis media Microtia / Atresia Congenital Cholesteatoma Paediatric Sensorineural Loss Sensorineural Hearing Loss (Nerve deafness) • Genetic and Idiopathic (70%) • Acquired (30%) • Low birth weight/ NICU residents • Hyperbilirubinaemia • Ear and Head trauma • Anoxia and Hypoxia • Ototoxic Drugs and Chemicals • Infectious Diseases • Recurrent otitis media Diagnosis SWISH (Statewide Infant Hearing Screening Programme) aims to test every child born in NSW and identify significant hearing loss by the age of 3 months Parental Family (other carers) clues physician Diagnosis History ✦ Risk factors for SNHL ✦ Auditory milestones: • 3 months: Startled by loud sounds and calmed by familiar sounds • 6 months: ability to localise • 9 months: respond to name & mimic environmental sounds • 12 months: First meaningful words • 18 months: Vocabulary of 20 words or more • 24 months: Small sentences Diagnosis Examination • Local • Auricle • Canal • Tympanic membrane (pneumatic otoscopy) • Regional • Syndromic features • Tuning Forks • Difficult under 6 yrs Diagnosis Investigations • Hearing test - refer to audiologist with children’s experience Diagnosis • Refer to ENT if concerned • Tests if suspecting SNHL – Imaging - CT, MRI (dysplasias, large vestibular aqueduct) – TFT (Pendred’s syndrome) – Urinalysis (Alport’s) • Liase with opthalmologist (Usher’s Syndrome), geneticist (Connexin 26) Hart CK, Choo DI Laryngoscope April 2013 Treatment for Conductive Hearing Loss - Chronic Otitis Media • Observation - minimise day care exposure and passive smoking, reflux disease (prevalence 48%) • Autoinflation/ otovent - low cost no adverse effects, reasonable to consider; cochrane review small studies no significant benefit. • Nasal Steroids, antihistamines,antibiotics - no evidence to support use. Largest effect when used for 4 weeks to 3 months. American Academy Otolaryngology, Pediatrics & Family Physicians Consensus 2005 Miura et al OHNS March 2012 Cochrane Review Oct 2010, Sept 2011 and Sept 2012 Treatment for Conductive Hearing Loss - Chronic Otitis Media • Middle Ear Ventilation Tubes (Grommets) - effect is small is normal speech and development. Likely significant effect in either speech/ hearing delayed child or developmental delayed child. Measures of disease specific quality of life improve in all studies. • Children <24 months untreated have a higher risk of speech and language delay. • Hearing Aids - poor compliance, fluctuating pathology therefore difficult to fit, damage. American Academy Otolaryngology, Pediatrics & Family Physicians Consensus 2005 Miura et al OHNS March 2012 Cochrane Review Oct 2010, Sept 2011 and Sept 2012 Bone Anchoured Hearing Aids for Conductive Hearing Loss Treatment for Paediatric Sensorineural Hearing Loss Hearing assistive techniques • Preferential seating • Techniques to use at home Rehabilitation • Hearing Aids • FM systems Cochlear Implantation Cochlear Implantation Operation Video QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. Summary Hearing loss in children is common and significantly impacts speech and development even in mild unilateral loss. Early diagnosis is the key to treatment success. www.HillsENT.com 9439 1199