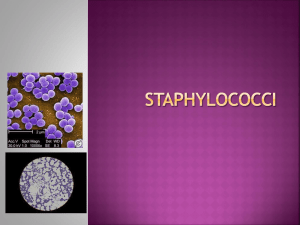
Staph. epidermidis
advertisement
Staphylococcus Department of pathogenic Biology of Gannan Medical College Biological characteristics 1. Morphology: Gram positive cocci arranged in irregular grape – like clusters Non-sporing and Nonmolite 2. Culture Facultative anaerobes temperature : 28~38℃ (37℃); pH : 4.5~9.8 (7.4) blood agar-----haemolysis Colony : 1~2 mm, circular, smooth, shiny surface, opaque, various pigments Staph. aureus Staph. epidermidi Staph saprophyticus 3. Classification: Table. Major properties of three species of taphylococci Main property Pigmentation Coagulase Hemolysin Leukocidins SPA Pathogenicity Staph. aureus Golden yellow + + + + +++ Staph. epidermidi Staph saprophyticus White Citrine -/ + - 4. Antigenic structure (1) SPA (staphylococcal protein A) cell wall protein MW 13,000~42,000 it combines nonspecifically with the Fcportion of human IgG antiphagocytosis coagglutination damage platelet activate B cell PHAGOCYTE Fc receptor SPA IgG BACTERIUM (2) polysaccharide (lipoteichoic acid LTA) polysaccharide A ------- Staph. Aureus polysaccharide B ------- Staph. epidermidis (3) Capsular Polysaccharide 5. Resistance: resistant to dry; heat (80℃,30min); salt(10~15%) sensitivity to: basic-dyes(crystal violet); antibiotics and sulfonamides (antibiotic resistance) Pathogenicity 1.pathogenic factor Surface structure:SPA ; Peptidoglycan; Capsule Enzyme :Coagulase;Fibrnolysin; Heatstable nuclease; Hyaluronidase; Lipase Toxin;Staphylolysin;Leukocidin ; Enterotoxin ;Toxic shock syndrome toxin-1 (TSST-1) ;Epidermolytic toxin Coagulase A enzyme that convers fibrinogen in citrated human or rabbit plasma into fibrin Extracellular coagulase an extracellular enzyme which activates a coagulase-reacting factor (CRF) normally present in plasma , causing the plasma to clot by theconversion of fibrinogen to fibrin (in tube). Bound coagulase---------fibrinogen to inhibit the phagocytosis of macrocytes and damage of bacteriacide substances in humor by coating the organisms with fibrin Staphylolysin Impairment of membrane permeadility; cytotoxic effects on phagocytic and tissue cells Protein five kinds: ~ Staphylolysin-: main pathogenic substance Leukocidin Kill PMNs and M Enterotoxin Protein nine types: A-H Heat stable (boiling for 30 min) Cause a food poisoning characterized by severe vomiting and diarrhea Toxic shock syndrome toxin-1 (TSST-1) Induces multisystsm effects superantigen effects Exfoliative toxin Causes the scalded skin syndrome in neonates, which results in widespread blistering and loss of the epidermis. 2.pathogensis local infection skin infection: hair folliculitis; boil; carbuncle; impetigo organ infection: pneumonia; meningitis. Systemic infection: Septicemia; pyemia toxin diseases Food poisoning (enterotoxin) TSS(Toxic shock syndrome) SSSS(staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome) Staphylococcal enteritis Laboratory diagnosis specimen: pus ; sputum ; blood ; food/faeces or vomit (food poisoning) ; mid-stream urine (pyelonephritis or cystisis) direct smear :gram stain isolation and identification: blood agar coagulose test Enterotoxin test and animal test Treatment Since strains of Staph. aureus vary in sensitivity to different antibiotics, treatment should be base on the results of sensitivity test made on a culture of the strain isolated from the patient.