Acute Oncology Presentations Caused by Disease
advertisement

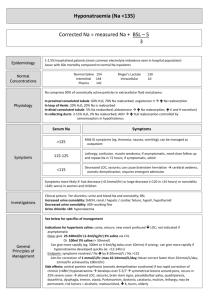
Acute Oncology Presentations Caused by Disease Dr Omar Din Consultant Clinical Oncologist Weston Park Hospital Acute Oncology Study Day 9th October 2013 Types of Emergency Treatment Related Febrile neutropenia Tumour Lysis Syndrome Extravasation Diarrhoea Nausea/vomiting Biochemical Hypercalcaemia Hyponatraemia (SIADH) Obstructive/structural SVCO Raised ICP Pathological fracture Spinal Cord Compression Airway Obstruction Pericardial Effusion Pleural effusion Ascites Case 1 • • • • 59 year old lady 6 month history of lumbar back pain Referred to rheumatology Bone scan Case 1 • • • • • • • Admitted Drowsy Dehydrated Abdominal pain Worsening back pain BP 90/60 P 110 Case 1 • • • • • • • • Bloods Hb 9.8 Na 135 K 4.0 Urea 9.4 Creat 135 Ca 5.3 Alk Phos 347 Malignant Hypercalcaemia • Ca >2.6 mmol/l • Causes: – Bone metastases – PTH-RP: – breast, renal, lung, head and neck, myeloma, lymphoma – (Primary Hyperparathyroidism) Hypercalcaemia - Symptoms • • • • • • • • Constipation Fatigue Nausea/vomiting Confusion Polyuria Polydipsia Abdominal pain Dehydration Hypercalcaemia - Treatment • IV Fluids - 3L normal saline over 24 hrs • IV Bisphosphonates – Zolendronic Acid (most potent) – Palmidronate • Stop frusemide whilst dehydrated, Ca/Vit D • Calcitonin for resistant cases • Treat underlying cause • Bloods – Hb 10.1 – Na 118 – K 4.2 – Urea 4.0 – Creat 60 • • • • • • • 9am Cortisol 500 TSH 2.1 Glucose 4.5 Lipids normal Serum osmolality 260 Urine osmolality 368 Urine Na 98 SIADH • Syndrome of inappropriate ADH secretion • Excess ADH leading to water retention and low serum sodium due to dilutional effect. • Low serum sodium and reduced plasma osmolality cf. urine osmolality • Urine Na >20mmol SIADH • • • • • Cancer; SCLC, NHL, HD, thymoma, sarcoma CNS disease (infection, trauma) Chest disease (infection) Drugs (thiazide, anti-epileptics, PPI, cytotoxics) Symptoms: nil, fatigue, nausea/vomiting, confusion, coma SIADH - treatment • Ensure Addison’s and Thyroid disease excluded (cortisol, TSH) • Fluid restriction 1l in 24 hours, daily U&E • Demeclocycline 600-1200mg/day divided • Discussion with endocrinology • Newer agents eg Tolvaptan (vasopressin receptor antagonists) • In EMERGENCY ONLY i.e. coma/fitting D/W Critical care. May need transfer to HDU for slow IV NaCl 1.8% - caution with osmotic demyelination • Treat underlying cause eg chemo for SCLC Case 3 • • • • • • • • 78 year old lady Breast cancer 2008, node +, Her2 + Admitted via A & E Headache Facial and arm swelling SOBOE Fixed raised JVP Conjunctival oedema Superior Vena Cava Obstruction • Definition; compression, invasion or occasionally intraluminal obstruction of the superior vena • Causes; SCLC, NSCLC, lymphoma account for 90% cases. Others include thymoma and germ cell. • • • • • • • Often insidious onset Compensatory collaterals over chest wall Neck/face swelling Headache Dizziness Syncope Conjunctival oedema Diagnosis • Timely identification of the cause is essential • CT Chest • Up to 60% of patients with SVC syndrome related to neoplasia do not have a known diagnosis of cancer – Need a tissue biopsy to guide subsequent management Histological Diagnosis • Sputum cytology, pleural fluid cytology, biopsy of enlarged peripheral nodes • Bone marrow biopsy for NHL • Bronchoscopy, mediastinoscopy, or thoracotomy are more invasive but sometimes necessary Treatment • • • • • • O2 Dexamethasone/PPI SVC Stent Anticoagulation if thrombus Does not require urgent radiotherapy – GET DIAGNOSIS Stridor – may require ICU admission • Histopathology • Treatment depends on cause • RT vs chemotherapy (SCLC, lymphoma, germ cell) Case 4 • • • • 64 year old man Haematuria PS 0 No PMH Case 4 • CT right renal mass, nodes, small volume lung metastases • Developed loin pain • Palliative nephrectomy • Obstructive LFTs • Biliary stricture - stented • Developed pain in left shoulder Pathological Fracture • broken bone caused by disease leading to weakness of the bone • metastatic tumours: breast, lung, thyroid, kidney, prostate • primary malignant tumours: chondrosarcoma, osteosarcoma, Ewing's tumour • Bloods: FBC, PSA, myeloma screen. • CXR. • Mammogram Pathological Fracture • Orthopaedic opinion – stabilisation/reamings/biopsy • Post operative radiotherapy – 20Gy in 5 fractions • Mirel’s Risk 1 2 3 Site Upper limb Lower limb Peritrochanter Pain Mild Moderate Severe Lesion Blastic Mixed Lytic Size <1/3 1/3-2/3 >2/3 8=15% risk 9=33% risk >9=High risk Case 4 • Treated with sunitinib • Shortly afterwards developed reduced visual acuity • Seen by opthalmology • Urgent phone call Choroidal Metastases • Choroid: vascular layer in and around eye • Breast, lung, prostate, kidney, thyroid, GI, lymphoma, leukaemia • Symptoms: flashing lights, visual disturbance • Urgent treatment: Radiotherapy to save vision • 20Gy in 5 fractions Brain Metastases • Lung, breast, melanoma • Headache, nausea, vomiting, seizures, change in behaviour, focal neurological deficit • CT/MRI • Dexamethasone up to 16mg/day • Risk of hydrocephalus – neurosurgeons ?shunt • Multiple mets – whole brain RT • Solitary met – excision or stereotactic radiosurgery Case 6 Pericardial effusion • Obstruction of lymphatic drainage or fluid from tumour on pericardium • Tamponade – tachycardia, hypotension, JVP, oedema • Echocardiogram • Urgent discussion with cardiothoracics • Percardiocentesis – fluid for cytology • Pericardial window • Complete pericardial stripping • Treat underlying cause Case 7 Lymphangitis Carcinomatosa • Breathlessness, dry cough, haemoptysis • diffuse infiltration and obstruction of pulmonary parenchymal lymphatic channels by tumour • Breast, lung, colon, stomach • 80% adeno • CXR – diffuse reticulonodular shadowing • CT or High Resolution CT Lymphangitis Carcinomatosa • • • • • Treatment of underlying condition Dexamethasone Chemotherapy Endocrine Therapy Prognosis poor – 50% die within 3 months of first symptom The End