Breast_Cancer_PPT

Physical Activity and
Reduction of Breast
Cancer Risk
Physical Activity vs. Exercise
Physical Activity
• Any form of movement using skeletal muscles.
• Movement required for daily life.
– Occupational physical activity
• Activities done for enjoyment.
Exercise
• Physical training
– Recreational physical activity
• Aerobic or anaerobic
• Higher intensities
Benefits of Physical Activity
• Physical activity can help maintain and/or reduce weight
• It helps to maintain and/or reduce body mass index (BMI)
– Underweight < 18.5
– Normal = 18.5- 24.9
– Overweight = 25.0-29.9
– Obesity > 30
Benefits Continued
• Helps us burn excess calories instead of turning into fat
• Increases lean muscle
• Helps retain and strengthen bone
• Strengthens the immune system
• Enhances mental and emotional well being
Definitions
• Risk- The likelihood of developing cancer based on lifestyle choices and family history
• Prevention- Lifestyle choices to reduce the risk of cancer
• Recurrence- The return of cancer after treatment
Pre vs. Postmenopausal Breast Cancer
Premenopausal
• Occurs in younger women
• Often linked to genetic predisposition
• Typically more severe and harder to treat
Postmenopausal
• More common form
• Linked to younger age of menarche and older age menopause
• Higher risk with no or few children, or older age of first birth
• Strongly linked to obesity after mid-life
Female Breast Cancer Incidence Rates* by State, 2007
Color on Map
Light green
Medium green
Medium blue
Interval
99.9 to 116.8
116.9 to 122.5
122.6 to 124.8
Rates are per 100,000 and are age-adjusted to the 2000 U.S. standard population.
Dark blue
Light Grey
124.9 to 139.2
Did not meet USCS data quality criteria
†Source: U.S. Cancer Statistics Working Group. United States Cancer Statistics: 1999 –2007 Incidence and Mortality Web-based Report.
Atlanta (GA):
Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, and National Cancer Institute; 2010. Available at: http://www.cdc.gov/uscs.
American Institute for Cancer Research
Summary
• Increased amounts of physical activity reduce risk of breast cancer.
• Stronger for postmenopausal women
Physical Activity and Risk of Breast
Cancer Among Postmenopausal
Women
• Objective
– Examine the associations of physical activity with breast cancer risk among postmenopausal women
• long-term activity
• recent activity
• change in activity
• specific types of activity
Study Design
• Nurses Health Study - 95,396 postmenopausal women
• Questionnaire in 1986
– time per week spent doing physical activities
• 7 more questionnaires over next 20 years
• Reports of breast cancer confirmed through medical records
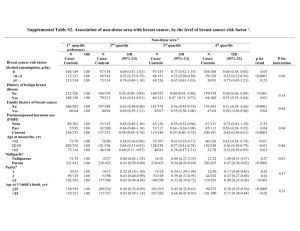
Results
• Moderate physical activity may reduce postmenopausal breast cancer risk
• 5 hours per week of brisk walking was sufficient to reduce the risk of breast cancer
• An increase in activity after menopause may be beneficial
Take Home
• Moderate physical activity like walking reduces breast cancer risk
• More exercise further reduces risk
• Physical activity reduces risk in women with a family history of breast cancer
The evidence is strong that a lifestyle including regular physical activity and maintaining a healthy weight reduces breast cancer risk for women of all ages
The American College of Sports Medicine and the American Heart Association recommend
30 minutes of moderately intense aerobic exercise 5 days a week and strength- training exercises twice a week
Summary
• Physical activity has many benefits
– Maintains healthy weight
• Physical activity reduces cancer risk
– moderate is good but vigorous is better
– Daily and consistent