מניעה וטיפול בטרשת עורקים,ההסתדרות הרפואית בישראל – החברה לחקר
Israel Medical Association-Society for Research, Prevention and Treatment of Atherosclerosis
דובי גביש
May 2013
? מהווה מטרה לטיפול תרופתיHDL האם
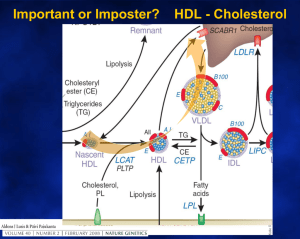
CHOLESTEROL TRANSPORT and
ATHEROSCLEROSIS
Atherogenic
VLDL,
LDL
Transport
Arterial
Wall
Liver
Lipid
Core
HDL
Bile
Antiatherogenic
Transport
Slowing and Reversing Atherosclerosis
Inflammation
HDL
VLDL
LDL
Libby (2001) Circulation 104:365
IVUS Trials:
REVERSAL, CAMELOT, ACTIVATE, ASTEROID
•Lowering LDL-C:HDL-C ratio to approx 1:1 stops atherosclerosis progression
Nicholls S, et al. JAMA. 2007;297:499-508.
PAV percent atheroma volume
BYOND LDL ?
HDL at a crucial crossroad for CVD
Atheroprotective functions of HDL
Anti-infectious
activity
Anti-thrombotic
activity
Anti-proteolytic
activity
Reverse cholesterol
transport/cellular
cholesterol efflux
Antiinflammatory
activity
HDL
Immune system
Anti-apoptotic
activity
Vasodilatory
activity/
endothelial
repair
Anti-oxidative
activity
Coronary Heart Disease and HDL-C
Hazard Ratio
3.5
3.0
N = 302,430
2.5
Unadjusted
2.0
Adjusted
1.5
1.0
0.8
0.75
1.0
1.25
1.5
1.75
2.0
HDL-C (mMol/L)
The Emerging Risk Factors Collaboration. JAMA 2009;302:1993-2000
Fig.?2 Kaplan?Meier curve for probability of disease-free survival stratified by low (?35?mg/dL) and normal (>35?mg/dL) HDL-C
levels.
Poh-Shiow Yeh , Chun-Ming Yang , Sheng-Hsiang Lin , Wei-Ming Wang , Po-Sheng Chen , Ting-Hsing Chao , Huey-Juan L...
Low levels of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol in patients with atherosclerotic stroke: A prospective cohort study
Atherosclerosis null 2013 null
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2013.03.015
Low HDL-C levels are common worldwide
100
Prevalence low HDL-C (%)
90
80
70
60
50
48.4*
44.0*
37.0**
40
35.0
30
20
6.6***
10
0
1.
2.
3.
Turkey1
(n=9000)
Korea2
(n=7300)
Mahley RW et al. J Lipid Res 1995;36:839-859.
Kim SM et al. Circ J 2006;70:820-826.
Aguilar-Salinas CA et al. J Lipid Res 2001;42:1298-1307.
Mexico3
(n=2256)
China4
(n=959)
ISRAEL
*35 mg/dL; **<40 mg/dL in men and <50 mg/dL in women;
*** <35 mg/dL
CHD Risk according to HDL-C Levels (FHS):
can it be modified?
4.0
4.0
Will increase
in HDL
3.0
CHD
risk ratio
2.0
2.0
1.0
1.0
0
65
25
45
HDL-C (mg/dL)
Kannel WB. Am J Cardiol. 52:9B–12B;1983.
result in CHD
risk
reduction?
Effect of lifestyle interventions on HDL
cholesterol
Intervention
Increase in HDL
Cholesterol
Aerobic exercise
5-10%
Stopping smoking
5-10%
Losing weight
Healthy diet (rich in omega-3
fatty acids or monosaturated
fatty acids)
Moderate alcohol intake
0.35mg/dL
per kg weight lost
Up to 5%
5-15%
Singh IM et al. JAMA 2007: 298: 786-98.
Effect of Statins on Apo A1 production
Apo A1 production (% of control)
Pitavastatin
Atorvastatin
Simvastatin
†
†
†
†
‡
*
0
1 3 5 10 30
Drug conc (M)
0
†
1 3 5 10 30
Drug conc (M)
0
1
5 10 30 50
Drug conc (M)
Hep G2 cells were treated for 48h with various concentrations of statins (1-30 μM and 50 μM).
The apo AI in the cultured medium was determined by ELISA kit.
*P<.05, †P<.001, ‡P<.01, Dunnett’s test.
Maejima. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2004;324:835
Management of Low HDL-C
• Therapeutic lifestyle changes
• Pharmacologic therapy
– Statins
– Niacin ER on top of statin
– CETP Inhibition
– Other new targets
All the effects of Niacin
Pharmacotherapy of low HDL cholesterol
% Change from baseline
15-35
5-15 10-15
52 5-25
0
7-30
20-50 2018-55
LDL-C
5
Triglycerides 0
HDL-C
The best HDL raiser today is Nicotinic acid
Change in Carotid Wall Area by MRI
Kaplan–Meier Curve AIM HIGH for the Primary End Point.
The AIM-HIGH Investigators. N Engl J Med 2011;365:2255-2267
Merck Announces HPS2-THRIVE Study of TREDAPTIVE™
(Extended-Release Niacin/Laropiprant) Did Not Achieve
Primary Endpoint
Release Date:
Thursday, December 20, 2012 8:30 am EST
Terms:
Prescription Medicine News [1]
.
In the study, adding the combination of
extended-release niacin and laropiprant to
statin therapy did not significantly further
reduce the risk of the combination of
coronary deaths, non-fatal heart attacks,
strokes or revascularizations compared to
statin therapy. In addition, there was a
statistically significant increase in the
incidence of some types of non-fatal
serious adverse events in the group that
received extended-release
niacin/laropiprant.
Comparison of the AIM-HIGH and the HPS2-THRIVE trial.
Landmesser U Eur Heart J 2013;34:1254-1257
Published on behalf of the European Society of Cardiology. All rights reserved. © The Author
2013. For permissions please email: journals.permissions@oup.com
Niacin (vitamin B3)—a lipid-modifying agent with a long history.
Rise & Fall of Niacin
Landmesser U Eur Heart J 2013;34:1254-1257
Published on behalf of the European Society of Cardiology. All rights reserved. © The Author
2013. For permissions please email: journals.permissions@oup.com
Major cardiovascular events in patients with LDL-C <
70 mg/dL in the TNT trial: effect of HDL level
Adjusted for: Age and gender, smoking, hypertension, BMI, fasting glucose, presence
of diabetes, prior CVD, on treatment triglyceride, baseline level of LDL-C
5 y risk of MCVEs (%)
HR (95% CI) vs Q1
10
Q2 0.85 (0.57-1.25)
Q3 0.57 (0.36-0.88)
Q4 0.55 (0.35-0.86)
Q5 0.61 (0.38-0.97)
8
6
4
2
0
(<37)
(37-42) (42-47) (47-52)
(>52)
Quintile of HDL-C (mg/dL)
No of Events
No of Patients
57
473
50
525
34
550
34
569
35
544
Barter et al, NEJM 2007, 357; 13, 1301-1310
Is there room for NIACIN?
Management of Low HDL-C
• Therapeutic lifestyle changes
• Pharmacologic therapy
– Statins
– Niacin ER on top of statin
– CETP Inhibition
– Other new targets
Figure. This schematic illustrates how CETP activity could potentially have proatherogenic or
atheroprotective effects.
Shah P K Circulation 2009;120:2408-2410
Copyright © American Heart Association
CETP LOF mutations Reduce
CVD!
The adverse outcome of the ILLUMINATE study in
patients receiving Torcetrapib indicates that potential
adverse effects outweighed beneficial effects
Tall, A. R. et al. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2007;27:257-260
מניעה וטיפול בטרשת עורקים,ההסתדרות הרפואית בישראל – החברה לחקר
Israel Medical Association-Society for Research, Prevention and Treatment of Atherosclerosis
דובי גביש
May 2013
? מהווה מטרה לטיפול תרופתיHDL האם
38
Lipid effects with dalcetrapib
35
*p<0.0001
%change from baseline
30
25
20
*p<0.01
15
10
*p=0.002
D 24 weeks
D 48 weeks
Placebo
5
D Dalcetrapib 900 mg/da
0
-5
HDL-C
* D 48 weeks vs. placebo
2010;31(4):480-8
LDL-C
ApoA-I
Stein EA et al. Eur Heart J
All CETP Inhibitors
43
g 1. DEFINE: Change from baseline lipids (mg/dL)
HDL-C
LDL-C
TG
Lp(a)
138% vs. placebo
60 vs. 6 mg/dL
- 39.8%
- 6.8%
- 36.4%
vs. placebo
HDL Forum November 2010
Cannon CP et al. N Engl J Med 2010: published on-line November 17.
Anacetrapib - Phase III trial (REVEAL)
The REVEAL (Randomized EValuation of the Effects of Anacetrapib
Through Lipid-modification) will assess whether there is clinical
benefit associated with anacetrapib. REVEAL is currently recruiting
30,000 participants for a randomized, double-blinded, placebocontrolled trial.
The study will compare patients with a history of vascular disease
(such as heart disease, cerebrovascular disease, and peripheral
vascular disease) on 100 mg of anacetrapib daily to those on
placebo, to determine if the addition of anacetrapib reduces the risk
of major coronary events (such as heart attack, death from heart
disease, or requiring a coronary revascularization.) Data will be
collected through 2017
Evacetrapibe CETP inhibitor
Fig. 1 Percent change from baseline in HDL and LDL cholesterol with statin plus evacetrapib 100<ce:hsp sp="0.25"/> mg/day or
statin alone. The relative percent change between the two groups is indicated.
Jane Stock
Controversies in dyslipidaemia management
Atherosclerosis Volume 221, Issue 2 2012 321 - 324
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2011.12.036
ACCELERATE
Evacetrapibe CETP inhibitor
Strategies of ongoing clinical trials to examine which lipid-targeted therapy should be added
to statin treatment in patients with high vascular risk.
Landmesser U Eur Heart J 2013;34:1254-1257
Published on behalf of the European Society of Cardiology. All rights reserved. © The Author
2013. For permissions please email: journals.permissions@oup.com
Don’t give up on HDL,
researchers plead
At a session on the subject, Dr Alan Tall
(Columbia University, New York)
summarized the situation:
"The HDL hypothesis is certainly under attack.
And there have been a lot of setbacks.
But we mustn't throw the baby out with the bathwater.
I think we need a new, modified HDL hypothesis."
Hughs S, Jun, 2012
Fig. 1
HDL good or bad?
Source: Atherosclerosis (DOI:10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2011.06.045 )
Terms and Conditions
Instrumental variable analysis using lipid levels corrected for statin use.
Shah S et al. Circ Cardiovasc Genet 2013;6:63-72
Copyright © American Heart Association
Dysfunctional HDL: מתי יש
1. Metabolic syndrome, Diabetes mellitus.
2. Atherogenic dyslipidemia.
3. Inflammatory diseases
4. Chronic renal disease.
5. Autoimmune disease
6. Women, increased HDL-C, no other cardiovascular risk
factors, evident atherosclerosis.
Assays for HDL function
HDL inhibits monocyte chemotaxis induced by LDL using
an in vitro reconstituted artery wall model by the coculture
of smooth muscle cells and endothelial cells.
Cell free antioxidant activity.
Inhibition of endothelial cell adhesion molecule expression.
Ability of HDL to act as an acceptor of cellular cholesterol.
Navab M. J Lipid Res. 2000;41:1495–1508.
Ansell BJ,
Circulation. 2003;108:2751–2756.
Cockerill GW. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 1995;15:1987–1994.
58
HDL Functionality as target?
More Efflux Less CAD risk
Efflux Capacity more important than just HDL
Cholesterol Efflux Capacity, High-Density Lipoprotein Function, and Atherosclerosis Amit V. Khera NEJM 364;127, 2011
61
Effect of recombinant Apo A-I Milano on
Coronary Atherosclerosis in Patients
With Acute Coronary Syndromes
A Randomized Controlled Trial
Steven E. Nissen, Taro Tsunoda, E. Murat Tuzcu, et al.
JAMA. 2003;290:2292-2300
NY-160626.038/020131YlsjoLS1
Raising HDL or ApoA-I reduced Atheroma
Atheroma Regression in a patient
who
received High-Dose ETC-216
(45mg/kg)
Atheroma Area
8.1 mm2
Atheroma Area
5.35 mm2
ETC-216 : Apo A-IMilano / Phospholipids
NY-160626.038/020131YlsjoLS1
Nissen S et al. JAMA. 2003; 290:2292-2300.
Future directions for HDL