• Define stress and eustress
• List several effects stress produces in your
body
• Compare common stressors among teens
• Understand the physiological response to
stress and what is happening at a
biochemical level.
Did any of you receive the reminder on your
phones
?
Do it now.
• What are we doing
1. Take out your
today?
corrections to your
1. Reviewing/ correcting
the decision making
homework. Turn in
homework
the original HW
paper too.
2. take a quiz
2. Take out your
Decision Making
3. work on stress packet
homework, both
pages 19-20 independently
assignments
What are Bernice’s options?
Essential Question: What is stress and how can it
harm the body?
?
Do it now.
What are we doing today?
1. Take out your
1. identify stress and
Stress Management eustress
packet. Did you
2 Understand where stress
comes from and it’s effect
complete p. 19-20?
on the body
2. Copy HW complete
3. Group work
pages 21-23 in the
stress management 4. stress activity
packet.
WHAT IS STRESS?
The body and mind’s reaction to
everyday demands and threats.
Click on pic for youtube.
Stress cannot be avoided
• It is an every day phenomenon
• Stress can have a good source(eustress)
• Stress can have a harmful sourse
(distress)
EUSTRESS
• IS GOOD STRESS
• EU – GREEK
PREFIX WHICH
MEANS GOOD
DISTRESS
• BAD STRESS
Positive Stress
•
•
•
•
Enables concentration
Increases performance
Energizes you into motion
Examples:
Sports
Exams (for some)
Work
Accomplish a to- do list
Negative Stress
Lack of motivation
Reduced effectiveness
Physical, mental and behavioral problems
Examples:
1. Socially disconnected (break up)
2. Death in family
3. Feelings of worthlessness
4. Illness/ disability
5. Losing something/someone
6. Overwhelming schedules
Where does stress come from?
• BIOLOGICAL STRESSORS
Heart Disease
Illness
ADD/Obsessive /Compulsive disorders
Diabetes
Anxiety attacks
•
•
•
•
ENVIRONMENTAL
COGNITIVE OR THINKING
PERSONAL BEHAVIOR
LIFE STITUATIONS
STRESSORS
• THINGS THAT PRODUCE A STRESS
RESPONSE
What causes your Stress?
• Open your stress management packet to
page 19. Look at the stressors that you
have had to deal with recently.
Compare your list with others in your group.
What stressors do you have in common with
other members in your group?
What happens when you do not deal
with stress?
Who would like to take the stress challenge?
Group Work
• Fill in the circle on your worksheet called
“Things that cause stress.” Add other
ideas that are not listed on page 19 of
your stress management packet.
• Now stop after you have 6 ideas.
Click on pic for youtube
“Effects of stress on the body”
Working in your group
•
•
•
•
Fill in the 4 boxes:
How my body reacts
How my heart feels ? Emotionally
How my head reacts or what I think
What is stress? youtube
Click on pic for you tube.
Essential question: What effect does stress have
on the body?
Do it now.
1.Turn in Homework:
Stress Management
Packet. I will collect it.
2. Take out corrected
work too.
2. Take out the note
taking sheet on stress
from our last class.
What are we doing
today?
1. Learn about the
biochemistry of stress
and the body and the
symptoms of untreated
stress.
2. Group work: Draw a
stress response
.
What happens during a stress
response?
• The adrenal gland on top of
each kidney is a key organ
in a stress response.
• The cortex or outer part
releases cortisol
• The medulla releases
epinephrine (adrenaline)
Click on here for
youtube
Adrenal Gland
You tube
What are the effects stress
hormones?
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Increase blood pressure and heart rate
Blood clots
Decrease digestion- weight gain
Stomach acids increase
Weaker immune system
Breathe faster and shallow
Sweat more
Muscle strain
Blood sugars rise
Anti-aging hormones decrease
Less sex hormones –and sex drive
Decrease memory
Increases fat ,cholesterol and glucose
Short term Physical Stress
Symptoms
•Dry Mouth
•Cool skin
•Cold hands and feet
•Increased sweating
•Rapid Breathing
•Faster heart beat
•Tense Muscles
•Feelings of nausea, or
'Butterflies in stomach
•Diarrhea
A desire to urinate
Long Term Physical Stress
Symptoms
Insomnia
change in appetite
sexual disorders
aches and pains
frequent colds
illnesses such as: asthma
back pain
digestive problems
headaches
feelings of intense and long-term tiredness
Immune system is weakened
Weight gain
Skin problems
Infertility
Faster aging
Behavioral/Social Stress
Symptoms
•Yawning
•Talking too fast or too loud
•Fiddling and twitching, nail biting, grinding
teeth, drumming fingers,
pacing, etc.
•Bad moods:
Defensiveness
Irrationality
Being irritable
Being critical
Aggression
Overreaction and reacting emotionally
More behavioral/Social affects
Reduced personal effectiveness:
Being more forgetful
Being unreasonably negative
Making less realistic judgments
Making more mistakes
Being more accident prone
Neglect of personal appearance
Changing work habits
Increased absenteeism
Let’s stop and produce stress!
• Who is up for a challenge of a stress
walk?
Read me first
Find a progressive muscle tape
to listen to. After you tried the
experience at home, write down the
web address and a paragraph about
your experience.
Take out your stress Management
Packets, I will collect them.
Next quiz: Covering depression and
stress will be Friday.
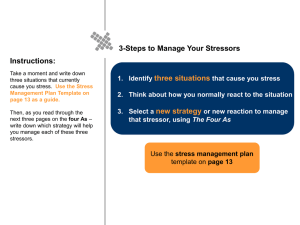
How to Manage Your Stress
1. ELIMINATE OR REDUCE YOUR
EXPOSURE TO THE STRESS
2. CHANGE THE WAY YOU PERCEIVE
THE STRESS
3. ACCEPT THAT YOU CANNOT
CHANGE THE STRESSOR
RELIEVING STRESS
•
•
•
•
•
EXERCISE
MUSIC THERAPY
MEDITATION
HUMOR OR LAUGHING
PROGRESSIVE
MUSCLE RELAXATION
• DEEP BREATHING
• MASSAGE
Click on boy for Progressive muscle relaxation tape.
Hans Selye 1936
Canadian physician coined the term stress
• The only person who controls your stress
level is you. Stressors may happen, but
your reaction to them will determine the
outcome in your body.
• “Its not stress that kills us, it is our reaction
to it.”
Stop here
• Teacher notes follow.
General Adaptation Syndrome
Alarm Stage
This is the immediate reaction to a stressor.
In the initial phase of stress, humans exhibit a
"fight or flight“ response, which causes one to
be ready for physical activity. However, this
initial response can also decrease the
effectiveness of the immune system, making
persons more susceptible to illness
during this phase.
Resistance Stage
• Your body will repair any damage caused
by the stress in this stage, however if the
stressor does not go away, the body
cannot repair the damage and stays alert.
•
•
•
•
•
High blood pressure
Hives
Insomnia
Lack of appetite
headache
Stage of exhaustion
At this stage, the stress has continued for some
time. The body's resistance to the stress may
gradually be reduced, or may collapse quickly.
Generally, this means the immune system, and
the body's ability to resist disease, may be almost
totally eliminated. Patients who experience longterm stress may succumb to heart attacks or
severe infection due to their reduced immunity.
For example, a person with a stressful job may
experience long-term stress that might lead to
high blood pressure and an eventual heart
attack.