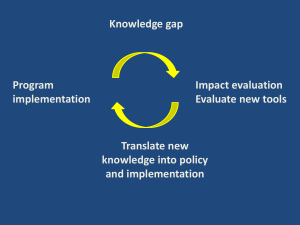
2.4 The agenda of the WHO in promoting global health and
advertisement

WORLD HEALTH ORGANISATION KEY KNOWLEDGE 2.3 – The agenda of the WHO in promoting global health and sustainable human development. KEY SKILLS Describe the role of International and Australian government and nongovernment agencies and organisations in promoting global health and sustainable development. The World Health Organisation • A branch of the United Nations and works to promote global health by providing leadership on global health issues and provides resources and support to countries that require assistance in improving the health of their citizens. • To address global health and promote sustainable human development WHO has a 6 point agenda. 1. Promoting development 6. Improving performance 2. Fostering health security The WHO agenda 3. Strengthening health systems 5. Enhancing partnerships 4. Harnessing research, information and evidence 1. PROMOTING DEVELOPMENT • Having improved health is essential for improving human development. • WHO works to promote sustainable human development by ensuring every person is able to access life-saving and healthpromoting resources such as health care and clean water. • Activities aimed at the most vulnerable e.g those living in poverty, disabled people, people living inn rural and remote areas. • WHO has a particular focus on the achieving the health related MDG’s to improve global health. They do this through: • Developing and publishing guides that educate health professionals and governments about the diagnosis, treatment, prevention and control of infectious disease such as malaria, tuberculosis and HIV • Developing global strategies to combat health issues, for example the Global Strategy on Dengue Fever • Carrying out and funding research into disease prevention and control • Monitoring health data on a global scale so trends can be identified and health issues addressed 2. FOSTERING HEALTH SECURITY • WHO worked to develop health security to reduce the spread of disease • • • • and therefore morbidity associated with such conditions. Health security prevents the outbreaks of diseases such as influenza and cholera. Many of these conditions are prone to epidemics and spread quickly. Both developing and developed countries are susceptible to outbreaks of disease and as a result all countries must work together. Factors such as globalisation, environmental degradation, the way food is produced and traded, and the way medicines are used all contribute to changing patterns in the spread of disease. In order to deal with these threats to global health, the WHO; • Supports national and international training programs to assist countries in preparing to deal with epidemics • Tracks the spread of diseases so interventions can be put in place to halt their progress • Encourages and assists countries to develop policies that decrease the risk of disease outbreaks • Developed the World Health Regulations, a document which outlines the measures that countries should take to reduce the spread of disease- includes; airport control, quarantine, resources to treat disease outbreaks. 3. STRENGTHENING HEALTH SYSTEMS • WHO works to ensure health systems are available to all, particularly the vulnerable and disadvantaged population groups. • In order to strengthen health systems the WHO works to assist with: • Providing adequate numbers of appropriately trained staff • Providing sufficient financing • Developing suitable systems for collecting vital statistics • Increasing access to appropriate technology, including essential drugs • The WHO provides policies on how to recruit and retain health workers. Health workers often experience poor living and work conditions • E.G of this agenda: The provision of anti-retroviral medication for those with HIV is an example of support that assists in achieving sustainable human development. These drugs work by maintaining a person’s immune function, which helps to reduce secondary infections and keeping them healthy. They are able to continue working and leading a productive life, and provide resources such as education send health care for their children (social sustainability). 4. HARNESSING RESEARCH, INFORMATION AND EVIDENCE • WHO develops evidence based health information to assist in improving global health. • Evidence is collected in the form of statistics, information and research and provides the basis for setting priorities, developing strategies and measuring results of interventions. • WHO; • develops evidence-based health information to assist in improving global health • new developments are being made for disease prevention and treatment and the management of health systems. The WHO works with other organisations to ensure the most up-to-date research is available for improving health of those in need. • standardise health terminology, the way research is carried out and the classification system used. This enables different groups to share resources and dates across the globe with regards to diagnosis, treatment and prevention of disease. • has a range of policy options that can be tailored to meet the needs of each country (road traffic accidents, violence against women and tobacco control). • Works with the governments and statistical institutions of various countries to collect data concerning trends and health-related issues 5. ENHANCING PARTNERSHIPS • WHO provides leadership in regards to global health issues. • While WHO is a leader in this area, the organization relies on the partnership, support and cooperation of many other partners including United Nation agencies, donors, governments, and private sectors. • As WHO is able to provide evidence based information they are able to encourage its partners to implement programs that are proven to promote global health. PARTNERSHIP EXAMPLE: GLOBAL FUND TO FIGHT AIDS, TUBERCULOSIS AND MALARIA. • Partnership between WHO, government bodies, national civil society organisations (e.g. local media), the private sector and communities living with or affected by the diseases. • The fund provides the resources required by the local experts who run the actual project. • These resources include financial grants, mosquito nets, education, essential drugs and diagnostic equipment. • By providing these resources the infection rate and the impact of theses conditions is reduced, which assists in prompting sustainable human development; as individuals are able to work productively, achieve a decent standard of living and contribute to decisions affecting their lives. Future generations will slso benefit as they will have a greater chance of leading long healthy lives in accord with their needs and interests. 6. IMPROVING PERFORMANCE • WHO aims to improve its organization and effectiveness by continually reviewing practices and introducing changes to the way it works when required. • WHO monitors its actions. • WHO works to ensure that its employees work in an environment that is motivating and rewarding in order to maximise performance • By improving their performance WHO is able to work more efficiently and therefore reach and improve the health and development of more people. Booklet activity- page 30 IDENTIFY THE WHO AGENDA BEING ADDRESSED IN THE EXAMPLES BELOW: Assists countries to provide health care Develops strategies to target HIV Develops strategies to target Malaria Develops and publishes resources to educate governments and those in health sectors Assists countries to develop policies to decrease the risk of epidemics Supports training programs to assist countries for disease outbreak Developed the Works Health Regulations (2007) that outlines the measures that a country should take in the event of a disease outbreak Provides funding to strengthen health systems Increases access to medical technology Increases access to essential medicines Increases access to HIV medication Takes a leadership role to standardize data and research so it can be shared globally Provides different policy options to help counties implement health actions Produce guidelines such as the Framework Convention on Tobacco Control. Provides grants to assist with techniques that may assist countries to control disease Global Fund to Fight AIDS Partnership Roll Back Malaria Partnership Partnerships for Maternal, Newborn and Child Health WHO is currently working on the ‘WHO Reform’ which assess the way they operate and enables them to make adjustments that will make them more efficient