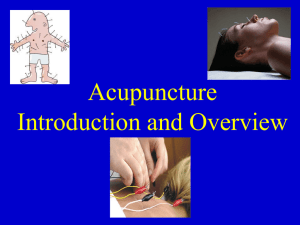
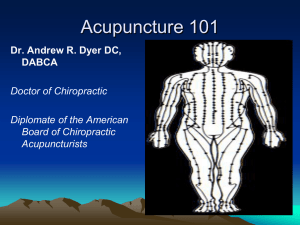
St meridian handout
advertisement

The Stomach Carl Clarkson MSc Acupuncture www.acuphys.co.uk enquiries@acuphys.co.uk References • Deadman et al (2007) A Manual of Acupuncture • Hopwood (2004) Acupuncture in Physiotherapy • Hui, K.K.S., Liu, J., Marina, O., Napadow, V., Haselgrove, C., Kwong, K.K., Kennedy, D., & Makris, N. (2005) The integrated response of the human cerebro – cerebellar and limbic systems to acupuncture stimulation at ST 36 as evidenced by fMRI • Joos, S., Schott, C., Zou, H, Volker, D., Martin, E. (2000) Immunodmodulatory effects of Acupuncturein the treatment of Allergic asthma: A randomised control study • Li & Lachner (2011) Glossary of Chinese Medicine References • Macioca – The practice of Chinese Medicine /The foundations of Chinese Medicine / Diagnosis in Chinese Medicine • Napadow, V., Dhond, R.P., Purdon, P., Kettner, N., Makris, N., Kwong, K.K., & Hui, K.K.S (2005) Correlating Acupuncture fMRI in the human brain stem with Heart Rate variability • Yim, Y., Lee, H., Hong, H., Kim, Y., Lee, B., Son, C., Kim, J.(2006) electro – acupuncture at acupoint St 36 reduces inflammationand regulates immune activityin collagen induced Mice • Zhang, D., Ding, G., Shen, X., Yao, Y., Zhang, Z., Zhany, Y. & Lin, Y. (2007) Influence of mast cell function on the analgesic effect of acupuncture of "Zusanli" (ST 36) in rats Dermatomes • Covers • V2 • S2 only dermatome Myotomes Upper / Middle Jiao • Face / neck – V2 / V3 (cranial nerves) – Massetor (clench your teeth) – Orbital muscles (helps control area around eyes) – Levator labii superious (helps to move nose) – Buccinator (helps to move mouth) • Trunk – Pecs – Abdominals Lower Jiao • Hip – Iliopsoas / pectineus / sartorious / Rec. Fem • Knee – Vastus lateralis / Tib. Ant • Ankle / Foot – Extensor digitorum Uses of ST • • • • • • • • • Headache Tooth / Jaw pain Fertility Constipation / digestive issues Immuno enhancing Fatigue Ant. Hip Knee Ankle Its Name! • Stomach meridian / Channel / Primary Channel • Stomach Channel of Foot Yangming (linked with LI) • Wei is the organ Research To many to list! • Brain activity – (Napadow et al. 2005, Hui et al. 2005) • Pain relief – ? mast cell involvement – Zhang et al. (2007) • Immunity – Yim et al. (2006) – Joos et al. (2000) 5 elements TCM Basics • Wei receives Qi (7am – 9am) • Yang (Fu) organ • Yang partner to Sp (Internally- externally linked) • 6 Channel partner of LI (6 Chaio’s) Links with other meridians • Yin (Zang) partner– SP • YangMing - LI • SI –Sends food to be further digested • LR – Linked by there ability to descend Qi (v.good in combo for digestive disorders) Its Job Western Similarities • Thought of as a bubbling cauldron – chamber of masteration • Vital to eat right food TCM • Regarded as most important of the Fu (Yang) organs • Along with Spleen, is known as the root of pre heaven Qi • Controls downward movement of Qi • Sp takes essence from the digestion • In charge of muscle bulk How to know ST is damaged Subjective • • • • • • • • • General Fatigue Apetite dysfunction Pain in epigastrium Eating late at night (depletes fluids and sets up disharmony throughout the system) Dehydrated / does not take on board fluids regularly Cold legs / feet Head pain Paralysis in the face / sudden deviation of the mouth Cramping of the lower leg / spasms of the thigh Objective • Pain on meridian • Weak muscles • Tongue coating – Quantity – Colour – Spread • Vomiting (rebellious Qi)/ belching / Hiccups Stomach deficiency Little or no coating at root or mid portion of tongue Cracks throughout tongue, especially in centre Point suggestions • Frontal headache – St 8 (usually in conjunction with LI 4) – St 36 • Jaw / tooth pain (lower) – St 5 – 7 – St 44 • Facial Palsy / Trigeminal Neuralgia – St 3-8 – St 36 • Fertility – St 25 – St 36 – St 40 Point Suggestions • Lower limb pain – – – – St 31- 34 (hip) St 34-36 (knee) in conjunction with SP St 37-40(shin disorders) St 41-44/45 (ankle / foot) • Fatigue – St 36 ( if recent onset) – St 36, St 40 (if prolonged) • Shoulder pain – St 38 Prevelant Points of St • • • • • CV 12 – Front Mu of St BL 21 – Back Shu of St Luo Connecting Point – ST 40 Yuan (source) – St 42 Xi Cleft – ST 34 – Acute epigastric pain Antique Points • Well – always last point / first point on meridian. Bled (not done by Physios!) • Spring – situated on border of palmer and dorsal aspect of extremity • Stream / river – both generally close to ankle / wrist • Sea – usually point just distal to knee / elbow Antique Points • Jing / Tsing (well) point – St 45 • Ying (Spring) point – St 44 • Shu (Stream) point – St 43 • Jing (river) point – St 41 • He (Sea) point – St 36 Sea Points • Sea of energy – St9 (CV 17, BL 10) – Typically used for lack of energy or breathlessness • Sea of nourishment – St 30(controls distribution of Qi throughout body), St 36 (controls digestion and bowels) – Anger, loss of apetite • Sea of Nourishment – St 37 (controls mov. Of yang towards Yin) , St 39 (controls mov. of yin towards Yang) – Tight feelings, strange bodily feelings Classical Points • Thirteen ghost point of Sun Si – Mao – St 6 • Returning the Yang – St 36(returns conciousness) • Heavenly star points – St 36 – St 44 • One of the original four command points – ST 36 • Window of Heaven Point – St 9 Misc • St 17 should not be needled • Chain & lock association – St 31, St 36, St 41 • St Earth meridian therefore Fire is mother, Metal is son – Mother point – St 41 – Son Point – St 45