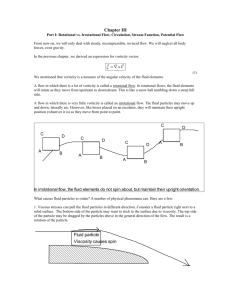
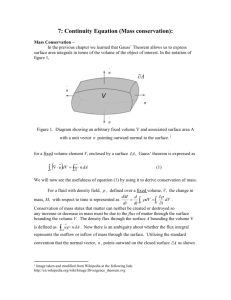
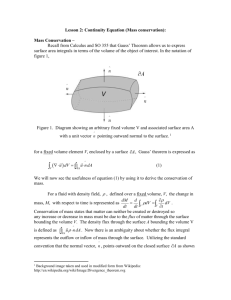
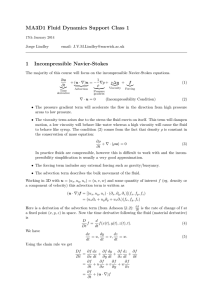
irrotational flow
advertisement

CHAPTER 8 ADDITIONAL SUBJECTS IN FUNDMENTALS OF FLOW Dr . Ercan Kahya Vorticity for the z axis: When vorticity is zero, irrotational flow Figure shows how the wood chips float Case (a): rotational flow Case (b): irrotational flow Although liquid makes a rotary movement, its microelements always face the same direction without performing rotation. In natural vortices such as hurricanes, tornados, eddying water currents has a basic structure with a forced vortex at the center and free vortex at the periphery. Given closed curve s, the integrated vs’ along this same curve is called circulation Γ . Taking counterclockwise rotation positive, Circulation dΓ of elemantary rectangle ABCD (area dA) & the circulation is equal to the product of vorticity by area. Integration gives Stokes theorem: surface integral of vorticity equal to the circulation If there is no vorticity inside a closed curve, then circulation around it is zero. Flow of viscous fluid Mass flow rate at inlet & outlet sections in x- & y-directions Fluid mass stored in the fluid element per unit time (x-dir.) : Fluid mass stored in the fluid element per unit time (y-dir.) : Mass change in unit time (right hand side) : Continuity Equation or Unsteady flow & compressible fluid & for real and ideal fluid For steady flow and incompressible fluid: For steady flow and incompressible fluid for axially symetric flow using cylindrical coordinates: For axially symetric flow using cylindrical coordinates: The strict solutions obtained for N-S equations to date are only for some special flows. Two such examples are: Flow of a viscous fluid between two parallel plates A flow in a long circular pipe is a parallel flow of axial symmetry. In this case, it is convenient to use the Navier-Stokes equation using cylindrical coordinates Under the same conditions as in the previous section, N-S equation simplifies to