Ultrasound
advertisement

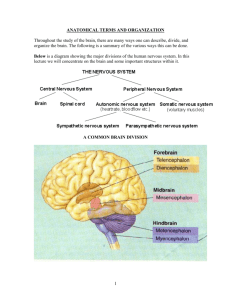
Ultrasound Michael Baram Objectives • Basic science • Terminology • Examples – Movies • What we should and should not be doing Disclosures • Becoming more of a techy. • I have lost my touch for subclavians • I tried to trade my kids in for a machine (It did not work) Anatomy of a wave • Velocity = wavelength x frequency • High frequency wave travel more linear and reflected easier Velocity through material Medium Speed (m/s) Blood 1566 Brain 1505-1612 Fat 1446 Kidney 1567 Liver 1556 Muscle 1542-1656 Bone 2070-5350 Water 1480 Air 333 Brass 4430 • Velocity of a wave is a constant through a given substance (at a constant temperature) • Assumption made all velocity about 1540 m/s How waves are made US- the perfect child Attenuation Reflection of Beam Partial reflection of a sound beam occurs at a tissue interface. Breast Mass or Cyst? Different Waves have different degrees of attenuation Low vs High Frequency 4 MHz 7 MHz Reasons for attenuation GAIN Shadowing • The lateral edge shadow is a thin acoustic shadow that appears behind edges of cystic structures. Shadowing • artifact is similar to reverberation Terminology Image Interpretation: • Anechoic / Echolucent - Complete absence of returning sound waves, area is black. • Hypoechoic - Structure has very few echoes and appears darker than surrounding tissue. • Hyperechoic / Echogenic - Opposite of hypoechoic, structure appears brighter than surrounding tissue. Terminology Image Acquisition / Probe Positions: • Transverse Plane - Also known as an axial plane or cross section, separates the superior from the inferior, or, the head from the feet. • Sagittal Plane - Oriented perpendicular to the ground, separating left from right. The "midsagittal plane" is a sagittal plane that is exactly in the middle of the body. • Coronal Plane - Also known as the frontal plane, separates the anterior from the posterior or the front from the back. • Oblique Plane - The probe is oriented neither parallel to, nor at right angles from, coronal, sagittal or transverse planes. • Longitudinal Plane - The longitudinal plane is perpendicular to the transverse plane an can be either the coronal plane or sagittal plane. Probe Types • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=fntJ7GLj CSU • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=VF_OG TSdSlo&feature=channel • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Sb1bM8 MnpRk&feature=channel • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XpN1R7 A0r_0&feature=channel What we Should and Should Not DO Thank you • Any questions Fast Exam • Subxiphoid bladder • http://folk.ntnu.no/stoylen/strainrate/Ultras ound/ • http://www.sonoguide.com/physics.html