SPH3U Graphs-of-Motion-Exam
advertisement
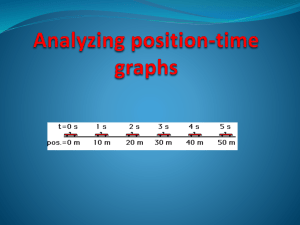
SPH3U Exam Review 1. The slope of a position-time (i.e. displacement-time) graph is equal to the: A. acceleration B. distance travelled C. time interval D. velocity 1. The slope of a position-time (i.e. displacement-time) graph is equal to the: A. acceleration B. distance travelled C. time interval *D. velocity 2. If the slope of a position-time graph is positive and increasing, the object must be: A. at rest B. travelling forward at constant speed C. travelling forward and speeding up D. travelling forward and slowing down 2. If the slope of a position-time graph is positive and increasing, the object must be: A. at rest B. travelling forward at constant speed *C. travelling forward and speeding up D. travelling forward and slowing down 3. The slope of a velocity-time graph is equal to the: A. acceleration B. distance travelled C. time interval D. velocity 3. The slope of a velocity-time graph is equal to the: *A. acceleration B. distance travelled C. time interval D. velocity 4. If the slope of a velocity-time graph is zero, the object must be: A. at rest B. travelling at constant speed C. slowing down D. either A or B 4. If the slope of a velocity-time graph is zero, the object must be: A. at rest B. travelling at constant speed C. slowing down *D. either A or B 5. The area under a velocity-time graph is equal to the: A. acceleration B. distance travelled C. time interval D. velocity 5. The area under a velocity-time graph is equal to the: A. acceleration *B. distance travelled C. time interval D. velocity 6. The velocity-time graph at right shows the motion of an object that is: A. travelling backward at a constant speed B. travelling forward and slowing down C. travelling backward and speeding up D. travelling backward and slowing down 6. The velocity-time graph at right shows the motion of an object that is: A. travelling backward at a constant speed *B. travelling forward and slowing down C. travelling backward and speeding up D. travelling backward and slowing down 7. Given the velocity-time graph at right, what is the displacement of the object after 5.0 s? A. -30 m B. -6 m C. 0 m D. 75 m 7. Given the velocity-time graph at right, what is the displacement of the object after 5.0 s? A. -30 m B. -6 m C. 0 m *D. 75 m 8. Which of the following position-time graphs might correspond to the velocity-time graph above? 8. Which of the following position-time graphs might correspond to the velocity-time graph above? 9. The position-time graph at right shows the motion of an object that is: A. travelling forward at a constant speed B. travelling forward and speeding up C. travelling forward and slowing down D. impossible to determine 9. The position-time graph at right shows the motion of an object that is: A. travelling forward at a constant speed *B. travelling forward and speeding up C. travelling forward and slowing down D. impossible to determine 10. Given the position-time graph at right, what is the speed of the object at 3.5 s? A. 15 m/s B. 31 m/s C. 54 m/s D. 95 m/s 10. Given the position-time graph at right, what is the speed of the object at 3.5 s? A. 15 m/s *B. 31 m/s C. 54 m/s D. 95 m/s 1. The graph at right depicts the motion of a motorbike down a straight section of road (positive is North). Sketch the corresponding velocity-time graph. Your graph should have 5 horizontal line segments: At 0 m/s from 0 to 10 s At 20 m/s from 10 to 25 s At 0 m/s from 25 to 30 s At -40 m/s from 30 to 45 s At 0 m/s from 45 to 60 s The graph at right depicts the straight-line motion of a dog running along a footpath (positive is North). Describe each segment of the motion in words. A: running forward at constant speed B: running forward and speeding up C: running forward and slowing down D: at rest E: running backward and speeding up F: running backward at constant speed 1.A vehicle with an initial velocity of 24 m/s [N] brakes and stops in 5.0 s. On a separate piece of graph paper, draw the (a) positiontime and (b) velocity-time graphs of its motion. 1.A vehicle with an initial velocity of 24 m/s [N] brakes and stops in 5.0 s. On a separate piece of graph paper, draw the (a) positiontime and (b) velocity-time graphs of its motion. 2. An object is dropped off the roof of a building. If the building is 65 m tall, on a separate piece of graph paper, draw the (a) position-time and (b) velocity-time graphs of its motion. 2. An object is dropped off the roof of a building. If the building is 65 m tall, on a separate piece of graph paper, draw the (a) position-time and (b) velocity-time graphs of its motion.