CHBT Module - 5
advertisement
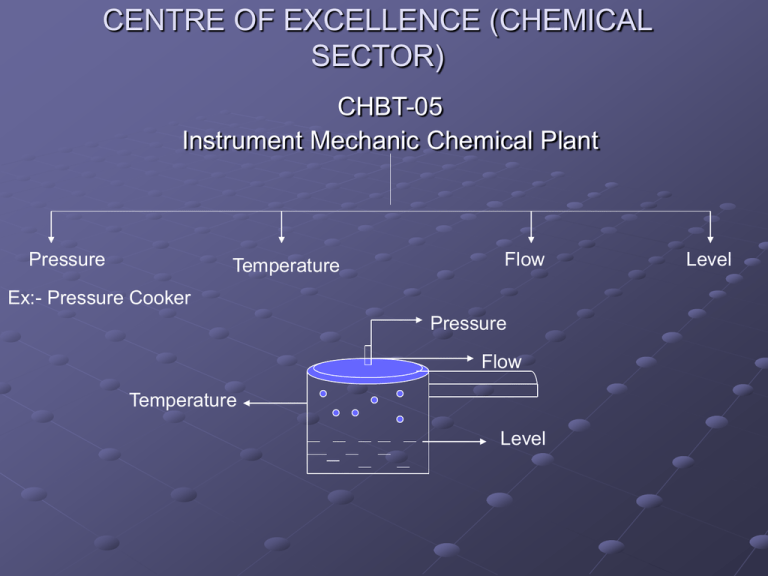
CENTRE OF EXCELLENCE (CHEMICAL SECTOR) CHBT-05 Instrument Mechanic Chemical Plant Pressure Temperature Flow Ex:- Pressure Cooker Pressure Flow Temperature Level Level Week No Lesson No 1 1 Introduction of instrumentation 2 Pressure 3 Pressure Measuring Instruments 4 Temperature Measuring Instruments 5 Bi – Metallic Thermometer 3 6 Glass & Gas Filled Thermometer 4 7 RTD & Thermocouple 5 8 Flow meter 6 9 Level Measuring Instruments 7 10 Hydrometer 11 pH Meter 12 Anemometer 13 Hygrometer 2 8 Name of Lesson PRESSURE Definition of pressure:-Pressure defined as force per unit of area is usually expressed In terms of familiar units of weight force & area or the height of a column of liquid that produce like a pressure at its base. -Pressure measuring devices may be divided in three groups. (1)Those that are based on the measurement of the height of a Liquid column. (2)Those that are based on the measurement of the distortion of an elastic pressure chamber. Liquid column methods: Means the pressure being measured is balanced against the pressure exerted by a column of liquid. The density of the liquid is known, the height of the liquid is measure of the pressure. P = ƍgh Device of this is called Manometer. When the height of the liquid is observed visually, the liquid columns are contained in transparent tubes. Liquids used in manometer are generally water and mercury. ƍ varies T Elastic – Element Method Pressure measuring devices are those in which the measure pressure deforms some elastic material (usually metallic) within its elastic limits, the magnitude of the deformation being approx. proportioned to the applied pressure. These devices may be classified into three types. (i) Bourden Tubes Elements (ii) Bellows Elements (iii)Diaphragm Elements Most frequently used process pressure indicating device is C-Spring Bourden Tube Pressure Gauge. These are available in various ranges and different MOC. Material are selected Gauges calibrated with Based on Pressure Pressure range Resistance to corrosion by the process Effect of temp. on calibration Vacuum Temperature Measurement of the hotness and coldness of a body or fluid is common place in the process industries. Temperature measuring devices utilize systems with properties that vary with temperature in a simple reproducible manner and known as reference or secondary thermometers. Temperature measuring devices are:(1)Liquid Filled System Thermometers (2)Bi-metallic Thermometers (3)Thermo Couple And RTD (4)Pyrometers Liquid filled system thermometers:Designed to provide an indication of temp. some distance from the point of measurement. The measuring element (bulb) contains a gas or liquid that changes in volume, pressure or vapour pressure with temp. These change is communicated through a capillary tube to a Bourden tube or other pressure or volume sensitive devices. (1)The Bourden tube responds to provide a motion related to the bulb temperature. (2)Systems responds to volume changes are completely filled with liquid. (3)System responds to pressure changes either are filled with gas or are partially filled with volatile liquid. Bi-metal Thermometers Thermostatic bi-metal can be defined as a composite material made up of strips of two or more metals fastened together. This composite, because of the differential expansion rates of its components, tends to change curvature when subject to a change in temperature. With one end of a straight strip fixed, the other end deflects in proportion to the temperature change, the square of the length and inversely as the thickness. Bi-metal thermometers are used at temperature ranging from 5800C and down to -1800C and lower. Flow Measurement:Flow defined as volume per unit of time at specified temperature and pressure conditions is generally measured by rate meters or positive displacement. Positive Displacement:- In which the flow is divided into isolated measured volumes when the number of fillings of these volumes is counted in some manner. Rate Meters:- Applies to all types of flow meters through which the material passes without being divided into isolated quantities. Orifice Meter Venturimeter Flow Measuring Instruments Rotameter Pitot Tube Turbine Flowmeter Orifice Meter The most widely used flow-meter involves placing a fixed area flow restriction (an orifice) in the pipe carrying the fluid. This flow restriction causes a pressure drop that can be related to flow rate. The sharp edge orifice is popular because its simplicity, low cost and the large amount of research data on its behaviour. Flow Orifice Plate Venturi - Meter It operated on exactly the same principle as the orifice. A venturi gives a definite improvement in power loses over an orifice and is often indicated for measuring very large flow rates. The initial higher cost of venturi over an orifice. Venturi-meter Rotameter It consists of a vertical tube with a tappered bore in which a float changes with the flow rate through the tube. For a given flow rate the float remains stationary since the vertical forms of differential pressure, gravity, viscosity and buoyancy are balanced. Level Measurement:It can be defined as the determination of the location of the interface between two fluids separable by gravity with respect to a fixed detum plane. The most common liquid measurement is that of the interface between a liquid and a gas and other are the interface between two liquids, between a granular or fluidized solid and a gas, and between a liquid and its vapour. Direct Method Level Measuring Devices Indirect Method Hook Type Level Indicator Float Type Level Indicator Electric Method Electric Methods Two electrical characteristics of fluids are conductivity and electric constant. An application of electrical conductivity is the fixed point level detection of a conductive liquid such as high and low water levels. A voltage is applicable between two electrodes inserted into the vessel at different levels. Both electrodes immersed in the liquid in a current flows. Capacitance type level measurements are based on the fact that the electrical capacitance between two electrodes varies with the di-electric constant of the material between them. Hydrometer Hydrometer is direct reading instrument. It is used to measure density. It works on the principle of buoyancy. It is of fixed weight and made up of good quality glass. It immerses objects in the liquid according to its density and reading is taking according to its stem level which indicates density of fluid. Hygrometer Hygrometer is used to measure moisture from atmosphere. It consists of hygroscopic material which depends on contraction or expansion giving result of moisture increase or decrease in atmosphere. Hygroscopic materials include human hair, animal fat, wood or paper. Hot Wire Anemometer It can measure flow rate of gas or liquid with the help of electrical equipments. PH Meter It is used to measure PH of liquids. It consists of electrode. The electrode is made up of Ag / AgCl which senses the PH of liquids.