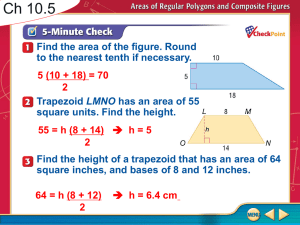
Geometry - BakerMath.org
advertisement

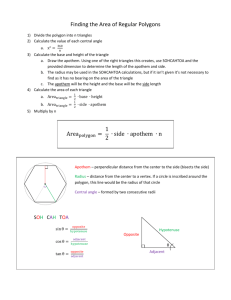
Geometry Areas of Regular Polygons Goals April 9, 2015 Find the area of equilateral triangles. Know what an apothem is and be able to find its length. Use the apothem to find the area of a regular polygon. Quick Review April 9, 2015 30-60-90 Triangles Right Triangle Trigonometry Area of a triangle 30-60-90 Triangle 30 2a a 3 60 a April 9, 2015 Trig Ratio Definition: Tangent Opposite A Adjacent Opposite Tangent of A = Adjacent April 9, 2015 Area of any Triangle A h b April 9, 2015 1 2 bh April 9, 2015 Area of an Equilateral Triangle A s h ? s base April 9, 2015 s 1 2 bh Finding h. s ?s 1 2 April 9, 2015 h s s We can solve for h by using the Pythagorean Theorem. Finding h. 2 h 2 h s 1 2 April 9, 2015 h s s 1 2 2 2 s 2 2 h 2 s h 2 s s 1 4 s 2 h 3 4 s 3 4 1 4 s 2 2 s 2 3 2 s Solving for Area 1 2 1 2 s s 3 2 s April 9, 2015 A s bh s 3 4 3 2 s 2 s Area of an Equilateral Triangle s s s April 9, 2015 A 3 4 s 2 Example Find the area. Solution: 8 8 8 A 3 4 3 4 s 2 8 2 3 16 64 4 1 6 3 2 7 .7 April 9, 2015 Your Turn Find the area. A 10 10 10 April 9, 2015 3 4 3 4 10 2 25 1 0 0 2 5 3 4 3 .3 Example 2 The area of an equilateral triangle is 15. Find the length of the sides. A 15 3 4 3 4 s 2 s 2 4 3 2 s 1 5 3 3 4 4 5.89 5.89 3 4 .6 4 s 5.89 s 2 3 4 .6 4 s 5 .8 9 April 9, 2015 Area of a Regular Hexagon Divide the hexagon into six equilateral triangles. Each triangle has an area of s April 9, 2015 A 3 4 s 2 Area of a Regular Hexagon Multiply this by 6: A 6 s April 9, 2015 A 3 3 2 3 4 s 2 s 2 Example Find the area of a regular hexagon with side length of 8. A 8 3 3 2 3 3 2 8 32 64 3 3 32 96 3 1 6 6 .3 April 9, 2015 2 Segments in a regular polygon. Center Radius April 9, 2015 Apothem Apothem April 9, 2015 The perpendicular distance from the center of a regular polygon to one of its sides is called the apothem or short radius. It is the same as the radius of a circle inscribed in the polygon. Apothem is pronounced with the emphasis on the first syllable with the a pronounced as in apple (A-puh-thum). Apothem Radius April 9, 2015 Apothem Another Way to Find the Area The area of the hexagon is equal to the area of one triangle multiplied by the number of triangles, n. Area = (Area of one ) (Number of s) April 9, 2015 Area of one triangle Radius r Apothem a s April 9, 2015 A 1 2 bh A 1 2 sa This is the Area of only one triangle. Area of one triangle Remember, there are n triangles. The total area then is 1 2 A r a s April 9, 2015 sa n The perimeter of the hexagon is s n. Perimeter s s s s r a s April 9, 2015 p=sn s A 1 2 sa n 1 2 a sn 1 2 ap Area of a Regular Polygon A 1 2 a = apothem p = perimeter April 9, 2015 ap This formula works for all regular polygons regardless of the number of sides. Example Find the area. 1. Draw a radius and an apothem. 2. What kind of triangle is formed? 12 a r 60 6 x 30-60-90 3. What is the length of the segment marked x? 6 April 9, 2015 Example Find the area. 4. So what is r? 12 5. And what is a? 12 12 r 6 April 9, 2015 a 3 6 6 3 6. The perimeter is? 72 (6 12) Example Find the area. The apothem is 6 3 and the perimeter is 72. The area is 12 12 6 3 A 1 2 ap 1 2 6 3 7 2 216 3 3 7 4 .1 2 April 9, 2015 Universal Formula Click Here to Skip April 9, 2015 Another Very Useful Formula Given the length of a side, s, of a regular polygon with n sides: A April 9, 2015 ns 2 4 tan 180 / n n = the number of sides s = the length of a side Previous Example Again A 12 ns 2 4 tan 180 / n 6 12 2 4 tan(180 / 6) 864 4 tan 30 864 2.3094 (graphing calculator) April 9, 2015 374.12 Notice! April 9, 2015 In a regular hexagon, the radius is always equal to the length of a side. This is because we divide the hexagon into equilateral triangles. A hexagon is the only shape where this is true. The Fly in the Ointment… April 9, 2015 If the polygon is anything other than an equilateral triangle, a square, or a regular hexagon, finding the apothem and the radius can be very challenging. Use what you know about 30-60-90 triangles, 45-45-90 triangles, and even trig to solve the problem. A harder example Find the area of the regular pentagon. Where did 36 come from? 36 6 April 9, 2015 360 Each central angle measures 1/5 of 360, or 72. The apothem bisects the central angle. Half of 72 is 36. A harder example Find the area of the regular pentagon. What is the apothem? 6 36 6 What is the perimeter? Don’t know. Let’s find it. April 9, 2015 A harder example Find the area of the regular pentagon. What trig function can be used to find x? 36 (SOHCAHTOA) 6 Equation: x April 9, 2015 TANGENT ta n 3 6 x 6 A harder example Solve the equation: ta n 3 6 36 6 6 ta n 3 6 x 6(.7 2 6 5) x x Use a scientific calculator or use the table on page 845. April 9, 2015 x 6 x 4 .3 6 A harder example x = 4.36 One side of the pentagon measures? 36 8.72 6 The perimeter is 4.36 April 9, 2015 8.72 (2 4.36) 43.59 (5 8.72) A harder example The area is: 36 8.72 6 1 2 ap 1 2 6 4 3 .5 9 1 3 0 .7 8 x April 9, 2015 A Final Example Find the area of a regular octagon if the length of the sides is 10. April 9, 2015 Step 1 Draw a regular octagon with side length 10. 10 April 9, 2015 Step 2 Locate the center and draw a central angle. 10 April 9, 2015 Step 3 Determine the measure of the central angle. 360 8 10 45 April 9, 2015 45 Step 4 Draw the apothem. 10 45 April 9, 2015 Step 5 The apothem bisects the angle and the side. Write their measures. 10 22.5 45 5 April 9, 2015 Step 6 Use a trig function to find the apothem. ta n 2 2 .5 10 a 22.5 a 5 April 9, 2015 5 a 5 ta n 2 2 .5 a 1 2 .0 7 Step 7 Find the perimeter. p = 10 8 p = 80 10 12.07 April 9, 2015 Step 8 Find the area. p = 80 1 2 ap 1 2 1 2 .0 7 8 0 4 8 2 .8 A = 482.8 10 12.07 April 9, 2015 A Skip This Using the area formula: A 10 ns 2 4 tan 180 / n 8 10 2 4 tan(180 / 8) 800 4 tan 22.5 800 1.6569 482.84 April 9, 2015 Summary April 9, 2015 The area of any regular polygon can be found be dividing the shape into congruent triangles, finding the area of one triangle, then multiplying by the number of triangles. Or, multiply the length of the apothem by the perimeter and divide that by 2. Practice Problems April 9, 2015