ppt
advertisement

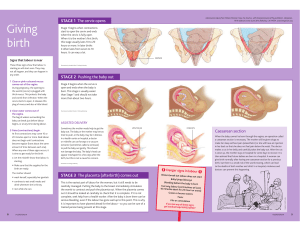
www.thegynaecologyclinic.com www.thegynaecologyclinic.com www.thegynaecologyclinic.com NORMAL & ABNORMAL LABOUR Part 1: Normal Labour HANGZHOU WOMENS HOSPITAL International Undergraduate Course, 2011 1. Glossary of terms 1. Cervical effacement is shortening of the cervical canal (from a length of 3 cm to a circular aperture. 2. A “show” results from loosening of the mucus plug in the cervix as a result of effacement and dilatation of the cervix. 3. First stage of labor is from onset of labor to full dilatation of the cervix. Second stage of labor is from full dilatation to delivery of the baby. Third stage of labor is from delivery to delivery of the placenta. 4. The birth canal is fully formed at the end of the second stage of labor. Its axis changes through 90 degrees (curve of Carus). 5. The lie of the baby is the relationship between the longitudinal axis of the baby and the longitudinal axis of the baby i.e. longitudinal, transverse, oblique. 6. The presentation of the baby is that part of its anatomy that is lowest in the birth canal i.e. cephalic, breech, face, shoulder, etc 7. The position of the baby is the relationship of the presenting part to the right or left side of the pelvis i.e. LOA, LOP, LOT, OP, OA, ROA, ROP, ROT. 8. The attitude describes the posture of the fetus i.e. flexion, deflexion, extension. 9. The denominator is an arbitrary part of the presentation that enables its description during labor. e.g. occiput in a vertex presentation, sacrum in breech presentation, mentum (chin) in a face presentation. Definition: Labour is the process by which contractions of the gravid uterus expel the fetus and the other products of conception after 24 weeks from the last menstrual period. Term Delivery:A term delivery occurs between 37 and 42 weeks from the last menstrual period. Preterm labour:Preterm labor is that occurring before 37 weeks of gestational age. Premature ROM: Rupture of the amnotic sac prior to the onset of labour Postdate pregnancy:Postdate pregnancy occurs after 42 weeks . Mechanism of normal labour “Powers” “Passenger” “Passages” Female Male Levator ani OI atla PC Vagina Rectum IC Changes to the uterus during labour Uterine contractions Rhythm: increase in frequency and duration in labor。 * Symmetry and polarity * Retraction * Symmetry and Polarity The intensity of the upper segment of the uterus is the most strong. Retraction: The myometrium of the upper uterine segment does not relax to its original length after contractions; rather, it becomes relative fixed at a shorter length. Changes to the cervix during labour Lie, presentation, position, attitude of the fetus in labour Engagement and station of the fetus in labour Mechanism of normal labour PROGRESS IN LABOUR Descent Internal rotation Extension PROGRESS IN LABOUR PARTOGRAM - Friedman CAPUT SUCCEDANEUM EPISIOTOMY – midline v mediolateral PERINEAL TEAR – first to fourth degree Third stage of Labour