The Boltzmann Constant - science
advertisement
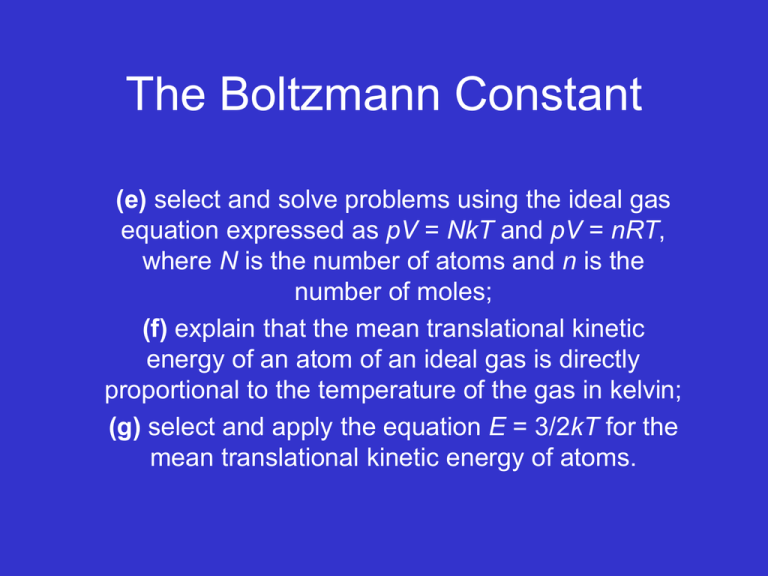
The Boltzmann Constant (e) select and solve problems using the ideal gas equation expressed as pV = NkT and pV = nRT, where N is the number of atoms and n is the number of moles; (f) explain that the mean translational kinetic energy of an atom of an ideal gas is directly proportional to the temperature of the gas in kelvin; (g) select and apply the equation E = 3/2kT for the mean translational kinetic energy of atoms. OUTCOMES MOST SHOULD • Understand the difference between R and k and when to apply them. • Be able to state that the Boltzmann constant is the gas constant for a single molecule whilst the molar gas constant is the constant used when dealing with quantities in moles. • Be able to explain that the mean translational kinetic energy of an atom of an ideal gas is directly proportional to the temperature of the gas in Kelvin. • Be able to select and apply the equation E = 3/2kT for the mean translational kinetic energy of atoms correctly in different situations. • Be able to select and solve problems using the ideal gas equation expressed as pV = NkT, where N is the number of atoms and n is the number of moles. SOME COULD • Be able to derive equation for the translational KE of an atom in an ideal gas E = 3/2kT. Solid Gas Volume Boltzmann constant Avogadro constant Mole Kinetic model Molar gas constant Kelvin Kinetic energy Ideal gas Pressure Temperature State of matter Liquid Boyle’s law