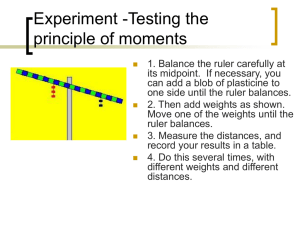
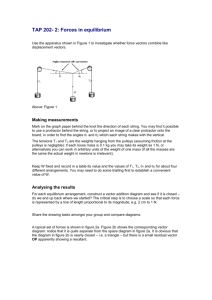
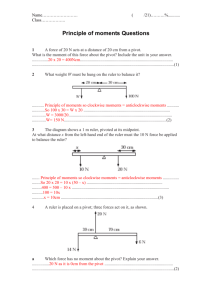
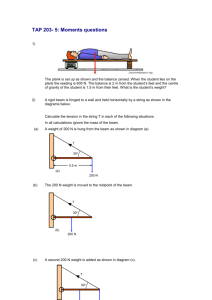
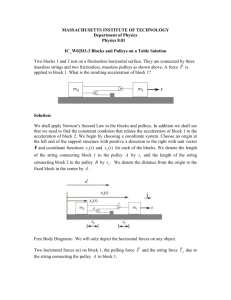
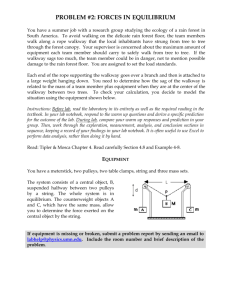
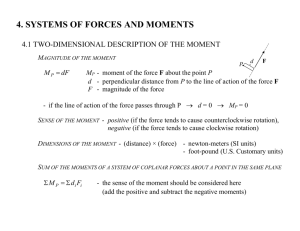
Principle of moments
advertisement

Principle of moments Done By : Low Zhen Jie Cheng Ivy Miao Jing Deborah Lye Our instrument Meter rulers The unknown mass A B Retort stand Materials used • • • • • 2 pulleys 2 metre rules Retort stand Weights String Why is our invention innovative and creative? • Instead of using the DOWNWARD force of gravity which is used in the weight balance, our group makes use of the UPWARD force by using pulleys to reverse the direction of gravity • Our machine uses not one, but two rulers. And it is innovative as the ruler on the bottom ensures accuracy of results. Equilibrium of forces • • • • • Clockwise moments= Anti-clockwise moments No net force No acceleration At rest Both sides of the balance are at rest and therefore have the same force – weight. How we determine the weight of the object • Put enough weights at the other side to roughly balance out the sides. • Also adjust the pulleys with the place the string is tied to the bottom of the ruler. • The moment on the left side has to be equal to that of the right side. – Meaning, the ruler at the bottom will need to balance. Calculation Left hand side: Mass of A × Perpendicular length Right hand side: Mass of B × Perpendicular length Why? By calculating the moments of a force! Moment= F x L, where F is the magnitude of the force and L is the perpendicular distance. In this case, L is where the string is tied to the ruler (and making sure the string is straight), and F is the weight of the object. • Since in the formula, F cannot be changed as the weight of an object is a constant. The L, perpendicular distance can change the moment of a force. Range of measurements of our instrument. • Between 0 – 1000 grams • Precision : +/- 0.5 grams