Lecture2_2014_Buoyan..
advertisement

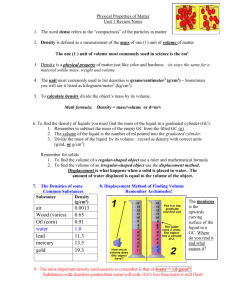
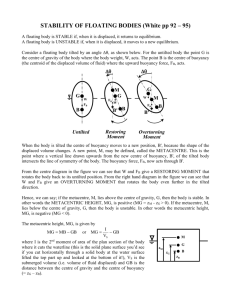
General Theme: ….Consider the evolution of convection in the absence of significant larger-scale forcing influences…or even boundary layer features…. The spectrum of convective storms and convective systems can largely be explained based on just two environmental parameters: …..Buoyancy ….Vertical Wind Shear Ordinary Cell: Multicell: Supercell: Archetypes: Building blocks of the observed spectrum Ordinary Cells: short lived (30-60 min), propagate with the mean wind Multicells: long-lived group of ordinary cells Supercells: quasi-steady, rotating, propagate right or left of the vertical wind shear vector Physical processes controlling cell types: •Buoyancy processes: basic updraft/downdraft, (ordinary cells) •Gust front processes: triggering of new cells, upscale growth, (multicells) •Dynamic processes: rotating updraft, dynamic vertical pressure gradient forcing, (supercells) http://www.meted.ucar.edu/convectn/csmatrix/ What Goes Up…… Must Come Down Ordinary Cell Evolution: What Goes Up…… Basic Equations: æ pö p ºç ÷ è p0 ø Rd Cp (Exner Function) du ¶p = -C p q v + fv + Fx dt ¶x dv ¶p = -C p qv - fu + Fy dt ¶y dw ¶p =- C p q v + B (Buoyancy) dt ¶z ( ) éq ¢ ù B º g ê + .61 qv - q v - qc - qr ú ëq û + ice…. Buoyancy Force: Archimedes Principal: Buoyancy is simply the difference between the weight of a body and the fluid it displaces. æ r2 - r1 ö F A= = gç ÷ M è r1 ø Parcel Theory: .…ignores pressure effects 1/2 Wmax = (2 CAPE) …real bubble in 3D simulation Buoyancy is Scale-Dependent!!! Diagnostic Pressure: Ñ ×(Momentum) ( ) ( ) ¶B Ñ × C p rq v Ñp = -Ñ × rv × Ñv + ¶z Dynamic Pressure: ( ) ( Ñ × C p rq v Ñp dn = -Ñ × rv × Ñv æ ¶B ö Buoyancy Pressure: Ñ ×(C p r q vÑp B ) = è ¶z ø **For wavelike disturbances: Ñ p » -p 2 ) Vertical Momentum Eq. (rewritten) ù ¶p dn é ¶p b dw = -C p q v + ê -C p q v + Bú dt ¶z ¶z ë û (dynamic) + (buoyancy) Basic 2D Equations: du ¶p = -C p q v + fv + Fx dt ¶x ⁄ dw ¶p =- C p q v +B dt ¶z Or, more simply, consider the 2D horizontal vorticity equation: dh ¶B =dt ¶x æ ¶u ¶w ö where h = è ¶z ¶x ø Buoyant Processes: Buoyancy is Scale-Dependent!!! Basic Equations: æ pö p ºç ÷ è p0 ø Rd Cp (Exner Function) du ¶p = -C p q v + fv + Fx dt ¶x dv ¶p = -C p qv - fu + Fy dt ¶y dw ¶p =- C p q v + B (Buoyancy) dt ¶z ( ) éq ¢ ù B º g ê + .61 qv - q v - qc - qr ú ëq û + ice…. Cold Pools: Density Currents Droegemeier and Wilhelmson, JAS, 1987 …2D …30 – 40 km …100 – 200 m You’ve all heard of “Kelvin” Helmholtz instability…???? Shallow (Trapped) Wave-Like Disturbances Density Current Internal Bore of Wavelength l • Gravity-wave related phenomena can be excited by antecedent convection • Statically stable nocturnal PBL provides an environment where such disturbances can maintain coherence From Simpson (1997), An Introduction to Atmospheric Density Currents Density Current: dh ¶B =dt ¶x Theoretical speed of propagation: c = 2ò 2 H o ( -B) dz c = 2g r¢ r H RKW Theory Rotunno et al. (JAS, 1988) “Optimal” condition for cold pool lifting C/∆u > 1 C/∆u = 1 C/∆u < 1