FLOW NETS - spin.mohawkc.on.ca
advertisement

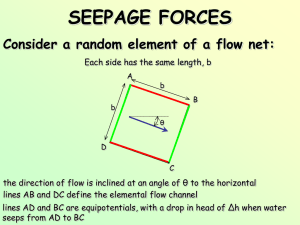
FLOW NETS Bernoulli's Equation water travels very slowly through soil as opposed to channel flow p v hz γw 2g 2 Total Head, m 0 Elevation Head, m Fluid Pressure Head, m Velocity Head, m FLOW NETS Bernoulli's Equation For Seepage through soil: Pore Water Pressure, kPa u hz γw FLOW NETS Total HeadHydraulic Loss, In terms h in Gradient of water Bernouli: seeping (Slope),from i: A to B: L h hA uA γw h head loss i or L distance over whichhead loss occurs A uB γw hB B zA zB datum FLOW NETS Say The The we path water The constructed ofenergy would the flow seep driving a tank would from the in be the the seepage, curved lab leftlike chamber, as h?this shown. one. through the soil and into the right chamber. h FLOW NETS If Lines Line we ab stretch ca and is the cefd theupstream tank, are the weequipotential boundaries have a mainly of Line bd is the downstream equipotential horizontal boundarychannel this where flow the forchannel the totalseepage head isflow h boundary where the total head is 0 from the left chamber to the right h FLOW NETS at In The If What bd ca order we water h divide would = to h 0would determine the the rise total seepage to the head the journey total be same at head into level theand half equally on pore the way water hydraulic spaced pressure drops grade mark at inline (at head anyfrom points point then each in x, wethe yget of ormass these z)? a flow ofpoints. soil net.we Each point the has flow equalchannel potential therefore the subdivide intoand smaller channels line through them is an “equipotential”. half way mark h=h h = 0.5h x y z h=0 FLOW NETS If we recompressed the tank the flow net would look something like this: Construction of Flow Nets To construct a flow net, you must start Downstream Equipotential with a scale drawing of theBoundary hydraulic structure: Upstream Equipotential Boundary 1. Draw Flow Channel Boundaries 2. Draw Equipotential Boundaries Construction of Flow Nets Not all The elements first trial: are “square” The bottom flow channel intersects the It may take several iterations to finally impervious layer flow net. come up with a satisfactory Construction of Flow Nets water pressure, zof 5. Using the given scale, elevation 4. 6. At The pointpore P, the total headthe is u10/12ths P = (hp – head, p)the w 3. Number equipotentials as shown: 1. free water surface ispoint, datum. To 2.Downstream determine Show =(3.33+5.2)x9.8 the And total the the total head, final head version h driving at any is: seepage. P = 83.3 kPa z is -5.2 m head driving the seepage P h = 4.5-0.5 = 4.0m hP 4.0 10 3.33m 12 FLOW NETS Here’s some useful relationships: 1. Each channel carries an equal flow: ∆q = k∆h 2. Each drop in head is equal to: h Δh Nd where Nd is the number of partitions or drops in potential 3. The total flow carried: where Nf is the number of flow channel partitions q = Nf∆q Nf q kh 4. Or, the total flow carried: Nd nd 5. And, the head at any point P: hp h Nd where nd is equipotential number (0 at downstream FWS)