Worksheet2_Solutions
advertisement
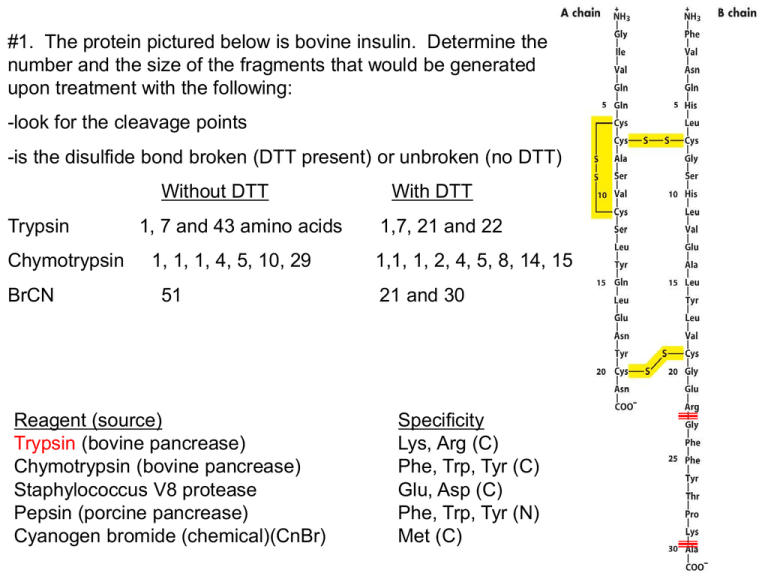
#1. The protein pictured below is bovine insulin. Determine the number and the size of the fragments that would be generated upon treatment with the following: -look for the cleavage points -is the disulfide bond broken (DTT present) or unbroken (no DTT) Without DTT Trypsin Chymotrypsin BrCN 1, 7 and 43 amino acids 1, 1, 1, 4, 5, 10, 29 51 Reagent (source) Trypsin (bovine pancrease) Chymotrypsin (bovine pancrease) Staphylococcus V8 protease Pepsin (porcine pancrease) Cyanogen bromide (chemical)(CnBr) With DTT 1,7, 21 and 22 1,1, 1, 2, 4, 5, 8, 14, 15 21 and 30 Specificity Lys, Arg (C) Phe, Trp, Tyr (C) Glu, Asp (C) Phe, Trp, Tyr (N) Met (C) #2. A peptide was cleaved into smaller fragments using chymotrypsin and CnBr. The fragments were separated by HPLC and then sequenced by Edman degradation. Determine the sequence of the original peptide from the following fragment sequences. Cleavage with chymotrypsin EAGPDGMECAF GPF EAAMCKW HR IAHTY Cleavage with CnBr ECAFHR CKWEAGPDGM IAHTYGPFEAAM -align the peptides IAHTYGPFEAAMCKW EAGPDGMECAFHR Reagent (source) Trypsin (bovine pancrease) Chymotrypsin (bovine pancrease) Staphylococcus V8 protease Pepsin (porcine pancrease) Cyanogen bromide (chemical)(CnBr) Specificity Lys, Arg (C) Phe, Trp, Tyr (C) Glu, Asp (C) Phe, Trp, Tyr (N) Met (C) #3. The following three peptides are subjected to anion-exchange chromatography at pH 7.5 using a NaCl gradient to elute the peptides. There are no disulfide bridges. What is the charge of each peptide at pH 7.4 and in what order will they elute from the column? Use Table 3.2 to find the pKa values. (1) MARKER (2) SADDLE (3) CRACKED pKa Form at pH 7.4 Charge amino group 9.3 HA +1 M pKa Form at pH 7.4 Charge amino group 9.2 HA +1 pKa Form at pH 7.4 Charge amino group C 10.7 8.4 HA HA +1 0 S A R K E 12.5 10.5 4.1 HA HA A+1 +1 -1 A D 3.9 A-1 D 3.9 A-1 L R 12.5 HA +1 A C 8.4 HA 0 K 10.5 HA +1 R 12.5 HA +1 E 4.1 A-1 E 4.1 A-1 carboxyl group 1.8 A-1 = +2 carboxyl group 2.1 A-1 = -3 D carboxyl group 3.9 2.0 AA-1 -1 =O The order of elution from an anion exchange column (binds negatively charged proteins) is MARKER, CRACKED, SADDLE or 1,3,2. #4. A smallpeptide was found to contain equimolar amounts of the following amino acids: arginine, glutamic acid, glycine, lysine, methionine and phenylalanine. Individual samples of the peptide were treated with the following agents with the results noted: a) trypsin: arginine and a pentapeptide Trypsin cuts on the C side of arginine thereforethe arginine must be the N-terminal residue. arg (glu, gly, lys, met, phe) b) cyanogen bromide: two tripeptides Cleavage occurs on the C side of met so met must must be the third residue in order for two tripeptides to form. arg, ?, met, ?, ?, ? c) S. aureus V8 protease: lysine and a pentapeptide Cuts at glu and asp on the C-side so lys must be C-terminal with a glu preceding it. arg, ?, met, ?, glu, lys d) chymotrypsin: a dipeptide and a tetrapeptide, with the latter showing absorbance at 260nm. If phe is second then we have a dipeptide containg phe and if it is fourth then the tetrapeptide contains phe. Since the tetrapeptide absorbs light at 260nm then it must contain the phe because the aromatic amino acids absorbs UV light. What is the primary structure of the peptide? Explain each piece of evidence given and the reasoning that led to your answer. arg, gly, met, phe, glu, lys #5 You have 2 globular proteins. Protein X has 300 amino acids and protein Y has 400 amino acids. Which one will emerge first using gel filtration chromatography? Gel filtration separates on the basis of size. The gel filtration resin consists of very small beads with tiny holes. The protein equilibrates between inside and outside the beads. The smaller proteins spend more time inside the bead and therefore move more slowly down the column. Thus, larger protein Y will emerge first and X second. #6 Below is an SDS gel in the presence of mercaptoethanol. Label the band of the highest and lowest molecular weight band and explain. The band closest to the top is the largest protein and the one closest to the bottom is the smallest. In SDS the protein unfolds and is like a big piece of spaghetti covered with SDS and therefore has a bunch of negative charge. Because it is longer and more stringer than the smaller protein it cannot move as fast through the agarose gel. The top is the - charge and bottom is the + charge. This way the protein moves toward the bottom because the protein is covered with SDS and therefore has a - charge. #7 a) Reverse-phase chromatography (HPLC) separates peptides based on molecular weight. F b) One method used to prevent disulfide bond interference with protein sequencing procedures is to reduce disulfide bridges and prevent their reformation with the addition of iodoacetic acid. T c) High molecular weight proteins will migrate farther during gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE). F d) -sheet protein structures can be stabilized by hydrogen bonding between distant residues on the same polypeptide. T e) -sheets are a type of secondary structure and are found in every protein. F f) In the α-helix, the hydrogen bonds that stabilize the helix occur mainly between electronegative atoms of the R groups. F g) Negatively charged peptides flow through a cation-exchange chromatography column without binding. T h) The enzyme hexokinase (972 amino acids) will elute from a gel filtration column before myoglobin (155 amino acids). T i) Separation of proteins in the first dimension of 2D gel electrophoresis is based on a protein’s molecular weight. F