Class Quiz 2
advertisement
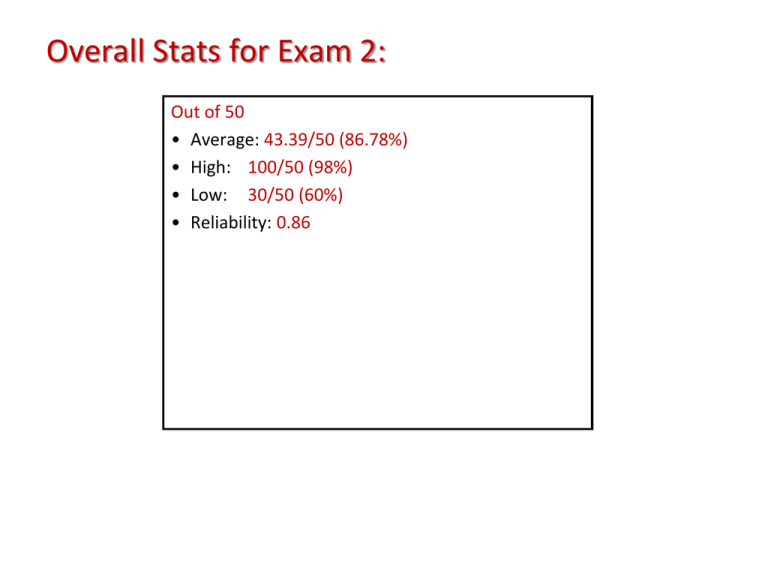
Overall Stats for Exam 2: Out of 50 • Average: 43.39/50 (86.78%) • High: 100/50 (98%) • Low: 30/50 (60%) • Reliability: 0.86 14. This term is used in dynamic pattern theory. It describes the overall organization of a movement. a. b. c. d. Stability Control parameter Order parameter Critical fluctuation 70% 16. This dynamic pattern theory term is specifically referred to in the notes as a partial solution to the degrees of freedom problem (other terms may also apply, but are not referred to this way) a. b. c. d. Control parameter Perception-action coupling Coordinative structure Collective variable 80% 19. When the attractor basin is ________, a perturbation (disturbance) to the movement will result in a _______________. a. Deep; new attractor state b. Stable; new attractor state c. Shallow; quick return to stability (same attractor state) d. Deep; quick return to stability (same attractor state) 79% 28. Imagine the image shown on the left represents the data from Kelso's finger wiggling experiment shown in the slides and the text. Could the current order parameter be in-phase finger wiggling? a. Yes 74% b. No c. cannot be reasonably inferred from the diagram 31. How is the run-walk data similar to Kelso’s finger wiggling data? a. The pattern of change in movement from walk to run is similar to the change from in-phase to anti-phase coordination b. The pattern of change in movement from walk to run is similar to the change from anti-phase to in-phase coordination 78% 72% 78% 60% 72% As you increase the value of the (41. control parameter), the (42. order parameter) will remain the same in terms of its coordination pattern, but its (43. stability) will often change. If the (44. stability) does change, then further manipulations of the (45. control parameter) may result in (46. critical fluctuation), at which point a transition to a new (47. order parameter) is imminent. It is worth noting that this transition often occurs at a different value of the (48. control parameter) when the (49. control parameter) is increasing than when it is decreasing, which is because the coordination pattern you are currently in seems to exert a sort of control over your movements (something Haken referred to as the slaving principle). We refer to this last phenomenon as (50. hysteresis) All others 84-97%