Risk Management
advertisement

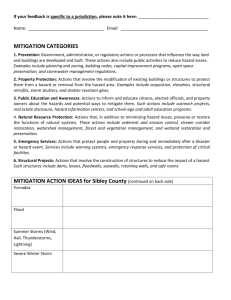
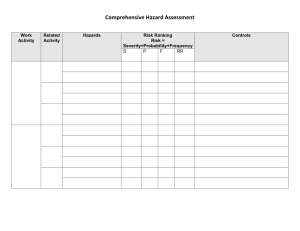
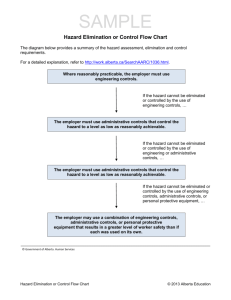
Risk Management What is risk? • You have some expected outcome – Of some event in the future • Risk is the deviation of the actual future outcome from the expected outcome • Other definitions: – Hazard: something negative that can happen in the future – Risk is the probability of the hazard Why risk analysis? • What does knowing the risk of some hazard buy you? – We know we can only care about future activities – We know (or hope) that our risk analysis provides some actionable outcomes – What are we really trying to decide? • Is the following statement be useful? – The estimated damage by hazard X would be 2 million dollars – The risk of hazard X is 1% Risk Examples • Let’s say you know the risk of permanent injury/death of a <insert you own “very fun activity” here> is 1/1000 instances. – Would you perform the activity? Why? Why not? – This activity was “optional”. What about: • Let’s say you have a disease and there is a treatment that works 25% of the time, does nothing 50% of the time, and results in immediate death 25% of the time – Would you perform this activity? Why? Why not? – The consequence of not performing this activity is death within five years. You must do it now, you can’t do it five years from now. Why identify risks? • Decide if it is “worth” doing something – What is to be gained vs what could be lost • Avoid risks when possible • Control risks when necessary • Like metrics, the outcome of risk analysis should be something actionable – Focus on future events Software Risks • Project risks – Schedule slips – Cost increases • Technical risks – The problem is harder to solve than you thought it would be – Threaten quality and timeliness • Business risks – Market risk, strategic risk, sales risk, management risk, budget risks Again, why analyze risk? Four treatments exist: • Do nothing – i.e. if you don’t try, you can never fail • Risk sharing – spending a little now to reduce impact later • Risk retention – the real “do nothing” – just accept the risk • Risk reduction – reduce the probability or impact Risk Management Paradigm control track RISK plan analyze identify Step 1: identification • Generic risks every project faces – Lots of checklists for these – over time, over budget, etc. • Product-specific risks – The server on a website goes down – The touch-screen on this self-checkout is slow – etc Step 2: Analysis • Estimate potential likelihood – 100% of a risk means it is a constraint • Estimate potential impact – Low to High – A monetary amount – Consider the nature, scope, and timing; examples? • Determine the risk exposure – Expose = probability x impact • Sort/prioritize risks – Decide which ones you will deal with Risk Exposure Example • Risk identification. Only 70 percent of the software components scheduled for reuse will, in fact, be integrated into the application. The remaining functionality will have to be custom developed. • Risk probability. 80% (likely). • Risk impact. 60 reusable software components were planned. If only 70 percent can be used, 18 components would have to be developed from scratch (in addition to other custom software that has been scheduled for development). Since the average component is 100 LOC and local data indicate that the software engineering cost for each LOC is $14.00, the overall cost (impact) to develop the components would be 18 x 100 x 14 = $25,200. • Risk exposure. RE = 0.80 x 25,200 ~ $20,200. Step 3: Risk planning • Risk Mitigation – How to avoid the risk • Risk Monitoring – What factors indicate the risk “is happening” • Risk Management – What are our contingency plans? Quiz review • • • • • What is risk? (formal definition) Give two examples of project risks Give two examples of technical risks Give two examples of business risks Explain the four treatments for risk: – – – – do nothing risk sharing risk reduction risk retention • How do you calculate risk exposure? In-class Exercise • Calculate the risk of failing your class because you slept through the final – apply the four risk treatments to this risk • Identify ten risks for your term projects – Calculate the risk exposure for each risk – Decide whether to, and how to, handle each of the risks you identified using one or more of the four risk treatments we dicussed • Due next class