Geometry Lesson 1.1
advertisement
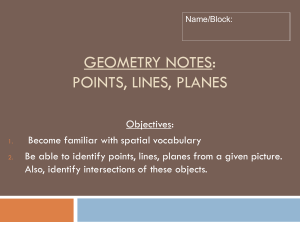
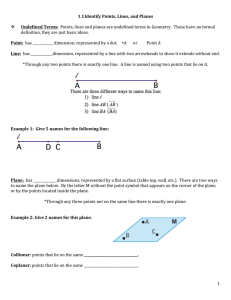
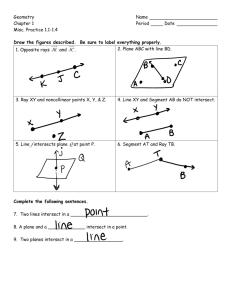
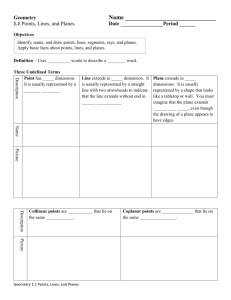
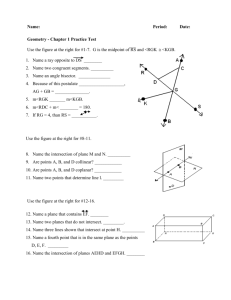
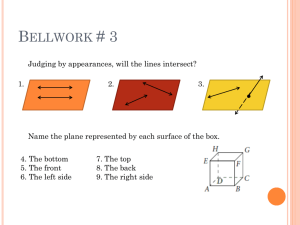
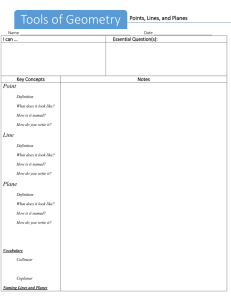
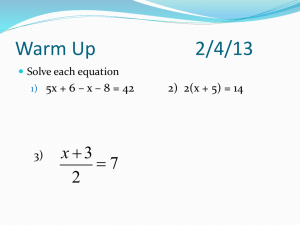
Geometry Lesson 1.1A Coordinate Plane Basics LG.1.G.2 Represent points, lines, and planes pictorially with proper identification, as well as basic concepts derived from these undefined terms, such as segments, rays, and angles Basic Terms in Geometry: 1. point – a location. It has no size. It is represented by a small dot and named a capital letter. A geometric figure is a set of points. 2. line – an infinite set of points that extends indefinitely in 2 directions. 3. Collinear Points: points that lie on the same line Examples: l D C B A 4. Noncollinear points: points that do not lie on the same line 5. Plane: an infinite set of points that extends indefinitely in all directions. 6. Space: the set of all points (3D) 7. Coplanar: points and lines that lie in the same plane Parts of a line A B C 8. Segment: Two endpoints and all the points between. •Ex: 9. Ray: One endpoint and all the points to one side of that endpoint. • Ex: 10. Opposite Rays: Two collinear rays with the same endpoint. They form a line. • Ex: Pay close attention to the notation for segment and ray. Types of Lines and Planes 11. Parallel Lines: Two lines that are in the same plane and never intersect 12. Parallel Planes: Planes that do not intersect 13. Skew Lines – Lines that are not parallel AND not intersecting Facts in Geometry 14. Theorem: A statement that is proven to be true 15. Postulate: A statement that is accepted as true without proof Some Basic Postulates a. Through any 2 points is exactly one line b. If 2 lines intersect, then they intersect at exactly one point c. If 2 planes intersect, they intersect in a line d. Through any 3 noncollinear points there is exactly one plane Postulates c & d fill in the blank: • Plane _________ and Plane_________ intersect in _______. Hidden Planes The Coordinate Plane • • • • • • • Label the following: x-axis y-axis origin Quadrants I – IV The point (3, -2) The point (1, 5)