Bernoulli`s Equation
advertisement
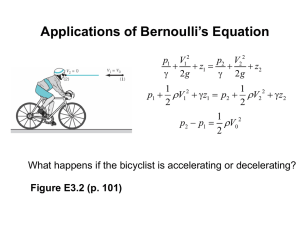
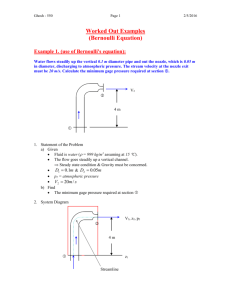
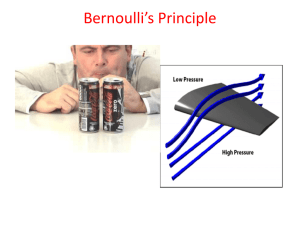
Lesson 22 BERNOULLI’S EQUATION • DESCRIBE the relationship between Bernoulli’s equation and the First Law of Thermodynamics. • DEFINE the term head with respect to its use in fluid flow. • EXPLAIN the energy conversions that take place in a fluid system between the velocity, elevation, and pressure heads as flow continues through a piping system. • Given the initial and final conditions of the system, CALCULATE the unknown fluid properties using the simplified Bernoulli equation. • DESCRIBE the restrictions applied to Bernoulli’s equation when presented in its simplest form. • EXPLAIN how to extend the Bernoulli equation to more general applications. • RELATE Bernoulli’s principle to the operation of a venturi. General Energy Equation Conservation of Energy Principle says energy can be neither created nor destroyed. Consequently, Q + (U + PE + KE + PV)in = W + (U + PE + KE + PV)out + (U + PE + KE + PV)stored where: Q = heat (Btu) U = internal energy (Btu) PE = potential energy (ft-lbf) KE = kinetic energy (ft-lbf) P = pressure (lbf/ft2) V = volume (ft3) W = work (ft-lbf) Simplified Bernoulli Bernoulli Equation Simplified Equation • Application of the general energy equation and the first law of thermodynamics. It assumes: – – – – steady flow system no work is done on or by the fluid no heat is transferred to or from the fluid no change occurs in the internal energy (i.e., no temperature change) of the fluid. • Under these conditions, the general energy equation becomes (PE + KE + PV)1 = (PE + KE + PV)2 Bernoulli's Equation 2 1 2 2 mgz 1 mv mgz 2 mv P1V1 P2 V2 gc 2g c gc 2g c where: m = mass (lbm) z = height above reference (ft) v = average velocity (ft/sec) g = acceleration due to gravity (32.17 ft/sec2) gc = gravitational constant, (32.17 ft-lbm/lbf-sec2) Bernoulli's Equation Multiplying all terms by the factor gc/mg gives 2 1 2 2 gc gc V V Z1 P1V1 Z 2 P2 V2 2g g 2g g Head • The height, typically in feet, of a column of water that a given pressure will support. • Comes from Bernoulli's Equation (final form) which is in units of length • Pressure head - Flow energy of a column of fluid whose weight is equivalent to the pressure of the fluid. (PVgc/g) • Elevation head - Potential energy of a fluid due to its elevation above a reference level (Z). • Velocity head - Height in feet that a flowing fluid would rise in a column if all of its kinetic energy were converted to potential energy (he kinetic energy of the fluid) (V2/2g). • Total head - Sum of the elevation head, velocity head, and pressure head of a fluid • Bernoulli’s equation states that the total head of the fluid is constant Energy Conversions in Fluid Systems • Bernoulli's Equation – Simplifies examination of how energy transfers take place among elevation head, velocity head, and pressure head. – May be applied to problems in which more than one flow may enter or leave the system at the same time – Used to solve series and parallel piping system problems • Continuity Equation Restrictions on the Simplified Bernoulli Equation • No fluid friction is allowed in solving piping problems – only applies to ideal fluids. • The second restriction on Bernoulli’s equation is that no work is allowed to be done on or by the fluid. • Simplified Bernoulli equation must be modified to deal with head losses and pump work. Extended Bernoulli Equation • Modification of the Bernoulli equation • Takes into account gains and losses of head • Very useful in solving most fluid flow problems. Extended Bernoulli Equation gc gc V12 V22 Z1 P1v1 H P Z 2 P2v2 Hf 2g g 2g g where: Z = height above reference level (ft) V = average velocity of fluid (ft/sec) P = pressure of fluid (lbf/ft2) v = specific volume of fluid (ft3/lbm) Hp = head added by pump (ft) Hf = head loss due to fluid friction (ft) g = acceleration due to gravity (ft/sec2) Venturi Meter