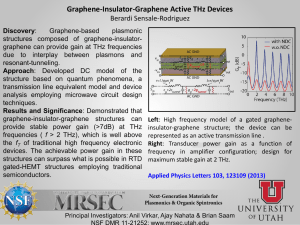
infra
advertisement

Sensor Physics Non contact temperature measurement Dr. Seres István SENSOR PHYSICS Thermometers based on thermal radiation Electromagnetic spectra c = lf Dr. Seres István name AC Radiovawes Longvawe range (LW) medium vawe range (MW) short vawe range (KW) Ultrashort range(URH) Microvawes Infrared radiation (IR) Visible light red orange yellow green blue violet Ultraviolet radiation (UV) Röntgen radiation Gamma-radiation 2 vawelength > 3000 km < 30 km < 10 km < 650 m < 180 m < 10 m 300 µm - 30 cm < 1,0 mm < 780 nm 640 - 780 nm 600 - 640 nm 570 - 600 nm 490 - 570 nm 430 - 490 nm 380 - 430 nm < 380 nm < 1 nm < 10 pm Frequency < 100 Hz > 10 kHz > 30 kHz > 650 kHz > 1,7 MHz > 30 MHz 1 GHz - 1 THz > 300 GHz > 384 THz 384 - 468 THz 468 - 500 THz 500 - 526 THz 526 - 612 THz 612 - 697 THz 697 - 789 THz > 789 THz > 300 PHz > 30 EHz http://fft.szie.hu SENSOR PHYSICS Thermometers based on thermal radiation Theory: black body Definition: it absorbs all the EM radiation Its model: hole in a wall Dr. Seres István 3 http://fft.szie.hu SENSOR PHYSICS Thermometers based on thermal radiation Theory: Planck law for radiation The power emitted by the unit surface of a T temperature object : J l , T Dr. Seres István 2 hc l 5 2 1 hc e l kT 1 4 http://fft.szie.hu SENSOR PHYSICS Thermometers based on thermal radiation Theory: Planck law for radiation If C2 e l T 1 , than the law can be written as: J l , T d l C 1 l e 5 C2 lT dl /the difference is < 1%, if lT < 3000mm∙K/ Dr. Seres István 5 http://fft.szie.hu SENSOR PHYSICS Thermometers based on thermal radiation Theory: Planck law for radiation J l , T d l C 1 l e 5 C2 lT dl Where (for what l) is the maximum value of the function? /the derivetive there is zero/ d ( J l , T ) dl Dr. Seres István 5 d ( C 1l e dl 6 C2 lT ) 0 http://fft.szie.hu SENSOR PHYSICS Thermometers based on thermal radiation Theory: Wien law Where (for what l) is the maximum value of the function? /the derivetive there is zero/ d ( J l , T ) dl 5 d ( C 1l e C2 lT ) dl 6 C1 l e C2 lT C C 2 2 C2 6 5 lT lT C 1 5l e l e 2 l T C2 5 0 lT l T C 2 ,898 10 Dr. Seres István 0 7 3 mK http://fft.szie.hu SENSOR PHYSICS Thermometers based on thermal radiation Theory: Wien law l T 5 C 2 2 ,8978 10 3 mK • the color of the warming iron is changing • the blue stars are hotter Dr. Seres István 8 http://fft.szie.hu SENSOR PHYSICS Thermometers based on thermal radiation Theory: Stefan-Boltzmann law J l , T d l C 1 l e 5 C2 lT dl How much is the integral of the function ( 0< l <∞)? – /partial integration/ W T 4 = 5,67∙10-8 W/m2K4St Dr. Seres István 9 http://fft.szie.hu SENSOR PHYSICS Thermometers based on thermal radiation Theory: Stefan-Boltzmann law W K T Tk 4 4 = 5,67∙10-6 W/m2K Tk the temperature of the environment, K – depends on the surfaces and distances Dr. Seres István 10 http://fft.szie.hu SENSOR PHYSICS Thermometers based on thermal radiation Theory: gray body Kirchhoff law E ( , T ) e( , T ) Independent from the material a ( , T ) properties Dr. Seres István 11 http://fft.szie.hu SENSOR PHYSICS Thermometers based on thermal radiation Theory: gray body Dr. Seres István 12 http://fft.szie.hu SENSOR PHYSICS Thermometers based on thermal radiation Infra thermometer The effect of the air, the transmission coefficient of the air at different vawelengths Dr. Seres István 13 http://fft.szie.hu SENSOR PHYSICS Thermometers based on thermal radiation Infra thermometer Effektív vawelength The calibration function of an infra thermometer: Where N is: Dr. Seres István 14 http://fft.szie.hu SENSOR PHYSICS Thermometers based on thermal radiation Infra thermometer Main parts: • detector termopile (seriel connection of thermocouples, photo-detektor –photovoltaic pyro-electric • optical system Dr. Seres István 15 http://fft.szie.hu