Chap26
advertisement

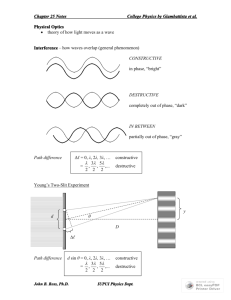
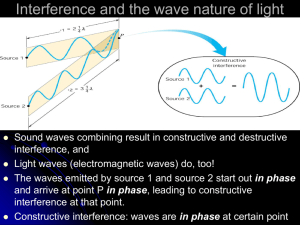
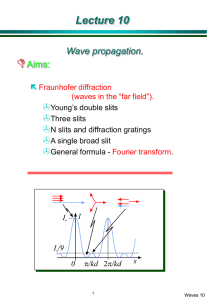
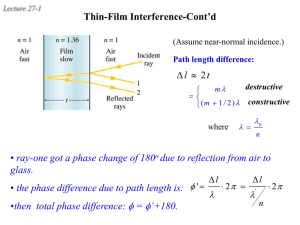
26 Interference & Diffraction --Physical/Wave Optics Thin film interference Interference & Coherent Sources Superposition & Interference Superposition: The net response at a given place and time caused by two or more stimuli is the sum of the responses which would have been caused by each stimulus individually (wikipedia) Key factor: phase. Double Slits Interference-1 Fringes 1 r2 r1 (m ) 2 ( m 0,1,2,...) ( m 0,1,2,...) r2 r1 m Double Slits Interference-2 r2 r1 d sin d sin m Constructive 1 d sin (m ) 2 Destructive ( m 0,1,2,...) y i f R d , sin t an R m ym R d Constructive Mirror Equation (m 1 / 2) d Destructive ym R ( m 0,1,2,...) Example: Determining m d Constructive ( m 0,1,2,...) ym R Interference in Thin Film 2t m Constructive 1 2t (m ) 2 Destructive ( m 0,1,2,...) Note: when nb > na, reflected wave undergoes an additional half cycle (i.e., /2) phase shift. Example: Interference Fringes (note: additional /2 phase shift from the bottom reflection) 2t m Destructive ( m 0,1,2,...) Newton Rings & Applications Non-reflective & Reflective Coatings Diffraction & Geometric Optics Diffraction—Reality Fresnel diffraction: Fraunhofer diffraction: near-field diffraction far-field diffraction Single Slit Diffraction Fresnel & Fraunhofer: Single Slit Huygens’s Principle: Every point of a wave front may be considered the source of secondary wavelets that spread out in all directions with a speed equal to the speed of propagation of the waves. Dark Fringes R ma sin 2 ( m 1,2,3,...) Norm al l y, i s ve ry sm al l sin , t an m a ( m 1,2,3,...) ym R y R Multiple Slits & Diffraction Gratings Constructive interference or bright fringes occur: d sin m ( m 0,1,2,3,...) Destructive interference or dark fringes occur: d sin (m 1 / 2) ( m 0 1,2,3,...) X-Ray Diffraction Circular Apertures & Resolving Power First Dark Ring occurs sin 1 1.22 D Resolving Power Rayleigh’s Criterion (increase D or reduce could improve the resolution) sin 1 res 1.22 D Holography Summary: Superposition, interference, & Coherent Sources Summary: Double Slits Interference Summary: Thin Film Interference Summary: Diffraction & Gratings Summary: X-Ray Diffraction Summary: Circular Apertures & Resolving Power sin 1 1.22 D Summary: Holography Ch 26 Homework Answers to multiple choice problems Problems: 1, 6, 11, 15, 25, 27, 47