chapter 12
advertisement

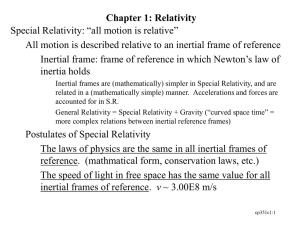
12.1 Characteristics of Sound
Range of human hearing ~ 20 – 20,000 Hz
Infrasonic (< 20 Hz)
Ultrasonic (> 20,000 Hz)
4/13/2015
Earthquakes, nuclear test detection, machines
Medicine (fetal development, tumor removal, etc.),
camera ranger, jewelry cleaning, animal
sonar/echolocation
APHY201
1
12.1 Characteristics of Sound
The speed of sound in a
material depends on the
material’s elastic and inertial
properties and its temperature.
elastic
v
inertial
vair (331 0.6T ) m/s
4/13/2015
APHY201
2
12.1 Characteristics of Sound
4/13/2015
When the pressure is high, the displacement is low.
APHY201
3
12.2 Intensity of Sound
For humans: threshold of hearing (I ~ 10-12 W/m2)
and pain (I ~ 1 W/m2)
We perceive differences in loudness as logarithmic
I
10 log
Io
4/13/2015
For humans: threshold of hearing (β = 0 dB) and
pain (β = 120 dB)
APHY201
4
12.4 Sources of Sound
The harmonics are determined by whether the
column is open at both ends or closed at one end.
vn
fn
2L
4/13/2015
vn
fn
4L
n 1, 2, 3,...
APHY201
n 1, 3, 5, ...
5
12.5 Quality of Sound
4/13/2015
APHY201
6
12.6 Interference of Sound Waves
The speakers emit at same
frequency and are in phase
The waves at C constructively
interfere (path difference = nλ)
and at D destructively interfere
(path difference = {n+½} λ)
What do you hear if the speakers
emit different frequencies?
4/13/2015
APHY201
7
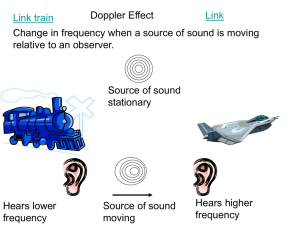
12.7 Doppler Effect
Apparent change in frequency due to the motion of
the sound source and/or the observer.
vsnd vobs
f f
vsnd vsource
4/13/2015
APHY201
8
In class:
Other problems ↓
13. (a) From Table 12-2, the intensity in normal conversation,
when about 50 cm from the speaker, is about 3x10-6 W/m2.
I
P
A
P IA I 4 r
2
3 10
6
W m 4 0.50 m 9.425 10 6 W
2
2
(b) The number of people needed to produce 100 W of sound is
1 person
7
7
100 W
1.06
10
1
10
people
6
9.425 10 W
4/13/2015
APHY201
9
49. (a) Observer moving towards stationary source.
vobs
30.0 m s
f 1
1550 Hz 1690 Hz
f 1
343m s
vsnd
(b) Observer moving away from stationary source.
vobs
30.0 m s
f 1
1550 Hz 1410 Hz
f 1
343m s
vsnd
4/13/2015
APHY201
10