PA Lesson 4-8
advertisement
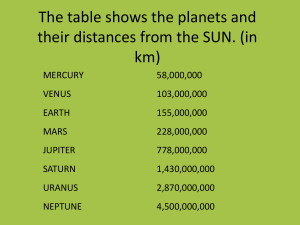
Lesson 4-8 Pages 186-190 Scientific Notation Lesson Check 4-7 What you will learn! 1. How to express numbers in standard form and in scientific notation. 2. How to compare and order numbers written in scientific notation. Scientific notation What you really need to know! When you deal with very large numbers like 5,000,000 or very small numbers like 0.0005, it is difficult to keep track of place value. Numbers such as these can be written in scientific notation. What you really need to know! A number is expressed in scientific notation when it is written as a product of a factor and a power of 10. The factor must be greater than or equal to 1 and less than 10. What you really need to know! It looks like a multiplication problem. The decimal point is going for a walk! Example 1: Express each number in standard form: 4 10 4 395 x 43,950. What you really need to know! Since our number system is based on 10, scientific notation always uses 10 raised to a power. Place Value Chart 2 10 1 10 0 10 Hundreds Tens Ones . -1 10 -2 10 -3 10 Tenths Hundredths Thousandths Example 2: Express each number in standard form: -6 10 6 79 x 0.00000679 Example 3: Express each number in scientific notation: 800,000 5 8.0 x 10 Example 4: Express each number in scientific notation: 1,320,000 6 1.32 x 10 Example 5: Express each number in scientific notation: 0 0119 -2 1.19 x 10 Example 6: Use the table: Estimate how many times farther Pluto is form the Sun than Mercury is from the Sun. (5.90 x 9 10 ) ÷ (5.80 x 7 10 ) Pluto is about 100 times farther from the Sun than Mercury! Example 7: The diameters of Mercury, Saturn, and Pluto are 4.9 x 103 km, 1.2 x 105 km, and 2.3 x 103 km respectively. List the planets in order of increasing diameter. Pluto, Mercury, Saturn Page 188 Guided Practice #’s 3-11 Read: Pages 186-188 with someone at home and study examples! Homework: Pages 189-190 #’s 12-48 even #’s 51-59 Lesson Check Ch-4 Page 733 Lesson 4-8 Lesson Check Ch-4 Study Guide and Review Pages 191-194 #’s 1-65 (Odd answers in back of book) Prepare for Test! Page 195 #’s 1-30 1.A number is divisible by 2 if it is even. (The ones digit is 2, 4, 6, 8, 0) A number is divisible by 3 if the sum of the digits equal a multiple of 3. A number is divisible by 5 if the ones digit is 0 or 5. A number is divisible by 6 if it is divisible by both 2 and 3. A number is divisible by 10 if the ones digit is 0. 2.A prime number has exactly two factors. Examples: 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 19, … A composite number has three or more factors. Examples: 4, 6, 8, 9, 10, 12, 14, 15, 16, 18, … 0 and 1 are neither prime or composite! 3.A fraction is in simplest form when the only common factor between the numerator and denominator is 1. Examples: a b 7x 8y 4. Yes 5. No 4 6. 3 7. (-2)3a4 8. 2 2 3 r r 9. 2 5 5 x y y 10. 7(1 + 3p) 11. 14 12. 18 13. 4ab 14. 3/5 15. 2/3 16. 7m2/4 9 17. 5 10 18. -24x 19. w4 2 20. 1/4 21. 1/t6 3 1/(yz) 22. 23. 0.09 24. 0.005206 25. 37,100 5 26. 3.45 x 10 6 27. 1.68 x 10 28. 7.2 x 10-4 29. 3/4 30. A Prepare for Test! Pages 196-197 #’s 1-21