Purposeful Plenaries
advertisement

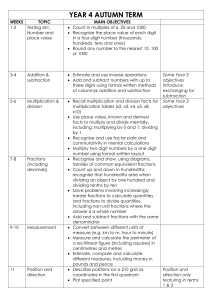
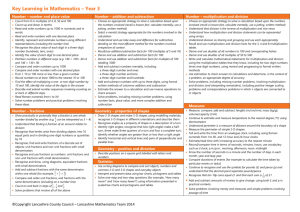
The New Curriculum for Mathematics Knowing, learning, understanding are not linear. . . A field of knowledge, such as mathematics, is a territory, and knowing is not just a matter of knowing all the items in the territory, but of knowing how they relate to, compare with, and fit in with each other. . . It is the difference between knowing the names of all the streets in a city and being able to get from any place, by any desired route to another place" Holt, J. (1984), How children fail The curriculum is now organised into programmes of study specific to each year group. * Number - Number and Place Value Addition and Subtraction Multiplication and Division Fractions * Measurement *Geometry – Properties of shapes Position and Direction *Statistics (Year 2) – Name change from Data * Number - Number and Place Value Addition and Subtraction Multiplication and Division Fractions (including decimals - Year 4) * Measurement *Geometry – *Statistics Properties of shapes Position and Direction (Year 4) * Number - Number and Place Value Addition and Subtraction Multiplication and Division Fractions (including decimals and percentages) * Measurement * Geometry – Properties of shapes Position and Direction * Statistics * Number - Number and Place Value Addition, Subtraction, Multiplication and Division Fractions (including decimals and percentages) * Ratio and proportion * Algebra * Measurement *Geometry – Properties of shapes Position and Direction *Statistics An emphasis on greater rigour, in particular arithmetic, and promoting efficient written methods of long multiplication and division. There is to be more demanding content in fractions, decimals and percentages. The removal of calculator and other ICT devices is encouraged as strong written and mental strategies should be developed Expectation that children will move through the programme of study at broadly the same pace Children who grasp concepts rapidly should be challenged with sophisticated problems before any acceleration through new content. (embedding) count to and across 100, forwards and backwards, beginning with 0 or 1, or from any given number (From Year 2) count in different multiples including ones, twos, fives and tens (From Year 2) represent and use number bonds and related subtraction facts within 20 (From Year 2) Using pictorial representations and arrays with the support of the teacher. (From Year 2) describe position, directions and movements, including three-quarter turns. (From Year 2) Describe and measure volume - NEW count in steps of 3 use place value and number facts to solve problems. recognise, find, name and write fractions 1/3 choose and use appropriate standard units to estimate and measure temperature (°C) Compare and order volumes tell and write the time to five minutes, count from 0 in multiples of 8 add and subtract numbers with up to three digits, using the efficient written methods of columnar addition and subtraction recall and use multiplication and division facts for the 8 multiplication tables progressing to formal written methods Measure, compare, add and subtract (mm) Measure the perimeter of simple 2D shapes Tell and write the time from an analogue clock 12hr and 24 hours clocks Estimate and read time with increasing accuracy to the nearest minute Use vocabulary am/pm Horizontal and vertical lines and pairs of perpendicular and parallel lines. solve problems, including missing number problems, involving multiplication and division, including integer scaling problems and correspondence problems in which n objects are connected to m objects. add and subtract fractions with the same denominator within one whole (e.g. 5/7 + 1/7 = 6/7 ) measure, compare, add and subtract: lengths (m/cm/mm); mass (kg/g); volume/capacity (l/ml) tell and write the time from an analogue clock, including using Roman numerals from I to XII count backwards through zero to include negative numbers multiply three-digit numbers by a one-digit number round decimals with one decimal place to the nearest whole number convert between different units of measure (e.g. kilometre to metre; hour to minute) read, write and convert time between analogue and digital 12 and 24-hour clocks describe positions on a 2-D grid as coordinates in the first quadrant Describe movements between positions as translations of a given unit to the left/right and up/down Plot specified points and draw sides to complete a given polygon. interpret and present continuous data using appropriate graphical methods including time graphs read Roman numerals to 100 (I to C) and understand how, over time, the numeral system changed to include the concept of zero and place value. recall multiplication and division facts for multiplication tables up to 12 × 12 multiplying together three numbers multiply two-digit and three-digit numbers by a onedigit number using formal written layout add and subtract fractions with the same denominator. solve addition and subtraction multi-step problems in contexts, deciding which operations and methods to use and why. know and use the vocabulary of prime numbers, prime factors and composite (non-prime) numbers establish whether a number up to 100 is prime and recall prime numbers up to 19 multiply numbers up to 4 digits by a two-digit number compare and order fractions whose denominators are all multiples of the same number recognise and use thousandths and relate them to tenths, hundredths and decimal equivalents read, write, order and compare numbers with up to three decimal places solve problems involving number up to three decimal places. convert between different units of measure (e.g. km and m; m and cm; cm and mm; kg and g; l and ml) understand and use basic equivalences between metric and common imperial units and express them in approximate terms estimate the area of irregular shapes Identify angles at a point and one whole turn (total 360o) read Roman numerals to 1000 (M) and recognise years written in Roman numerals. the formal written method of short division recognise and use square numbers and cube numbers, and the notation for squared and cubed add and subtract fractions with the same denominator and related fractions; multiply proper fractions and mixed numbers by whole numbers, supported by materials and diagrams. Estimate volume (e.g. using 1 cm3 blocks to build cubes and cuboids) and capacity (e.g. using water) read, write, order and compare numbers up to 10 000 000 multiply multi-digit numbers up to 4 digits by a two-digit whole number using the formal written method of long multiplication divide numbers up to 4 digits by a two-digit whole number using the formal written method of long division add and subtract fractions with different denominators and mixed numbers, using the concept of equivalent fractions multiply simple pairs of proper fractions, writing the answer in its simplest form (e.g. 1/4 × 1/2 = 1/8 ) divide proper fractions by whole numbers (e.g. 1/3 ÷ 2 = 1/6 ). use, read, write and convert between standard units, converting measurements of length, mass, volume and time from a smaller unit of measure to a larger unit, and vice versa, using decimal notation to three decimal places calculate the area of parallelograms and triangles recognise when it is necessary to use the formulae for area and volume of shapes compare and classify quadrilaterals and regular polygons illustrate and name parts of circles, including radius, diameter and circumference Construct pie charts http://www.ted.com/talks/conrad_wolfram_t eaching_kids_real_math_with_computers.ht ml