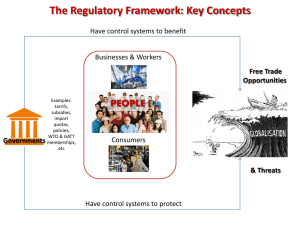
Visual C Sharp
advertisement
Visual C Sharp – File I/O - 1
Variables and arrays only temporary
- lost when a program terminates
Files used for long term storage
(Data bases considered later in course)
We will cover:
File types
File and Directory classes
File open and save dialogs
Sequential-access files
Random-access files
Stream-input/output features
Visual C Sharp – File I/O - 2
File Types – Text (ASCII) or Binary
Text files - ASCII characters with CR and LF.
Handled in a line-by-line, or sequential manner.
Binary Files - Typed and Untyped files
Binary files all values - can’t be displayed - .EXE file.
Typed files - known format using data types - database.
Untyped files - no rigid structure, sizes can vary.
E.g. EXE program files, BMP bitmap graphic files.
- Program using it knows how to deal with it.
Visual C Sharp – File I/O - 3
Files and streams
C# views files as a sequential stream of bytes.
File ends with EOF marker or after a byte count.
You open the file, read and write to it, then close it.
Uses StreamReader and StreamWriter Classes
They implement methods to read and write files.
Similar classes used to read/write to Internet or serial I/O
Visual C Sharp – File I/O - 4
File and Directory Classes (static classes)
Can perform Directory or File handling:
Directory:
CreateDirectory, Delete, GetFiles, Exists
File:
Exists – does file exist?
Create – creates file
CreateText – creates a text file
AppendText – appends or creates
Delete – deletes the file
Open – opens with desired R / W attributes
OpenRead – opens for read-only
OpenText – returns StreamReader (later)
OpenWrite – returns FileStream (later)
Need ‘using System.IO’
Visual C Sharp – File I/O - 5
First of all – Menu and Dialog controls
Text Editor example
MenuStrip control used to create menus (File Edit Help)
C# has FileDialog controls open and save files
– OpenFileDialog & SaveFileDialog
Rich Text box control will display text files
RT box has more functions than textbox – cut, paste etc.
Visual C Sharp – File I/O - 6
File Dialog controls
Open and Save dialogs
– non visual (not on form – appear when program runs)
ShowDialog displays the familiar open and save dialogs:
Visual C Sharp – File I/O - 7
MenuStrip control:
Enter required main menu commands (File, Edit, Help)
Add submenus: File>Open, Help > About etc.
To add code – click File’, double-click ‘Open’
Add code:
if (openFileDialog1.ShowDialog( ) != DialogResult.Cancel)
{
richTextBox1.LoadFile(openFileDialog1.FileName,
RichTextBoxStreamType.PlainText);
// more detail later
}
ShowDialog method displays the familiar file handling
dialog
Visual C Sharp – File I/O - 8
Code to display FileDialogs. Use:
openFileDialog1.ShowDialog( ) and
saveFileDialog1.ShowDialog( )
Need to check for OK or Cancel.
if (openFileDialog1.ShowDialog( ) != DialogResult.Cancel)
{
// filename is: openFileDialog1.FileName
}
N.b.
File I/O needs namespace:
using System.IO
Visual C Sharp – File I/O - 9
Open/Save File dialog properties:
CheckFileExists’, ‘DefaultExt’ InitialDirectory etc.
File filter. Can set in code:
openFileDialog1.Filter = "All files (*.*)|*.*|Text
files(*.TXT)|*.txt";
Visual C Sharp – File I/O - 10
Rich Text Box file handling
Easiest way to open and save text files is to use RTB
Open file:
if (openFileDialog1.ShowDialog() != DialogResult.Cancel)
{
richTextBox1.LoadFile(openFileDialog1.FileName,
RichTextBoxStreamType.PlainText);
}
RTB has methods, e.g:
RTB.Find method – finds strings in RTB (Search)
Visual C Sharp – File I/O - 11
Rich Text Box file handling – Save file
For MenuStrip File>Save, add:
if (saveFileDialog1.ShowDialog( ) != DialogResult.Cancel)
{
RichTextBox1.SaveFile(saveFileDialog1.FileName,
RichTextBoxStreamType.PlainText);
}
Text editor created in a few lines of code.
Visual C Sharp – File I/O - 12
Using StreamReader to read file into RichTextBox:
StreamReader streamRdr = new
StreamReader(openFileDialog1.FileName);
richTextBox1.Text = streamRdr.ReadToEnd( );
streamRdr.Close( );
Writing file using StreamWriter
StreamWriter streamWr = new
StreamWriter(saveFileDialog1.FileName);
streamWr.Write(richTextBox1.Text)
streamWr.Close( );
Why use? – may not want to use RT box to read file
Visual C Sharp – File I/O - 13
Example code snippet – read file:
string filename;
filename = txtFilename.Text; // read from textbox
if ( File.Exists(filename) )
{
string inputString = File.ReadAllText(fileName);
textBox1.Text = inputString;
}
Visual C Sharp – File I/O - 14
Example code snippet - write:
string filename;
filename = txtFilename.Text; // read from textbox
if ( File.Exists(filename) )
{
File.WriteAllText(filename, txtFileName.txt);
textBox1.Text = inputString;
}
Visual C Sharp – File I/O - 15
File class methods:
AppendText - Returns a StreamWriter which appends to a file
or creates a new file.
Create - Creates a file and returns FileStream.
CreateText - Creates a text file and returns a StreamWriter.
Delete - Deletes the specified file
Open - Opens a file and returns a FileStream with specified
read/write permission.
OpenText - Returns a StreamReader associated with the
specified file.
Visual C Sharp – File I/O - 16
Binary files:
// Read:
byte[] fileByteArray = new byte[1000];
fileByteArray = File.ReadAllBytes("test.bin");
// have to do something with the binary files to display them
// could split into upper and lower ‘nibbles’ and add 40hex
// makes chars @ABC.. MNO
// To Write:
File.WriteAllBytes("test.bin", fileByteArray);
Visual C Sharp – File I/O - 17
Sequential-Access File Handling
Non-text files? E.g. Student record (integer, string, double)
Could create our own Record, Class, or even object for this.
Search - Start at beginning and read data until its found
•
Maybe necessary to do this lots of times
Tell compiler our Class can be saved as bytes –
‘Serializable’ attribute
FileStream class used to writing of binary data
(instead of StreamReader/Writer)
Visual C Sharp – File I/O - 18
Random Access File Handling
Allows instant access to information
- Individual records accessed without searching through file
Easiest when all records are a fixed length
Data can be inserted without destroying other data in file
Records can be updated without rewriting the entire file
Uses file-position pointer - points to next byte to be read or
written - can be repositioned to any point in file
Uses class BinaryWriter and BinaryReader instead of
serialization
By attaching a FileStream to it, bytes can be read/written
directly to a file
Visual C Sharp – File I/O - 19
Exception handling
Exceptions: File may not exist, divide by zero, convert alpha
string to number
Use Try .. Catch code
int number1=123, zero = 0;
try
{
number1 = number1 / zero;
}
catch (DivideByZeroException)
{
MessageBox.Show("Something's wrong here");
}
Visual C Sharp – File I/O - 20
Summary
File types
MenuStrip control
Text Editor example – RTBox
Open / Save Dialogs
Files and Streams
Sequential-access files
Random-access files