Inequality adjusted HDI
advertisement

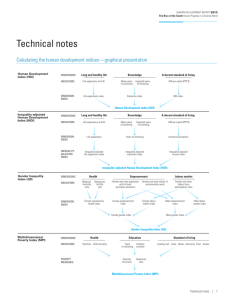
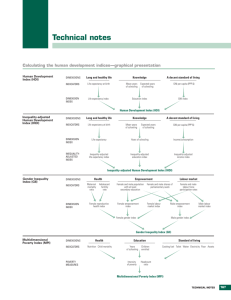
New Human Development Measures DOHA, 9-11 May, 2011 HDR 2010 HDR 2010 Measures • The main composite measures: - Revised HDI Inequality-adjusted HDI Multi-dimensional poverty index (replaces HPI) Gender inequality index (replaces GDI and GEM) HDR 2010 Human Development Measures Empirical measure Deprivation Components of Human Development Material Education Health Social Multidimensional Poverty Index Average Level Human Development Index Vulnerability Political Empowerment indicators Indicators of human security, sustainability, environment, well-being, decent work, etc. Inequality-adjusted HDI Inequality Gender Inequality Index Inequality-adjusted HDI The country-average HDI conceals wide disparities in distribution of HD across population within a country • False impression: Equal distribution of HD within the country • Inequality in dimensions of HDI • Inequality in concentration of income and other forms of material wealth • Inequality in distribution of other characteristics (e.g., years of education) is often recognized but rarely measured. 4 Distributions of HDI dimensions Distribution of years of schooling Example: Montenegro, Source: MICS 2006 Disposable Income, simulated 40 Montenegro 20 16.38 10 14.98 8.772 7.221 6.971 3.298 .3566.731.4635 .2496.2853.1605 .39221.07 .6062 1.141 .2139.0713 0 Percent 30 36.64 0 5 10 ys 15 20 5 Expected length of life, from life tables Life expectancy Japan Burundi Cameroon South Africa Mongolia Pakistan Russian Federation 83.2 51.4 51.7 52.0 67.3 67.2 67.2 Atkinson measure(ε=1) 0.039 0.478 0.444 0.302 0.226 0.329 0.115 6 Inequality-adjusted HDI • Needs for distributional data at the level of household or individual • Variables relevant to three dimension: Household consumption or income per capita Mean years of schooling Expected length of life • Source of data: Nationally representative household surveys UN Life tables 7 Inequality-adjusted HDI Distributional data on life expectancy: • Abridged Life Tables from UN Population Division based on mortality data and on survival models Household survey data on income and education: • World Bank: International Income Distribution Database (LSMS and similar household surveys) • EU-SILC (on income and living conditions for EU member states) • LIS (for OECD and other countries) • MICS, DHS (for education) 8 Inequality adjusted HDI 9 Inequality-adjusted HDI 10 Inequality-adjusted HDI 11 Inequality-adjusted HDI Example: Slovenia Life expectancy Mean years of schooling Expected years of schooling Education index Logarithm of GNI GNI HDI IHDI Loss Indicator Dimension Inequality Inequality-adjusted index measure (A1) index 78.8 0.930 0.043 (1–0.043) ∙ 0.930 = 0.890 9 0.682 0.040 16.7 10.16 25,857 0.828 0.811 0.782 0.780 0.238 0.040 (1–0.040) ∙ 0.782 = 0.751 0.122 (1–0.122) ∙ 0.238 = 0.209 0.8280.932=0.772 1-0.772/0.822=0.068 12 Inequality-adjusted HDI Policy relevance: • Allows a direct link to inequalities in dimensions • Inform policies towards inequality reduction • Evaluation tool for various policy options aimed at inequality reduction • Leads to better understanding of inequalities across population and their contribution to the overall loss of development 13 Inequality-adjusted HDI Limitations: • IHDI is not association sensitive – does not account for multiple deprivation • Negative and zero values are adjusted • Limited international comparability since data refer to different time points 14 Inequality-adjusted HDI Loss (%) NA (0,11.5] (11.5,28.0] (28.0,45.5] 15 Inequality adjusted HDI 0 10 Loss due to inequality (%) 20 30 40 50 Sub-Saharan Africa Arab States South Asia E. Asia and Pacific LA and Caribbean CE Europe and CIS Developed HDI Health Education Income 16