An introduction to audio/video compression
advertisement

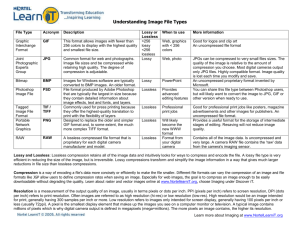
An introduction to audio/video compression Dr. Malcolm Wilson Introduction • Review digital video. • Need for compression. • Lossy and lossless compression. • How to apply techniques to still video (jpeg). Digital Video • Samples represent pixel values of a video frame. • Typically 480x640x3=1M (approx) per frame • Sample size 8-10 bits typically. Video datarates • With 8 bits samples at 25 frames per second we have a datarate of 200 Mbits per second. •Broadcast video (10 bit and includes audio) 270 Mbits per second. Why do we need compression? Modems Broadband USB 1.1 USB 2.0 IEEE 1394 Ethernet DVD CD-ROM EIDE Hard SCSI Hard 56kbit s-1 8Mbit s-1 12Mbit s-1 480Mbit s-1 400Mbit s-1 100kbit s-1 14Mbit s-1 50Mbit s-1 100MB s-1 160MB s-1 Lossless Compression • Achieve datarate reduction without discarding information. • Run Length Coding Eg: 5 5 5 5 5 5 May be coded 5 6 Lossless Compression Entropy (Huffman) Coding • Assign shorter codes to the more probable values. • Possible when there is statistical bias in image data. Lossy Compression • Achieving datarate reduction by discarding information. • Missing out samples from data stream/reducing sample size generally noticeable. Transforms • Frequency transforms (DCT) separate frequency components. • Transformed image allows efficient coding of high frequency data. Example DCT Basis Pictures • Picture broken into 8x8 pixel blocks (typically). • Any 8x8 pixel (picture) block made by adding different proportions of basis pictures. • So store the proportions. DCT basis functions (Basis pictures). Original Picture Using one (dc) basis picture Using 6 basis pictures Video compression • Most 8 x 8 blocks do not contain high frequency components. • Code high frequency components using less bits (introduces noise). Video compression • We are left with a sequence of values. •Zig-Zag scan. • Many values of zero towards the bottom right hand corner. • Use RLE to reduce the datarate further. Variable length coding • More likely that any non-zero value will have a run of zeros before it. • Non-zero value more likely to have a low value than a high one. • Use Huffman coding. Summary • Compression is needed to replay video from computer peripherals and to economise on storage. • Lossless techniques can allow some compression of video. •Lossy techniques can be used by considering psychological factors. Summary •We need to transform the signal to achieve unnoticable lossy compression. •Lossless techniques may then be used to achieve further compression. Psychological Considerations • Our eyes are not as sensitive to colour detail. • Colour information –Less bandwidth • Our eyes are less sensitive to high frequency noise.