Chapter 3_3 - Missouri State University
advertisement

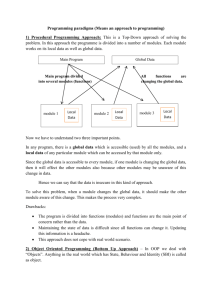
Chapter 3. Expressions and Interactivity CSC125 Introduction to C++ Formatting Output Ex. Input 6 integers n1,n2,n3,n4,n5,n6 in the range of [0,10000], and display them on the screen as a table shown below: n1 n2 n3 n4 n5 n6 Cout uses just the number of spaces needed to print each number Formatting output A stream manipulator setw(aNumber) : establish print fields of a specified width. aNumber is the field width for the value immediately following it. Minimum number of spaces to print the value in. Formatting Output #include <iomanip> Cout goes back to its default method of printing Any number larger than the minimum will cause cout to override the setw value. Formatting Output The field width of a floating-point number includes a position for the decimal point The field width of a string includes all characters in the string, including spaces These values printed in the field are rightjustified by default. Formatting Output Right justified. double x=146.789, y=24.23,z=1.2; cout<<setw(10)<<x<<endl; cout<<setw(10)<<y<<endl; cout<<setw(10)<<z<<endl; Left justified. double x=146.789, y=24.23,z=1.2; cout<<left<<setw(10)<<x<<endl; cout<<setw(10)<<y<<endl; cout<<setw(10)<<z<<endl; The setprecision(aNumber) Manipulator Floating-point values may be rounded to a number of significant digits You can control the number of significant digits with which floating-point values are displayed. Unlike setw(), setprecision manipulator remains in effect until it is changed to some other values. Fixed vs Scientific Stream manipulator, fixed, forces cout to print the digits in fixed-point notation. float f1=3.2472, f2=12.9e3; double d=327.815; cout<<fixed<<f1<<endl<<f2<<endl; cout<<scientific<<d<<endl<<f2<<endl; cout<<setprecison(2); cout<<fixed<<f1<<endl<<f2<<endl; cout<<scientific<<d<<endl<<f2<<endl; Fixed vs Scientific setprecision(x): when used with fixed or scientific, print floatingpoint value using x digits after the decimal. Without fixed or scientific, print floating-point value using x significant digits showpoint By default, floating-point numbers are not displayed with trailing zeroes Six significant digits are specified. showpoint manipulator Happy Moon Festival Formatted Input format field width for use with cin Useful when reading string data to be stored in a character array: Can const int SIZE = 5; char fName[SIZE]; cout << "Enter your name: "; cin >> setw(SIZE) >> fName; cin reads one less character than specified in setw() directive Procedural and Object-Oriented Programming Procedural programming: focus is on the process. Procedures/functions are written to process data. Object-Oriented programming: focus is on objects, which contain data and the means to manipulate the data. Messages sent to objects to perform operations. cin.getline() To read an entire line of input, use cin.getline(): const int SIZE = 81; char address[SIZE]; cout << "Enter your address: "; cin.getline(address, SIZE); cin.getline takes two arguments: Name of array to store string Size of the array Reading a charcter To read a single character: Use cin: char ch; cout << “Press any key to continue"; cin >> ch; Problem: will skip over blanks, tabs, <CR> Use cin.get(): cin.get(ch); Will read the next character entered, even whitespace Mixing cin >> and cin.get() cin and cin.get() in the same program can cause input errors that are hard to detect Mixing How to solve it? To skip over unneeded characters that are still in the keyboard buffer, use cin.ignore(): cin.ignore(); // skip next char cin.ignore(n, c); // skip the next // n char. or until a //character c is met.