Chapter 1
advertisement

Chapter 1
Introduction to
Programming
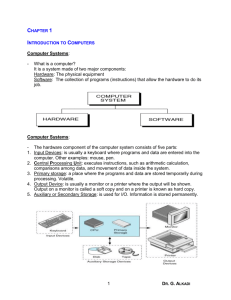
Computer Hardware
• CPU
• Memory
– Main or primary
– Secondary or auxiliary
• Input device(s)
• Output device(s)
Computer Program
• A list of instructions that direct the
computer hardware to perform a particular
data processing tack or solve a specific
problem. The program is coded in a
particular programming language such as
C++, Fortran, and Visual Basic.
• Software = a program or a collection of
programs
Programming Languages
• Low level machine language: 0’s and 1’s; the
native language of the machine; machinedependent.
• Intermediate level assembler language:
mnemonics; suggestive symbols or letters;
Machine dependent; requires translator known as
assembler.
• High level procedural language: resembles
English and/or standard notation of math;
machine-independent (portable); requires
translator known as compiler or interpreter.
Types of Instructions
• Input: e.g., cin in C++
• Process: many operator including +, -, *, /
to perform arithmetic and other types of
processing.
• Output: e.g., cout in C++
Types of Computer Software
• Systems software
– Operating system: Windows, Unix
– Compiler: C/C++ compiler
– …
• Applications software
– Payroll program: usually custom-designed/developed.
– Airline reservation software: usually customdesigned/developed; very expensive.
– Word processor: perform generic word-processing tasks
for general consumers.
Algorithm
• Step-by-step instructions that lead to the
solution of a problem.
• Example: What is the algorithm that
computes the average of three arbitrary
values? What is the algorithm that adds
integers from 1 to 100? (not unique! Some
are better or more efficient that others.
Efficient in what sense?)
Algorithms continued
• Tools to help develop/specify/visualize an
algorithm
– Flowchart: a set of symbols (p9); less popular
today but helpful to beginners to visualize the
steps.
– Pseudocode: informal English statements;
easier to convert to a program using a
structured programming language such as C or
Fortran.
Computer Problem Solving Steps
1. Understand/formulate/specify the problem
2. Develop the algorithm, which is
independent of computer languages.
3. Convert the algorithm to a program
(Computer language must be chosen)
4. Test/debug (steps 1 thru 4 may be
iterative)
5. Deliver
How to run or execute (test) a
C++ program
• Need a C++ translator known as a compiler,
which convert C++ source program (or
source code) to machine language program
(or object code).
• There are several popular C/C++ compilers
available commercially or in the public
domain: Borland/Turbo C/C++, Microsoft
Visual C/C++, gcc compiler, etc.
Turbo C/C++ program
development environment
• The Integrated Development Environment
or IDE
–
–
–
–
Editor
Preprocessor and compiler
Debugger
Others
A simple C++ program
• The program displays/prints a greeting
message “Hello World”
• Steps 1 and 2 are quite clear, we go straight
to steps 3, namely code the program in C++
A simple C++ program continued
#include <iostream.h>
int main ( )
{
cout << “Hello World!” << endl;
return 0;
}
Another simple program. What does it do?
#include <iostream.h>
int main ( )
{
double x, y, z, avg;
cout << “Enter 3 values: “;
cin >> x >> y >> z;
avg = ( x + y + z ) / 3;
cout << “The average of three arbitrary values is “
<< avg;
return 0;
}
C++ language elements (tokens)
• Keywords: 62 reserved word including return;
each has special meaning and must not be
misspelled.
• Identifier: names chosen by the programmer; it is
usually used to name or identify a memory
location (known as a variable) or a function.
• Operators: specifies operations
• Constants: may be numeric or non-numeric
• Punctuation symbols such as ;.
Tokenize the above programs
In the two programs
• What are the keywords?
• What are the identifiers?
• What are the punctuators?
• What are the constants?
• What are the operators?
Question?
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
What does #include <iostream.h> mean?
What are the rest of the lines in the program for?
Why return 0?
What are cin and cout?
What is >>?
What is <<?
Are the ordering of lines (instructions) in the
program important?
• Can one use u, v, and w in place of x, y, and z?
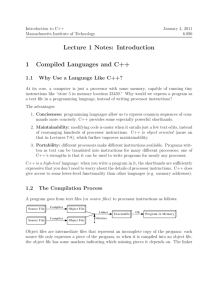
Divide and conquer: a modular
approach to a complex problem