Jeopardy Review
advertisement
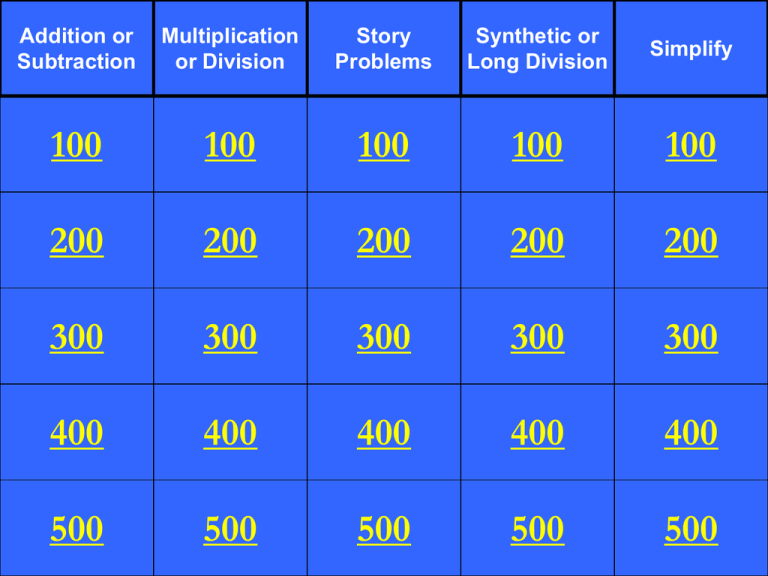
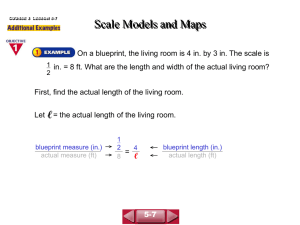
Addition or Subtraction Multiplication or Division Story Problems Synthetic or Long Division Simplify 100 100 100 100 100 200 200 200 200 200 300 300 300 300 300 400 400 400 400 400 500 500 500 500 500 Perform the indicated operation and simplify your answer completely 2t 1 5t 2t 4 t2 L C D : 5 t ( t 2) t 2 2 t 1 2 t 4 5t t2 5t t 2 5t (2 t 1)( t 2) 5 t ( t 2) 2t t 4t 2 2 5 t ( t 2) 5 t (2 t 4) 5 t ( t 2) 10 t 20 t 2 5 t ( t 2) 8 t 17 t 2 2 5 t ( t 2) Perform the indicated operation and simplify your answer completely. 3x x 1 2 5 x 2x 1 2 3x ( x 1)( x 1) x 1 3x x 1 ( x 1)( x 1) 5 ( x 1)( x 1) 5 x 1 ( x 1)( x 1) x 1 3 x ( x 1) 5( x 1) ( x 1)( x 1)( x 1) 3x 3x 5x 5 2 ( x 1)( x 1)( x 1) 3x 2x 5 2 ( x 1)( x 1)( x 1) Perform the indicated operation and simplify your answer completely. 3 x2 4x 7 x 2 4 x 7 1 x 2 x 2 1 3 3 x2 (4 x 7 ) x2 3 4x 7 x2 4 x 10 x2 2(2 x 5) x2 Solve the following equation. Do not forget to check for extraneous solutions. 1 x6 4 x 1 3x 2 x 7x 6 2 1 x6 1 x6 ( x 6)( x 1) 1 4 x 1 4 x 1 3x 2 ( x 6)( x 1) ( x 6)( x 1) 1 3x 2 ( x 6)( x 1) 1( x 1) 4( x 6) 3 x 2 x 1 4 x 24 3 x 2 5 x 25 3 x 2 2 x 23 x 23 2 ( x 6)( x 1) 1 Solve the following equation. Do not forget to check for extraneous solutions. 5 x5 x x5 1 5 x5 x5 1 x x5 x5 1 1 5 x ( x 5) 5 xx5 55 All real numbers except x 5 x5 1 Perform the indicated operation and simplify your answers completely. x 6x 8 x 3 2 x 4x 3 x 2 2 ( x 2)( x 4) x 3 ( x 1)( x 3) x 2 ( x 4) ( x 1) Perform the indicated operation and simplify your answers completely. x9 2x 4 x 81 2 x2 x9 2( x 2) ( x 9)( x 9) x2 Keep it…Switch it…flip it. x9 x2 2( x 2) ( x 9)( x 9) 1 2( x 9) Perform the indicated operation and simplify your answer completely. a b 2 ab 2 a 2 ab b 2 2 2a b 2 2 ( a b )( a b ) ( a b )( a b ) 2 2 ab 2a b ( a b )( a b ) 2 a a b b ab ( a b )( a b ) 2 ab ( a b ) (a b) Perform the indicated operation and simplify your answer completely. 4x 9 y 2 2 8 x 27 y 3 3 4 x 6 xy 9 y 2 2 4 x 12 xy 9 y 2 2 (2 x 3 y )(2 x 3 y ) 4 x 6 xy 9 y 2 2 (2 x 3 y )(4 x 6 xy 9 y ) (2 x 3 y )(2 x 3 y ) 2 2 1 2x 3y Perform the indicated operation and simplify your answer completely. 8 y 27 3 64 y 1 3 4y 9 2 16 y 4 y 1 2 (2 y 3)(4 y 6 y 9) 2 (4 y 1)(16 y 4 y 1) 2 (2 y 3)(4 y 6 y 9) 2 (2 y 3)(2 y 3) 16 y 4 y 1 2 16 y 4 y 1 2 (4 y 1)(16 y 4 y 1) (2 y 3)(2 y 3) 2 (4 y 6 y 9 ) 2 (4 y 1)(2 y 3) The weight (M) of an object on the moon varies directly as its weight (E) on Earth. A person who weighs 95 kg on Earth weighs 15.2 kg on the moon. How much would a 105 kg person weigh on the moon? Moon weight = k • Earth weight 1 5 .2 k 9 5 .1 6 k Moon weight = 0.16 • Earth weight y 0.16 105 y 16.8 kg The time (t) required to drive a fixed distance varies inversely as the speed (r). It takes 5 hours at 80km/h to drive a fixed distance. How long would it take to drive the fixed distance at 60 km/h? time = 5 k speed k 80 4 0 0 km / h k time = t 400 speed 400 60 t6 2 3 hours A panda can eat leaves from a certain bamboo stem in 14 minutes. Together, two pandas could eat the leaves from the same stem in 9 minutes. How long would it have taken the second panda to eat the leaves from the stem by itself? 1 14 9 1 t 1 9 L C D : 126t 14 1 126 t 1 126 t 1 12 6 t 14 1 t 1 9 1 9t 126 14t 1 2 6 5t 2 5 .2 m in . t A car travels 300 km in the same time that a freight train travels 200 km. The speed of the car is 20 km/hr more than the speed of the train. Find the speed of the car and the speed of the train. car train d 300 km 200 km r r + 20 r t t t Car time = train time 300 Train speed 4 0 km / h Car speed 6 0 km / h r 20 200 r 300 r 200( r 20) 300r 200 r 4000 100r 4000 r 40 t d r A paddleboat can move at a speed of 2 km/hr in still water. The boat is paddled 4km downstream in a river in the same time it takes to go 1 km upstream. What is the speed of the river? c = speed of the current upstream downstream d 1 km 4 km r 2-c 2+c t t t t upstream time = downstream time 1 2c 4 2c 1(2 c ) 4(2 c ) 2 c 8 4c 5c 6 6 c km / h 5 d r Divide using long division. (2 x 3 x 5) ( x 1) 2 2x 1 x 1 2 x 3x 5 2 2x 2x 2 x5 x 1 4 2x 1 4 x 1 Divide using synthetic division. ( x 4 x 6 x 4 x 1) ( x 1) 4 3 2 1 1 6 4 4 1 1 3 3 1 1 3 3 x 3x 3x 1 3 2 1 0 Divide using synthetic division. (4 x x 7) ( x 2) 3 2 4 0 1 7 8 16 34 4 8 17 41 4 x 8 x 17 2 41 x2 Divide using long division. ( y 11 y 6) ( y 3) 3 2 y 8 y 24 2 y 3 y 11 y 0 y 6 3 2 y 3y 3 2 8 y 0 y 2 8 y 24 y 2 24 y 6 24 y 72 y 8 y 24 2 66 y3 66 Divide using long division. ( y y 54) ( y 3) 4 2 2 2 2 y y 3 y 0 y y 0 y 54 4 2 y 3 y 2 4 3 2 2 y 0 y 54 2 6 2y 2 y 2 2 48 y 3 2 48 Simplify. 4x 9 2 4 x 12 x 9 2 (2 x 3)(2 x 3) (2 x 3)(2 x 3) (2 x 3) (2 x 3) 1 The complex fractional expression x 1 y x y 2 xy can be simplified by multiplying the numerator and denominator by: A. ( x y )( x y ) C. x y B . xy D. x y 2 B Simplify completely. 3 x 1 2x 5 1 3 3 2x 5 52x 6 10 x 2x x x 1 1 1 2x 2x 1 2 x 1 1 2x 2x 2x 1 2(3 5 x ) 1 2x Simplify. 5 4 x2 x 3 3 x 2 5 4 x ( x 2) 2 x2 x 2 3 x ( x 2) 3 x 2 x ( x 2) 2 5 4 x ( x 2) 2 1 x 1 x2 2 3 x x ( x 2) x ( x 2) 3 x 1 1 2 5 x 4( x 2) 2 3 x ( x 2) 3 x ( x 2) 2 5x 4x 8 2 3x 6 x 3x 6 x 2 3 5x 4x 8 2 3x 3x 6 x 3 2 5x 4x 8 2 3 x ( x 2)( x 1) 2 Simplify. 5x 1 5y 6y 1 1 1 10 x y 1 12 x y 1 1 5 5 10 5 xy 5 x y 1 0 xy x y xy x 1 y 1 xy 1 6 12 6 xy 12 xy y 1 xy 1 y xy 5 y 5 x 10 6 x 12 5( y x 2) 6( x 2)