Flowering in Plants
advertisement
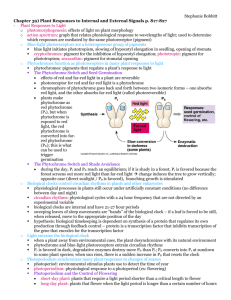
How do plants know when to flower? The Phytochrome System Flowering of plants is determined in part by the length of the day. long days & short nights short days & long nights Plants are of three general types: Example short-day strawberry long-day spinach day-neutral sunflower Short-day plants flower in spring or autumn when the day lengths are shorter than the critical day length.. For example, the common cocklebur (Xanthium strumarium) is induced to flower only when exposed to 16 hours or less of light. Examples of short-day plants : poinsettias strawberries primroses. Long day plants flower chiefly in the summer and will flower only when exposed to light for longer than a critical length. Spinach has a critical daylength of 13 hours. Examples of long-day plants spinach lettuce henbane What determines if plants are long or short-day is not so much the length of the exposure time but whether it is longer or shorter than some critical interval. Day-neutral plants flower without respect to daylength. Examples of day-neutral plants cucumber corn sunflower cucumber Plants contain a photoreceptor called phytochrome (P) which comes in two forms which are interconvertible, and Pfr. Pr Pfr Pr Pr absorbs red light and Pfr absorbs far-red light. Visible light lies between 400 and 700 nm. Red light Far Red 730 nm 660 nm light The Electromagnetic spectrum Pr Dark reversion Slowly reverts during the night. Red light Far-red light Straight away Pfr Straight away Physiological response