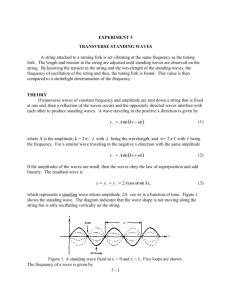
SPH3U Waves-and-Sound-Exam
advertisement

SPH3U Exam Review 1. The speed of sound in water is ____________ the speed of sound in air. A. faster than B. slower than C. the same as D. Sound does not travel through water. 1. The speed of sound in water is ____________ the speed of sound in air. *A. faster than B. slower than C. the same as D. Sound does not travel through water. 2. In a sound wave, rarefactions are areas of: A. high amplitude B. low amplitude C. high pressure D. low pressure 2. In a sound wave, rarefactions are areas of: A. high amplitude B. low amplitude C. high pressure *D. low pressure 3. If the frequency of a sound wave is increased, the sound will have: A. a faster speed B. a higher pitch C. more energy D. all of the above 3. If the frequency of a sound wave is increased, the sound will have: A. a faster speed *B. a higher pitch C. more energy D. all of the above 4. 1 m away from a sound, the intensity is 60 dB. What is the intensity 10 m away? A. 6 dB B. 30 dB C. 40 dB D. 50 dB 4. 1 m away from a sound, the intensity is 60 dB. What is the intensity 10 m away? A. 6 dB B. 30 dB *C. 40 dB D. 50 dB 5. If you move toward a sound with a frequency of 200 Hz, the apparent frequency of the sound will be __________ 200 Hz. A. less than B. greater than C. equal to D. It cannot be determined. 5. If you move toward a sound with a frequency of 200 Hz, the apparent frequency of the sound will be __________ 200 Hz. A. less than *B. greater than C. equal to D. It cannot be determined. 6. Two loudspeakers are placed about 70 cm apart. Each speaker is emitting sound with the same frequency. As you walk slowly past the loudspeakers, you hear alternating soft and loud sounds. This effect is best explained by: A. diffraction B. interference C. reflection D. refraction 6. Two loudspeakers are placed about 70 cm apart. Each speaker is emitting sound with the same frequency. As you walk slowly past the loudspeakers, you hear alternating soft and loud sounds. This effect is best explained by: A. diffraction *B. interference C. reflection D. refraction 7. A tuning fork has a frequency of 256 Hz. When the tuning fork and a piano key are sounded together, beats of frequency 2 Hz are heard. What is the frequency of the sound produced by the piano? A. 254 Hz B. 258 Hz C. 512 Hz D. either A or B 7. A tuning fork has a frequency of 256 Hz. When the tuning fork and a piano key are sounded together, beats of frequency 2 Hz are heard. What is the frequency of the sound produced by the piano? A. 254 Hz B. 258 Hz C. 512 Hz *D. either A or B 8. Resonance occurs when the frequency of the forcing vibration is _____________ the natural frequency of the object. A. the same as B. greater than C. less than D. both A and B 8. Resonance occurs when the frequency of the forcing vibration is _____________ the natural frequency of the object. *A. the same as B. greater than C. less than D. both A and B 9. An open air column is made to resonate in air at 25oC and air at 0oC. The pitch of the sound produced is: A. higher in air at 25oC B. higher in air at 0oC C. the same in both cases D. It cannot be determined. 9. An open air column is made to resonate in air at 25oC and air at 0oC. The pitch of the sound produced is: *A. higher in air at 25oC B. higher in air at 0oC C. the same in both cases D. It cannot be determined. 10. An air column open at one end only is increased in length. The air column first resonates with a given tuning fork when the length of the air column is 20 cm. The next length that will resonate with the same tuning fork is: A. 30 cm B. 40 cm C. 60 cm D. 80 cm 10. An air column open at one end only is increased in length. The air column first resonates with a given tuning fork when the length of the air column is 20 cm. The next length that will resonate with the same tuning fork is: A. 30 cm B. 40 cm *C. 60 cm D. 80 cm 1. What is ultrasound? What is infrasound? 1. What is ultrasound? What is infrasound? Ultrasound: sound of frequencies above the range of human hearing (> 20 kHz) Infrasound: sound of frequencies below the range of human hearing (< 20 Hz) 2. Sketch the standing wave patterns of the first and second harmonics of an open air column. Label nodes and antinodes. 2. Sketch the standing wave patterns of the first and second harmonics of an open air column. Label nodes and antinodes. Node Antinode Node Antinode Antinode Node Antinode Antinode 1. A lightning flash is seen 8.0 s before the rumble of the thunder is heard. Find the distance to the lightning flash if the temperature is 21oC. 1. A lightning flash is seen 8.0 s before the rumble of the thunder is heard. Find the distance to the lightning flash if the temperature is 21oC. 0.6 21C m s v 332 0.6 C T m s v 332 m s v 344.6 ms m s C 1. A lightning flash is seen 8.0 s before the rumble of the thunder is heard. Find the distance to the lightning flash if the temperature is 21oC. v 344.6 ms t 8.0 s d ? d v d vt t d 344.6 ms 8.0 s 2756.8 m or 2.8 km 2. A string resonates with a fundamental frequency of 1024 Hz. The speed of sound in the string is 1800 m/s. (a) Sketch the standing wave pattern and (b) calculate the length of the string. 2. A string resonates with a fundamental frequency of 1024 Hz. The speed of sound in the string is 1800 m/s. (a) Sketch the standing wave pattern and (b) calculate the length of the string. 2. A string resonates with a fundamental frequency of 1024 Hz. The speed of sound in the string is 1800 m/s. (a) Sketch the standing wave pattern and (b) calculate the length of the string. f 1024Hz v 1800 ms ? L? v v f f 1800ms 1.758m 1024Hz L 12 1 2 1.758m 0.88m