Objective: To calculate density.
advertisement

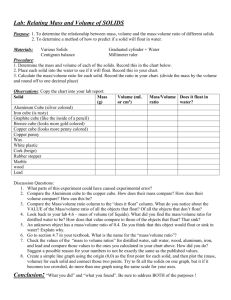
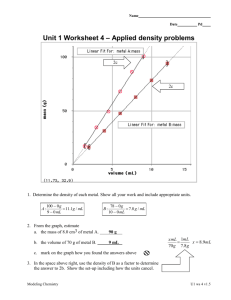
Objective: To calculate density. - Volume of a cube or block = length x width x height - Volume of irregular shaped object = use water displacement Density density = mass/volume OR d = m/v d= Example: An object has a mass of 22 g and a volume of 11 cm3. What is the density of this object? Example #1 1. An object has a mass of 18.9 g and a volume of 7.0 mL. What is the density? 2. What is it? (refer to table of densities on page 17)? 3. Will it float? Example #1: Answer 1. An object has a mass of 18.9 g and a volume of 7.0 mL. What is the density? d = m/v = 18.9 g / 7.0 mL = 2.7 g/mL 2. What is it? (refer to table of densities on page 17)? Aluminum 3. Will it float? 2.7 g/mL > density of water (1.0 g/mL) SINK Example #2 1. A liquid has a mass of 4.743 g and a volume of 6.0 mL. What is the density? 2. What is it (refer to the table of densities on page 17)? 3. Will it float? Example #2: Answer 1. A liquid has a mass of 4.743 g and a volume of 6.0 mL. What is the density? d = m/v = 4.743 g/6.0 mL = 0.79 g/mL 2. What is it (refer to the table of densities on page 17)? ethanol 3. Will it float? 0.79 g/mL < density of water (1.0 g/mL) float Example #3 What is the density of a cube with a length of 5.0 cm and a mass of 26 g? Example #3: Answer What is the density of a cube with a length of 5.0 cm and a mass of 26 g? Volume = length x width x height Volume = 5.0 cm x 5.0 cm x 5.0 cm = 125 cm3 Density = m/v = 26 g/125 cm3 = 0.21 g/cm3 Example #4 An irregularly shaped stone was lowered into a graduated cylinder holding a volume equal to 2.0 mL. The height of the water rose to 7.0 mL. If the mass of the stone was 25 g, what was the density? Example #4: Answer An irregularly shaped stone was lowered into a graduated cylinder holding a volume equal to 2.0 mL. The height of the water rose to 7.0 mL. If the mass of the stone was 25 g, what was the density? Volume = 7.0 mL – 2.0 mL = 5.0 mL Density = m/v = 25 g / 5.0 mL = 5.0 g/mL Density Equation • Density = Mass/Volume d = m/v • Mass = Density x Volume m=dxv • Volume = Mass/Density v = m/d Example #5 If the density of an object is 8.7 g/mL and the volume is 15 mL, what is the mass of the object? Example #5: Answer If the density of an object is 8.7 g/mL and the volume is 15 mL, what is the mass of the object? Mass = d x v Mass = 8.7 g/mL x 15 mL Mass = 130.5 g 130 g Example #6 If the density of an object is 3.6 g/mL and the mass is 60.0 g, what is the volume of the object? Example #6: Answer If the density of an object is 3.6 g/mL and the mass is 60.0 g, what is the volume of the object? Volume = m/d Volume = (60.0 g) / (3.6 g/mL) Volume = 16.67 mL 17 mL Example #7 If the density of an object is 5.5 g/mL and the mass is 1.2 kg, what is the volume of the object? Example #7: Answer If the density of an object is 5.5 g/mL and the mass is 1.2 kg, what is the volume of the object? Volume = m/d Volume = 1200 g/(5.5 g/mL) Volume = 218 mL 220 mL Example #8 5.0 mL of the ethanol has a mass of 3.9 g, and 5.0 mL of benzene has a mass of 4.4 g. Which liquid is denser? Example #8: Answer 5.0 mL of the ethanol has a mass of 3.9 g, and 5.0 mL of benzene has a mass of 4.4 g. Which liquid is denser? Ethanol Benzene Density = Mass/Volume Density = Mass/Volume Density = 3.9 g/5.0 mL Density = 4.4 g/5.0 mL Density = 0.78 g/mL Density = 0.88 g/mL Benzene is more dense.