Ch3
advertisement

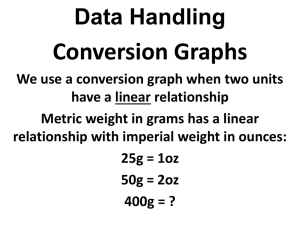
Ch # 3 Unit system and dimensional analysis. Measurement of Mass The standard unit of mass in the SI system is the kilogram. 1 kilogram is equal to the mass of a platinum-iridium cylinder kept in a vault at Sevres, France. 1 kg = 2.205 pounds Metric Units of mass Unit Abbreviation Gram Equivalent Exponential Equivalent kilogram gram kg g 1,000 g 1g 103 g 100 g decigram dg 0.1 g 10-1 g centigram cg 0.01 g 10-2 g milligram mg 0.001 g 10-3 g microgram g 0.000001 g 10-6 g Mass and Weight • Matter: Anything that has mass and occupies space. • Mass : The quantity or amount of matter that an object possesses. – Fixed – Independent of the object’s location • Weight: A measure of the earth’s gravitational attraction for an object. – Not fixed – Depends on the object’s location. • Mass : The quantity or amount of matter that an object possesses. – Fixed – Independent of the object’s location. • Weight: A measure of the earth’s gravitational attraction for an object. – Not fixed – Depends on the object’s location. Measurement of Volume • Volume is the amount of space occupied by matter. • In the SI system the standard unit of volume is the cubic meter (m3). • The liter (L) and milliliter (mL) are the standard units of volume used in most chemical laboratories. Density Density is the ratio of the mass of a substance to the volume occupied by that substance. mass d= volume Mass is usually The density of gases is expressed expressed in in grams grams per and liter.volume in mL or cm3. g ddd=== 3 mL cm L Density varies with temperature d d 4oC H 2O o 80 C H 2O 1.0000 g g = = 1.0000 1.0000 mL mL 1.0000 g g = = 0.97182 1.0290 mL mL A 13.5 mL sample of an unknown liquid has a mass of 12.4 g. What is the density of the liquid? M 12.4 g D 0.919 g/mL V 13.5mL A graduated cylinder is filled to the 35.0 mL mark with water. A copper nugget weighing 98.1 grams is immersed into the cylinder and the water level rises to the 46.0 mL. What is the volume of the copper nugget? What is the density of copper? Vcopper nugget = Vfinal -Vinitial = 46.0mL - 35.0mL = 11.0mL M 98.1g D 8.92 g/mL V 11.0 mL 46.0 mL 35.0 mL 98.1 g The density of ether is 0.714 g/mL. What is the mass of 25.0 milliliters of ether? Method 1 (a) Solve the density equation for mass. mass d= volume mass = density x volume (b) Substitute the data and calculate. 0.714 g 25.0 mL x = 17.9 g mL The density of ether is 0.714 g/mL. What is the mass of 25.0 milliliters of ether? Method 2 Dimensional Analysis. Use density as a conversion factor. Convert: mL → g g =g The conversion of units is mL x mL 0.714 g 25.0 ml x = 17.9 g mL The density of oxygen at 0oC is 1.429 g/L. What is the volume of 32.00 grams of oxygen at this temperature? Method 1 (a) Solve the density equation for volume. mass d= volume mass volume = density (b) Substitute the data and calculate. 32.00 g O2 volume = = 22.40 L 1.429 g O2 /L % error • Measured value-accepted value ____________________________x 100 Accepted value Measurement of Temperature Heat • A form of energy that is associated with the motion of small particles of matter. • Heat refers to the quantity of this energy associated with the system. • The system is the entity that is being heated or cooled. Temperature • A measure of the intensity of heat. • It does not depend on the size of the system. • Heat always flows from a region of higher temperature to a region of lower temperature. Temperature Measurement • The SI unit of temperature is the Kelvin. • There are three temperature scales: Kelvin, Celsius and Fahrenheit. • In the laboratory temperature is commonly measured with a thermometer. Degree Symbols degrees Celsius = oC Kelvin (absolute) = K degrees Fahrenheit = oF To convert between the scales use the following relationships. o K = C + 273.15 o o o F = 1.8 x C + 32 o F 32 o o o o = = 1.8 x C FC- 32 1.8 180 Farenheit Degrees = 100 Celcius degrees 180 =1.8 100 It is not uncommon for temperatures in the Canadian plains to reach –60oF and below during the winter. What is this temperature in oC and K? o o o F - 32 C= 1.8 60. - 32 o C= = -51 C 1.8 It is not uncommon for temperatures in the Canadian planes to reach –60oF and below during the winter. What is this temperature in oC and K? o K = C + 273.15 o K = -51 C + 273.15 = 222 K The Metric System • The metric or International System (SI, Systeme International) is a decimal system of units. • It is built around standard units. • It uses prefixes representing powers of 10 to express quantities that are larger or smaller than the standard units. International System’s Standard Units of Measurement Quantity Name of Unit Abbreviation Length Mass meter kilogram m kg Temperature Kelvin K Time second Amount of substance m s mole Electric Current ampere A Luminous Intensity candela cd Prefixes and Numerical Values for SI Units Numerical Value Power of 10 Equivalent Prefix Symbol exa peta E P 1,000,000,000,000,000,000 1018 1,000,000,000,000,000 1015 tera T 1,000,000,000,000 1012 giga G 1,000,000,000 109 mega M 1,000,000 106 kilo k 1,000 103 hecto h 100 102 deca da 10 101 — — 1 100 Prefixes and Numerical Values for SI Units Numerical Value Power of 10 Equivalent Prefix Symbol deci d 0.1 10-1 centi c 0.01 10-2 milli m 0.001 10-3 micro 0.000001 10-6 nano n 0.000000001 10-9 pico p 0.000000000001 10-12 femto f 0.00000000000001 10-15 atto a 0.000000000000000001 10-18 Dimensional Analysis Dimensional analysis converts one unit to another by using conversion factors. unit1 x conversion factor = unit2 Basic Steps 1. Read the problem carefully. Determine what is to be solved for and write it down. 2. Tabulate the data given in the problem. – Label all factors and measurements with the proper units. Basic Steps 3. Determine which principles are involved and which unit relationships are needed to solve the problem. – You may need to refer to tables for needed data. 4. Set up the problem in a neat, organized and logical fashion. – – Make sure unwanted units cancel. Use sample problems in the text as guides for setting up the problem. Basic Steps 5. Proceed with the necessary mathematical operations. – Make certain that your answer contains the proper number of significant figures. 6. Check the answer to make sure it is reasonable. Metric Units of Length Unit Abbreviation Metric Equivalent Exponential Equivalent kilometer meter km m 1,000 m 1m 103 m 100 m decimeter dm 0.1 m 10-1 m centimeter cm 0.01 m 10-2 m millimeter mm 0.001 m 10-3 m micrometer m 0.000001 m 10-6 m nanometer nm 0.000000001 m 10-9 m angstrom Å 0.0000000001 m 10-10 m How many millimeters are there in 2.5 meters? The conversion factor must unit1 x conversion factor = unit2 accomplish two things: m x conversion factor = mm • It must cancel meters. • It must introduce millimeters The conversion factor takes a fractional form. mm mx = mm m The conversion factor is derived from the equality. 1 m = 1000 mm Divide both sides by 1000 mm 1m 1000 mm conversion = 1 factor 1000m 1000 mm Divide both sides by 1 m 1 m 1000 mm conversion = 1 factor 1m 1m How many millimeters are there in 2.5 meters? Use the conversion factor with millimeters in the numerator and meters in the denominator. 1000 mm = 2500 mm 2.5 m x 1m 3 2.5 x 10 mm Convert 16.0 inches to centimeters. Use this conversio n factor 2.54 cm 1 in 2.54 cm 16.0 in x = 40.6 cm 1 in Convert 3.7 x 103 cm to micrometers. Centimeters can be converted to micrometers by writing down conversion factors in succession. cm m meters 1m 10 μm 7 x 3.7 x 10 cm x = 3.7 x 10 μm 100 cm 1m 6 3 Metric Units of mass Unit Abbreviation Gram Equivalent Exponential Equivalent kilogram gram kg g 1,000 g 1g 103 g 100 g decigram dg 0.1 g 10-1 g centigram cg 0.01 g 10-2 g milligram mg 0.001 g 10-3 g microgram g 0.000001 g 10-6 g Convert 45 decigrams to grams. 1 g = 10 dg 1g 45 dg x = 4.5 g 10 dg An atom of hydrogen weighs 1.674 x 10-24 g. How many ounces does the atom weigh? Grams can be converted to ounces by a series of stepwise conversions. 1 lb = 454 g -24 1.674 x 10 1 lb -27 gx 3.69 x 10 lb 454 g 16 oz = 1 lb -27 3.69 x 10 16 oz -26 x 5.90 x 10 oz lb 1 lb An atom of hydrogen weighs 1.674 x 10-24 g. How many ounces does the atom weigh? Grams can be converted to ounces using a linear expression by writing down conversion factors in succession. 1 lb 16 oz -26 x x 5.90 x 10 oz 1.674 x 10 g 454 g 1 lb -24