Gases and Heat
advertisement

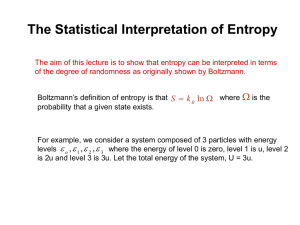
Gases and Heat Chapter 18 Boltzmann’s Version of pV=nRT pV = NkBT N = Number of molecules kB = Boltzmann’s Constant (1.38 X 10-23 J/K) Mean Free Path • Average distance between collisions • Also used to describe electrons moving through wires • Light passing through glass, water l= 1 4\/2 p (N/V)r2 l = mean free path r = 0.5 X 10-10 m (monoatomic gases) 1.0 X 10-10 m (diatomic gases) Example A nitrogen molecule (N2, diatomic) is at 1.0 atm of pressure and 20oC a. Convert the temperature and pressure to the proper units b. Calculate the value N/V using Boltzmann’s Equation c. Calculate the mean free path of the molecule. Root-Mean Square Speed • Velocity has a direction • Overall, in a container of gases, the velocity is zero • Average speed is not zero vrms = \/(v2)avg vrms = 3kBT m m is the mass of one molecule (kg) Example 1 Nitrogen molecules (N2) are at room temperature, 20oC. a. Calculate the mass of one molecule (kg) b. Calculate the rms speed Example 2 Cesium atoms can be cooled to 1.0 mK (m is 10-6) a. Calculate the mass of 1 cesium atom b. Calcuate the rms speed Translational Energy Eavg = 3/2 kBT (for one molecule) Eavg = 3/2NkBT = 3/2 nRT (for all molecules) N = number of molecules n = number of moles Example A balloon contains 2.00 grams of Helium at 25.0oC a. Calculate the average energy of one atom of Helium. b. Calculate the average energy of the sample. Second Law of Thermodynamics 2nd Law – Natural processes tend to move toward a state of greater disorder – Heat goes hot to cold (Clausius) – No device converts all heat to work (KelvinPlanck) DS >0 Calculating Entropy DS = Q T • Reversible process • Constant Temperature • T in Kelvin Calculating Entropy: Example 1 How much entropy is produced when 30 grams of ice melts at 0oC? Q = mLfusion Q = (0.030 kg)(3.33 X 105 J/kg) Q = 9,990 J DS = 9,990 J 273 K = 36.6 J/K Calculating Entropy: Example 2 How much entropy is produced when 500 g of water boils and vaporizes at 100oC? Q = mLvaporization Q = (0.500 kg)(22.6 X 105 J/kg) Q = 11.3 X 106 J DS = 11.3 X 106 J= 3030 J/K 373 K Calculating Entropy: Example 3 How much entropy is produced when 300 g of lead melts at 327 oC? The latent heat of fusion of lead is 2.45 X 104 J/kg Q = mLvaporization Q = (0.300 kg)(2.45 X 104 J/kg) Q = 7.35 X 103 J DS = 7.35 X 103 J = 12.3 J/K 600 K Entropy and the Universe • Natural processes tend to move towards a state of greater disorder • DSuniverse > 0 • Only local order can be produced • Cleaning your room example • Eventually the entire universe will be the same temperature (no heat engines possible). Heat death. Thermal Pollution • Thermally polluting power plants – Coal plants – Oil plants – Nuclear plants • Non-thermally polluting power plants – Hydroelectric – Tidal energy – Wind – Solar