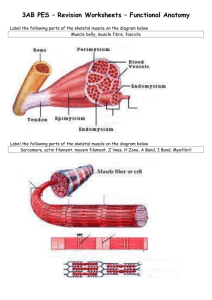
Summation/Wave Summation

Wave Summation
o The degree to which a muscle contracts is dependent upon several factor – including the number of motor units recruited by the brain o The number recruited, will determine the FORCE that can be generated within the muscle.
o The greater the strength required – the greater the number of motor units
(and therefore muscle fibres) that contract.
o The frequency with which impulses arrive at the muscle fibres o The motor unit will respond to a stimulus (impulse) by giving a ‘ twitch ’ – a brief period of contraction followed by relaxation
• When a second impulse is applied to the Motor Unit before it completely relaxes from the previous stimuli, the sum of both stimuli occurs – increasing the total contraction o THIS IS MULTIPLE WAVE SUMMATION
Wave Summation
• When rapid firing of stimuli occurs, giving muscles little or no time for relaxation – Tetanus/tetanic contractions take place
• An increase in total contraction can be explained by the release of calcium ions which causes greater cross bridge attachment of myosin onto actin.
• Prac:
• High degree of force to be generated over a relatively short period of time
– such as a shot putter.
• Multiple Wave summation – muscle fatigue will soon kick in.
Spatial Summation
• Athletes requiring muscular forces over an extended period of time, will recruit motor units slightly out of synchronisation.
• Therefore they will not all contract at the same time.
• Whole muscle shares the workload – so when some motor units contract, others will be recovering.
• This spreads fatigue throughout the muscle, therefore delaying the
‘fatiguing effects’ throughout the muscle.
• M.U 1+3 contracting simultaneously, while MU 2+4 are recovering (see diagram) `